Critical Nursing Arrhythmias Quiz Part 1
By:Mohamed Mamdouh
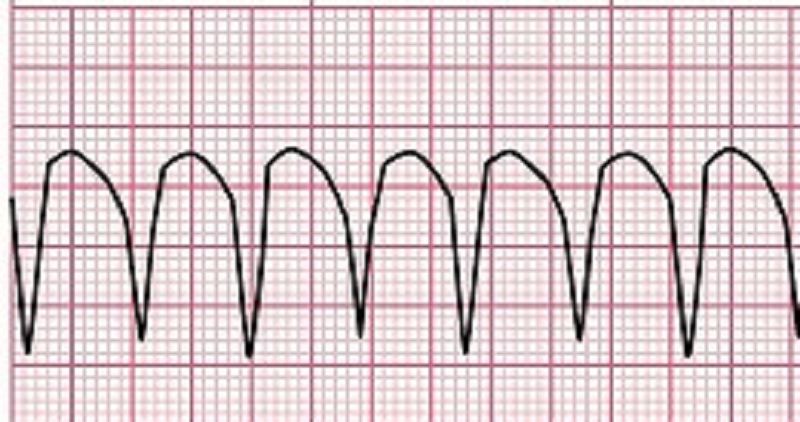
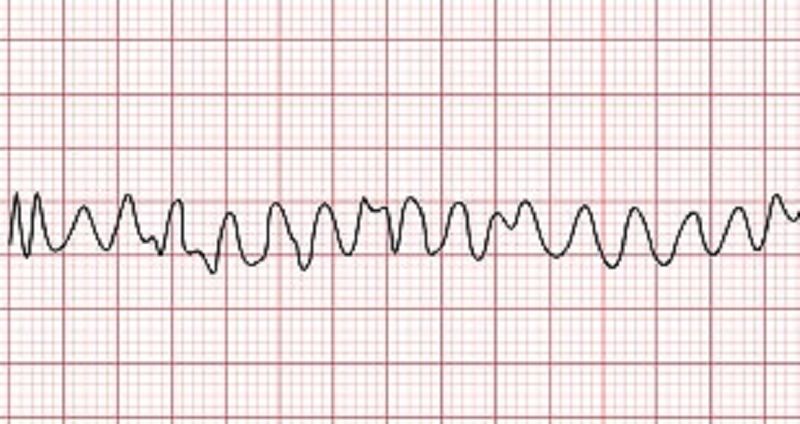
Select the options below that describe the rhythm above
A. Monomorphic
B. Regular atrial rhythm
C. QRS complex >0.12 seconds
D. Irregular ventricular rhythm
E. Regular ventricular rhythm
F. Ventricular rate >100 bpm
G. Atrial rate >80 bpm
H. Polymorphic
I. Ventricular tachycardia
J. Ventricular fibrillation
TRUE or FALSE: Torsades de pointes is known as a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia.
True
False
Your patient is unresponsive and the cardiac monitor shows Torsades de Pointes as the patient’s rhythm. As the code team is attempting to resuscitate the patient, you look through the patient’s electronic health record to try to determine a potential cause for this rhythm. What found in the patient’s record is a cause of this rhythm?
A. Magnesium level 2 mg/dL
B. Amiodarone
C. Potassium 5 mEq/L
D. Glyburide
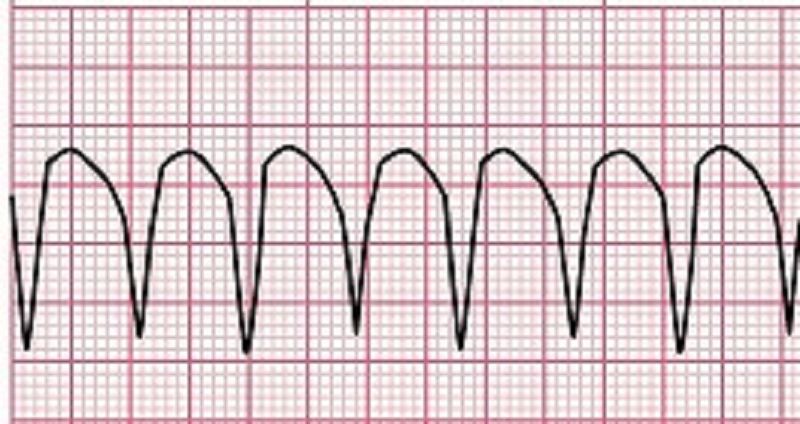
The patient is experiencing the rhythm above. You assess the patient and find the patient is having no symptoms and a pulse is present. What type of treatment do you anticipate will be ordered for this patient?
CPR
Defibrillation
Amiodarone IV
Digoxin IV
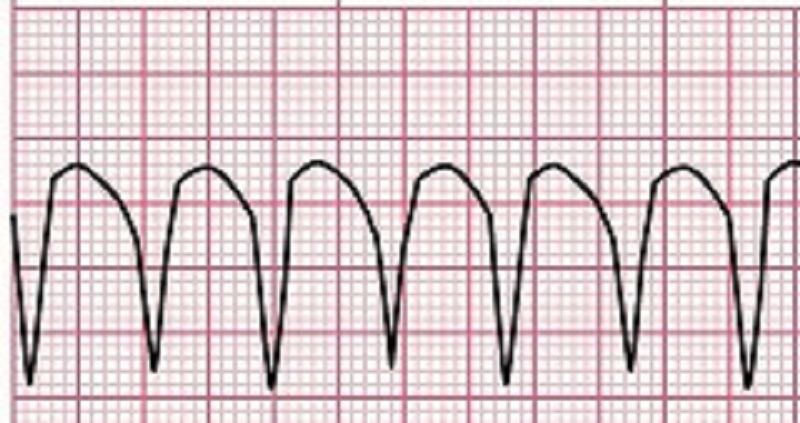
The patient is experiencing the rhythm above. The patient is presenting with a blood pressure of 70/42, mental status changes, and is clammy and pale. A pulse is present. The nurse preps the patient for?
CPR
Synchronized cardioversion
Defibrillation
Atropine IV
A patient is experiencing ventricular tachycardia and is unresponsive with no pulse. After activating the emergency response system, the nurse would immediately?
Prep the patient for defibrillation
Administer IV epinephrine
Secure the airway
Start chest compressions
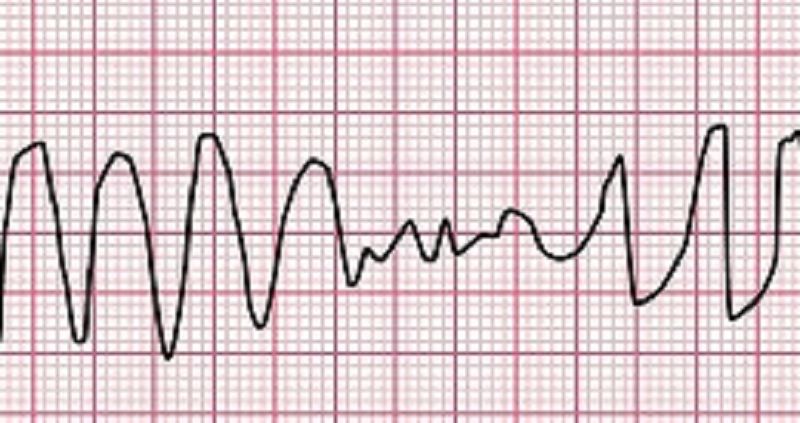
The following rhythm is noted in your patient. The patient is unresponsive and has no pulse. What order below the nurse should NOT use in this rhythm?
IV Amiodarone
IV Magnesium Sulfate
Defibrillation
IV epinephrine
Select the options below that describe the rhythm above:
A. Irregular atrial rate
B. Regular ventricular rate
C. Fine fibrillatory waves
D. Coarse fibrillatory waves
E. Torsades de Pointes
G. Asystole
H. Ventricular tachycardia
I. Ventricular fibrillation
TRUE or FALSE: Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a lethal rhythm that results in the quivering of the ventricles which leads to a rapid fall in cardiac output.
True
False
TRUE or FALSE: A patient experiencing fine ventricular fibrillation has a better chance of being revived than a patient in coarse ventricular fibrillation.
True
False
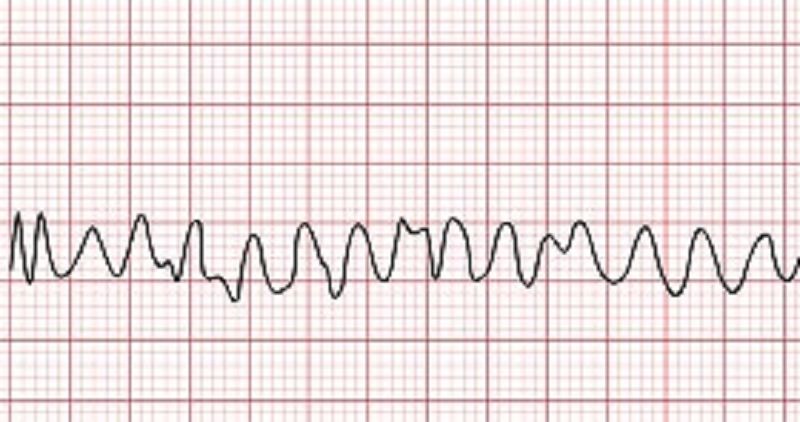
The nurse sees the rhythm above on the ECG. The patient is unresponsive and has no pulse. The nurse calls a code blue and takes what step next?
Prepare for defibrillation
Administer Epinephrine
Start high-quality CPR
Notify the physician
What other medications can be administered to a patient experiencing Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) during a code resuscitation attempt? Select all that apply:
Atropine
Epinephrine
Amiodarone
Lidocaine
You’re patient is in ventricular fibrillation (v-fib). You’ve started CPR and the airway is supported. A rhythm checked in performed and shows the patient is still in ventricular fibrillation. The NEXT action the code team will take in addition to performing high-quality CPR is to?
Administer Atropine
Defibrillate
Administer Epinephrine
Synchronized cardiovert
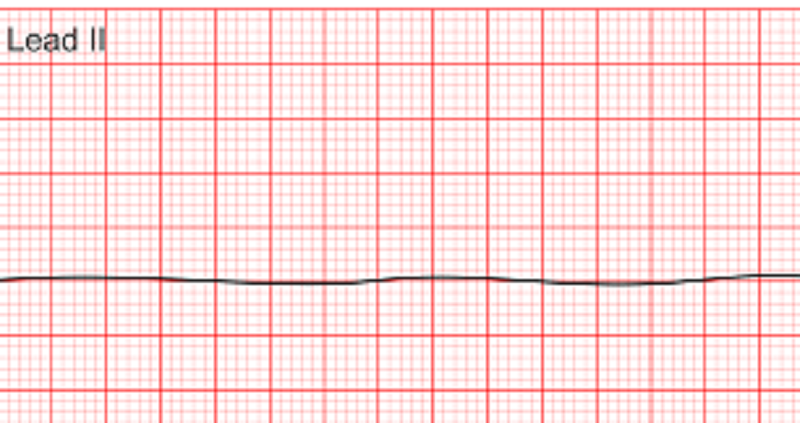
Select the options below that describe the rhythm above
Erratic, unorganized ECG waveform
Absent P-wave, QRS complex, T-wave
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib)
Asystole
Irregular atrial rate
Irregular ventricular rate
TRUE or FALSE: Asystole requires immediate defibrillation to increase the patient's chances of survival.
True
False
The cardiac monitor is showing asystole for the patient's rhythm. However, the patient is alert and oriented with a strong pulse when palpated. The nurse should perform what action next?
A. Press the code blue button
B. Start CPR
C. Check the monitor’s cable and electrode connection
D. Continue to monitor
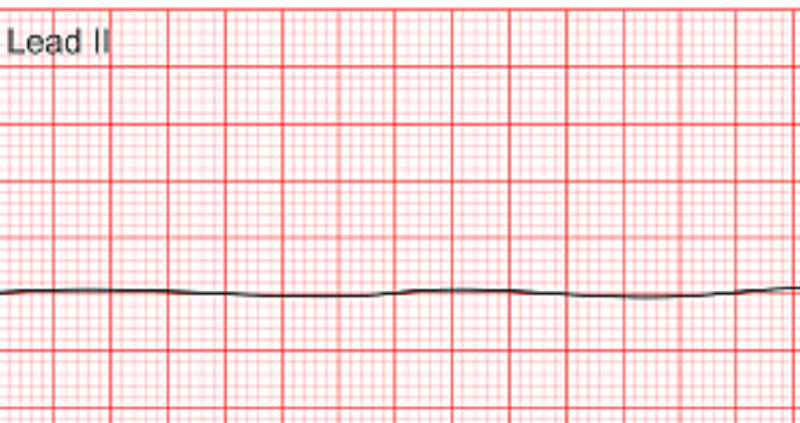
The patient has the rhythm above displaying on the cardiac monitor. The patient is unresponsive and no pulse is present. The nurse calls a code blue and then should do what next
Prepare the patient for defibrillation
Check the H’s and T’s
Administer Atropine
Start CPR
What medication can be administered during resuscitation to a patient who is in asystole?
Amiodarone
Epinephrine
Atropine
Adenosine
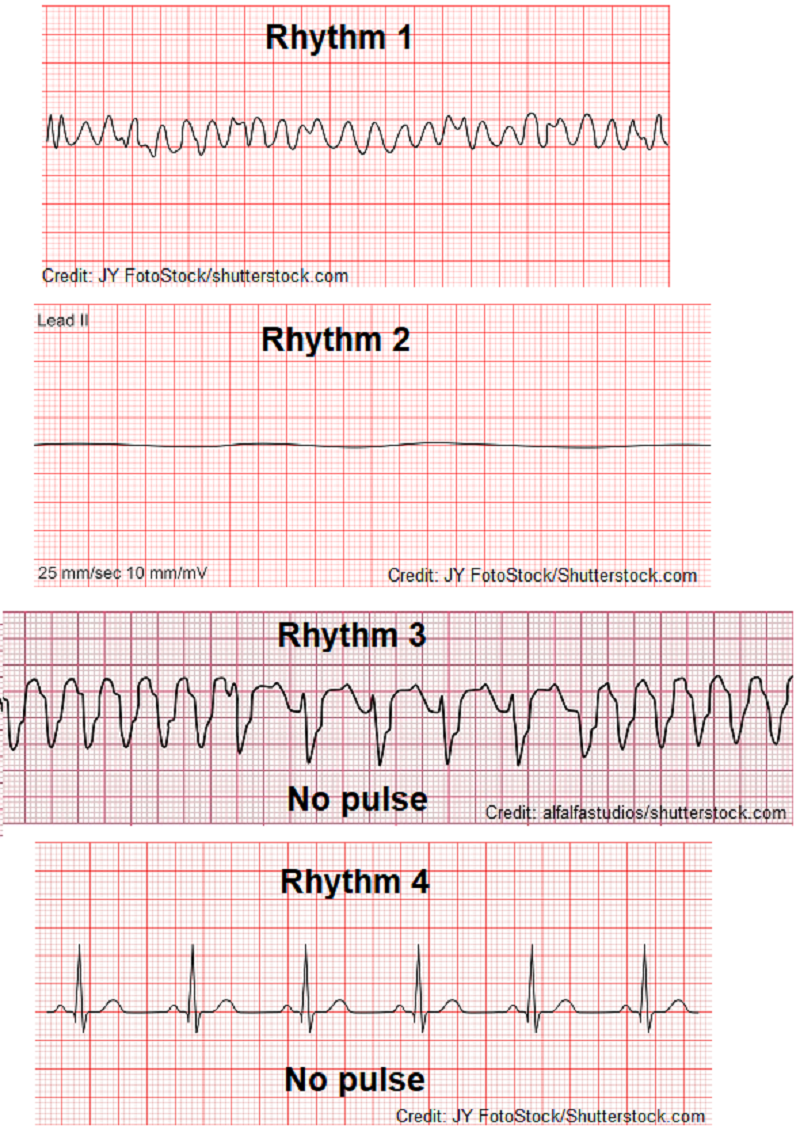
Which rhythm above is NOT treated with defibrillation? Select all that apply
A. Rhythm 1
B. Rhythm 2
C. Rhythm 3
D. Rhythm 4
Which of the following is NOT found in the rhythm Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)?
Organization
Pulse
P waves
QRS complexes
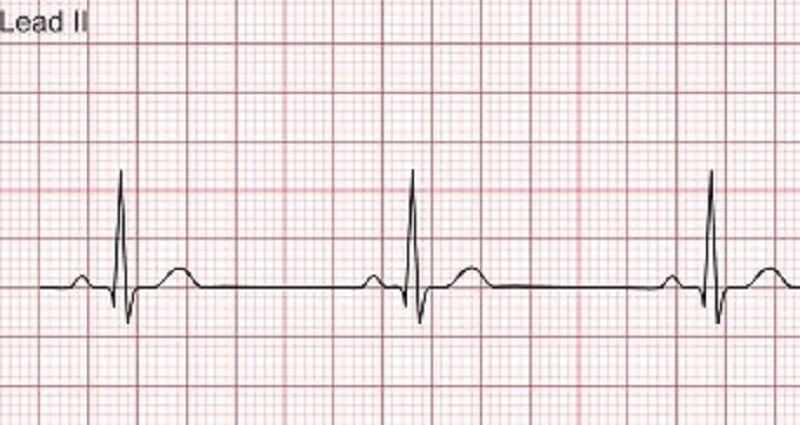
The nurse observes the rhythm above on the cardiac monitor. The nurse assesses the patient and finds that the patient is unresponsive and has no pulse. The nurse calls a code blue and starts CPR. A rhythm checked is performed and the same rhythm is noted with no pulse. What is an INCORRECT action by the code team for treatment of this rhythm?
Continue CPR
Administer Epinephrine
Defibrillation
Support the airway
True or False: PEA (Pulseless Electrical Activity) can have many presentations on the ECG and can sometimes appear as a complete flat line
True
False
Which medication below can be used during a code to treat PEA (Pulseless Electrical Activity)?
Atropine
Amiodarone
Lidocaine
Epinephrine
Your patient is coding and high-quality CPR is being performed. The last rhythm checked showed PEA (Pulseless Electrical Activity). The team is checking the potential causes of this situation by assessing the H's and T's. Select all the possible causes of this rhythm using this mnemonic
A. Hypothyroidism
B. Hypoxia
C. Hypertension
D. Typhoid fever
E. Thrombolysis
F. Hyperkalemia
G. Hypovolemia
H. Trauma
I. Toxins
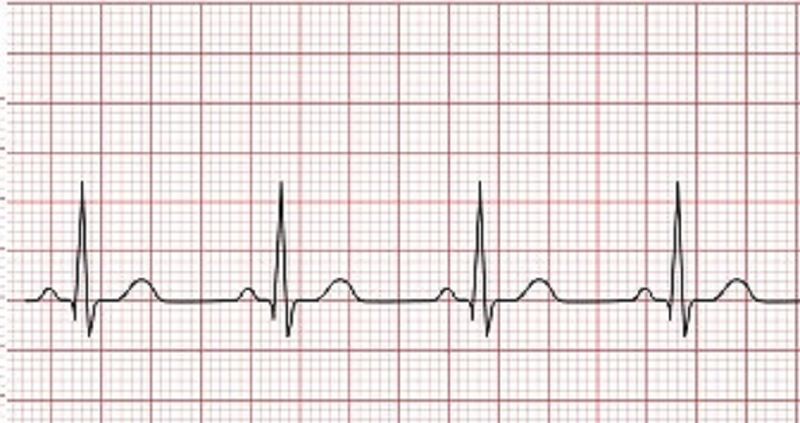
Select the options below that best describe the rhythm above
A. Regular atrial rhythm
B. Irregular ventricular rhythm
C. PR Interval < 0.20 seconds
D. QRS complex > 0.12 seconds
E. Equal atrial and ventricular rate
F. Atrial rate > than ventricular rate
G. First-Degree Heart Block
H. Sinus bradycardia
I. Normal Sinus Rhythm
What should the PR Interval measure for Normal Sinus Rhythm?
A. 0.35-0.44 seconds
B. > 0.12 seconds
C. 0.12-0.20 seconds
D. > 0.20 seconds
TRUE or FALSE: Both the atrial and ventricular rate is the same for Normal Sinus Rhythm.
True
False
Which statement below is FALSE regarding Normal Sinus Rhythm?
A. The QRS complex should measure <0.12 seconds.
B. The atrial rate should be 60-100 bpm
C. The ventricular rate should be 40-60 bpm
D. A p wave should accompany every QRS complex.
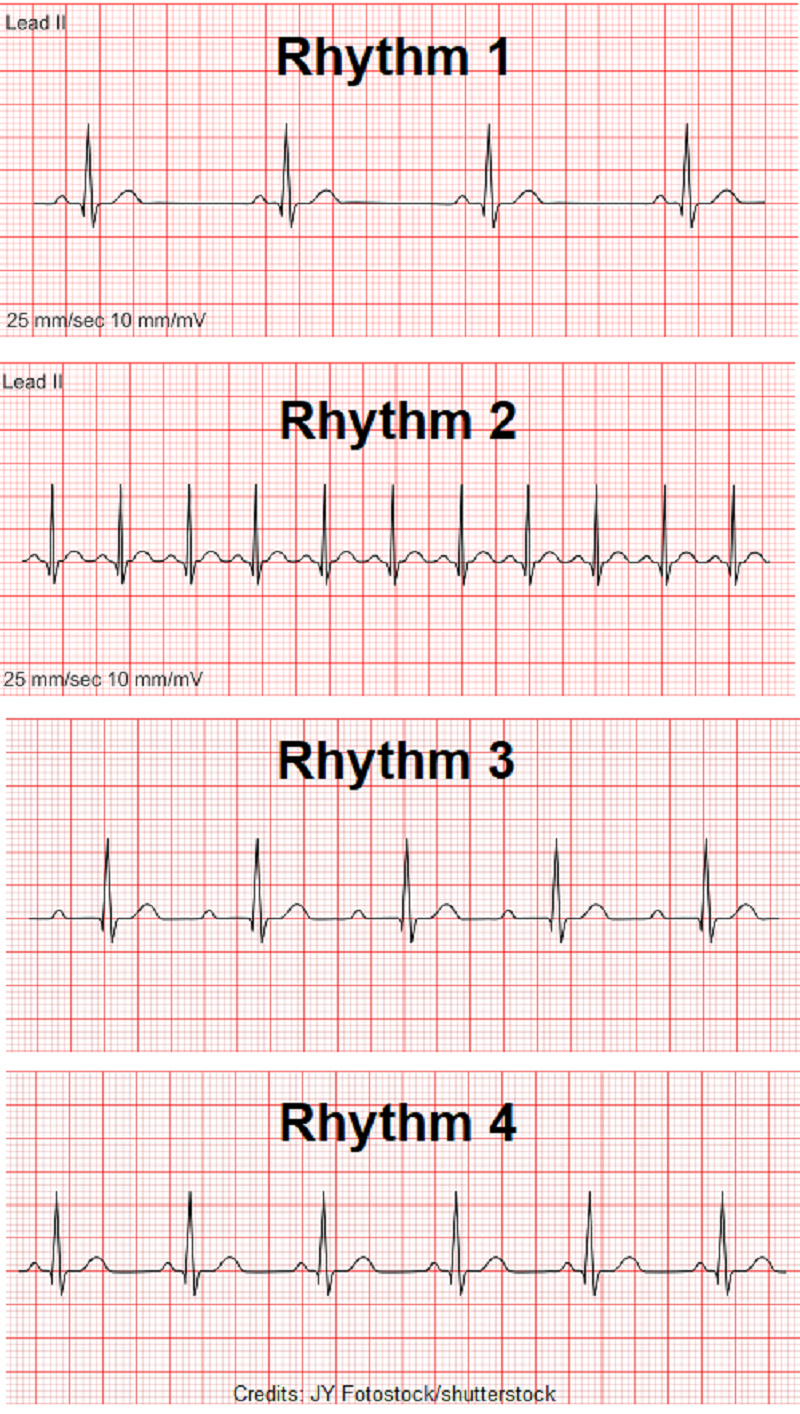
Which rhythm above represents Normal Sinus Rhythm?
A. Rhythm 1
B. Rhythm 2
C. Rhythm 3
D. Rhythm 4
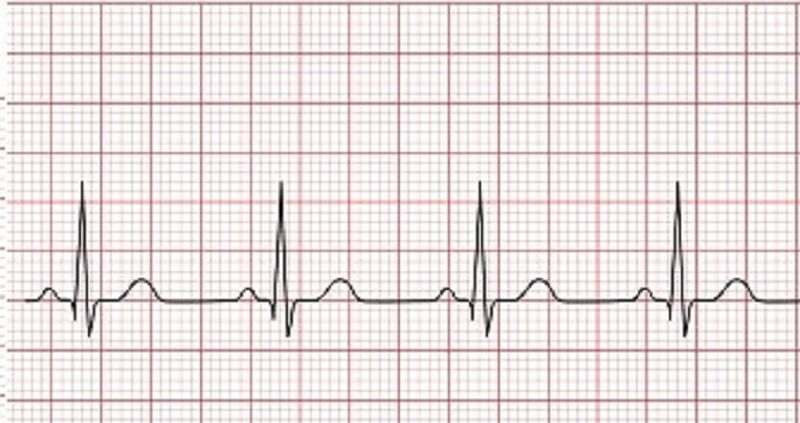
The nurse notes the rhythm above on the cardiac monitor. The nurse does a pulse check and a pulse is present. What next action by the nurse is most appropriate?
A. Continue to monitor
B. Prepare for the administration of Atropine
C. Start chest compressions
D. Activate the emergency response system
Sinus tachycardia originates from what part of the electrical conduction system?
A. Bundle of His
B. Bundle Branches
C. AV Node
D. SA Node
You're analyzing an ECG strip. In order for the rhythm to be identified as Sinus Tachycardia, what must be present in the rhythm? (Select all that apply):
A. One p wave present in front of every QRS complex
B. Atrial rate >100 bpm
C. Ventricular rate >100 bpm
D. Regular atrial rate and irregular ventricular rate
E. Regular atrial and ventricular rate
F. Atrial rate <60 bpm
G. QRS complex <0.12 seconds
H. PR interval 0.12-0.20 seconds
I. PR interval >0.20 seconds
You're providing care to a 55-year-old male. You note on the bedside monitor the patient has a heart rate of 116 bpm. You obtain an ECG and discover the patient rhythm is Sinus Tachycardia. You assess probable causes of this rhythm. Which finding below could be a cause of this patient's heart rhythm?
A. Digoxin therapy
B. Pain rating of 2 on 1-10 scale
C. Temperature 39.7C
D. Blood glucose of 86 mg/dL
Your patient is experiencing Sinus Tachycardia with a rate of 160 bpm. Which findings below demonstrate the patient is experiencing a decrease in cardiac output? Select all that apply:
A. Blood pressure 220/120 mmHg
B. Blood pressure 70/42 mmHg
C. Crackles throughout the lung fields
D. Decreased capillary refill time
E. Cool extremities
What are possible causes of Sinus Tachycardia? Select all that apply:
A. Exercise
B. Atropine
C. Pain
D. Sick Sinus Syndrome
E. Cardiogenic shock
F. Hypothyroidism
Your patient develops Sinus Tachycardia with a heart rate of 136 bpm. The patient is post-op from hip surgery. The patient reports chest pain that is worst with each breath in and has shortness of breath. These findings can correlate with what serious condition?
A. Cardiogenic shock
B. Pulmonary embolism
C. Sick Sinus Syndrome
D. Hypovolemic shock
Which statement below best describes why Sinus Tachycardia could lead to decreased cardiac output?
A. “The atrial kick is decreased leading to inadequate atria emptying.”
B. “The ventricles don’t have enough time to fill completely so less blood is pumped out of the heart.”
C. “The rapid firing of the SA node leads to rapid atrial contraction and causes blood to pool in the atria.”
D. “The ventricles are unable to properly contract and push blood forward so less blood is pumped out of the heart
What medication below is NOT a treatment for Sinus Tachycardia?
A. Verapamil
B. Metoprolol
C. Antipyretics
D. Dopamine
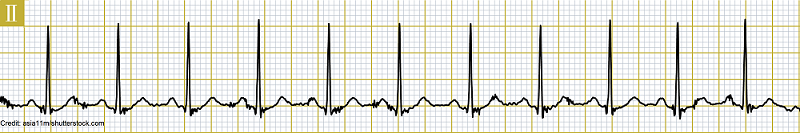
What is the rate of the rhythm above?
A. 110 bpm
B. 120 bpm
C. 130 bpm
D. 140 bpm
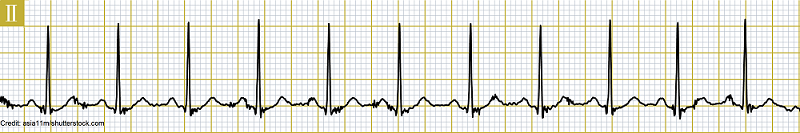
What is the PR Interval?
A. 0.06 seconds
B. 0.12 seconds
C. 0.16 seconds
D. 0.20 seconds
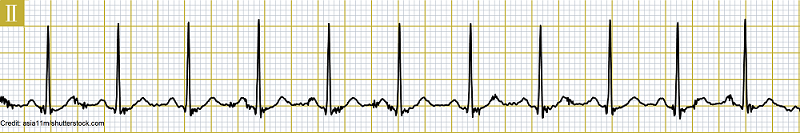
What is the QRS complex duration?
A. 0.06 seconds
B. 0.12 seconds
C. 0.08 seconds
D. 0.20 seconds
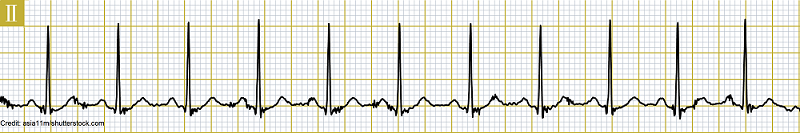
What is the atrial rate?
A. 100 bpm
B. 110 bpm
C. 120 bpm
D. 130 bpm
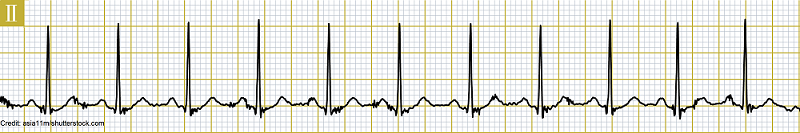
True or False: The rhythm above is Sinus Tachycardia.
True
False
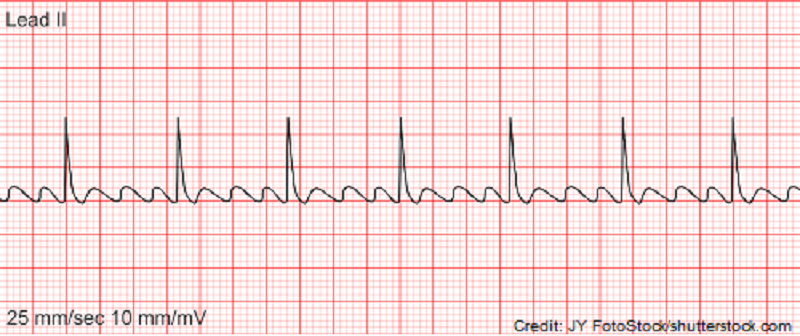
Select the options below that describe the rhythm above:
A. P-waves present
B. Fibrillary waves present
C. Flutter waves present
D. Atrial rate <100 bpm
E. QRS complex less than 0.12 seconds
F. PR interval <0.20 seconds
G. Atrial fibrillation
H. Atrial flutter
I. Normal sinus rhythm
Which statement is correct about atrial flutter?
A. The ventricular rate will always be irregular.
B. P-waves will be present.
C. This rhythm has a saw-tooth appearance.
D. The PR interval will be >0.20 seconds.
True or False: Atropine is the first-line treatment to help control the rate in a patient with atrial flutter
True
False
Your patient's ECG shows atrial flutter. What complication can arise from this type of rhythm?
A. Pericarditis
B. Stroke
C. Hypoglycemia
D. Endocarditis
True or False: Treatment for unstable atrial flutter is synchronized cardioversion
True
False
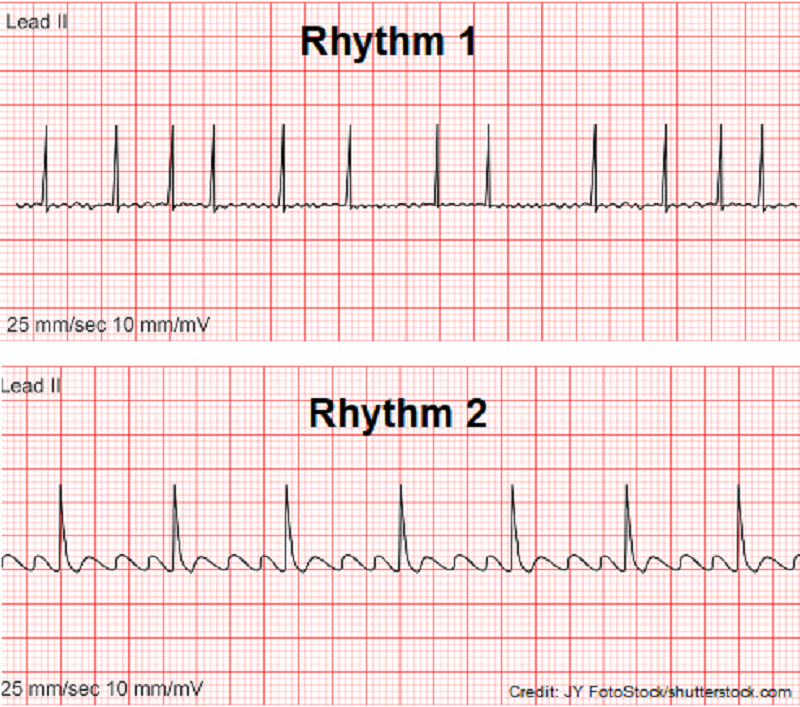
Fill-in-the-blank: Rhythm 1 is _________________ , and Rhythm 2 is _____________.
A. Atrial fibrillation; atrial flutter
B. first-degree heart block; atrial flutter
C. Atrial flutter; atrial fibrillation
D. Atrial flutter; sinus bradycardia
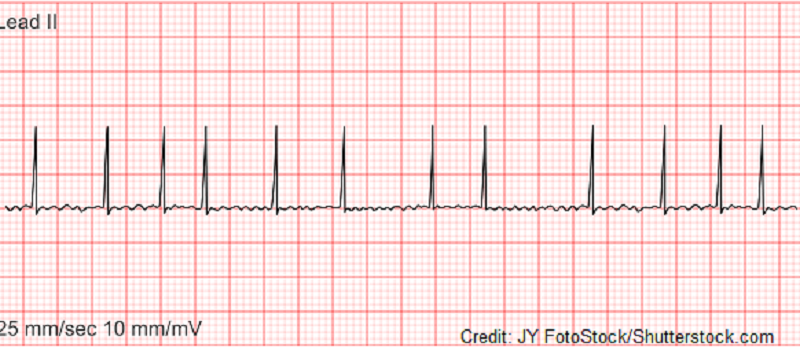
Select the options below that describe the rhythm above:
A. Atrial rate <60 bpm
B. Regular atrial rate
C. Irregular ventricular rate
D. Ventricular rate >100 bpm
E. QRS complex absent
F. Fibrillary waves present
G. Atrial Flutter
H. Atrial Fibrillation
I. Sinus Tachycardia
The nurse is assessing an ECG strip. Which finding on the ECG strip is NOT a characteristic present in atrial fibrillation (a-fib)?
A. Fibrillary waves
B. Unmeasureable atrial rate
C. saw-tooth waves
D. Irregular ventricular rate
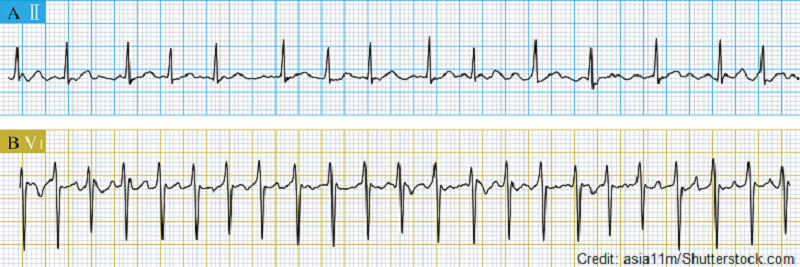
The patient's ECG shows the rhythm above. The patient is symptomatic and experiencing shortness of breath and chest pain. The patient's blood pressure is 80/44 with the heart rate fluctuating between 130-150s. The nurse calls a rapid response and prepares the patient for?
A. Ablation
B. Synchronized cardioversion
C. Defibrillation
D. Pacemaker implantation
Which statements below best described a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation? Select all that apply
A. It can be performed before a cardioversion to assess for blood clots in the heart.
B. This procedure destroys electrical pathways in the heart to help return a patient’s heart rhythm to normal.
C. During this procedure, an ultrasound probe is inserted in the patient’s mouth down through the esophagus where it takes ultrasound pictures of the heart.
D. During the procedure, a transducer is placed on the chest that sends ultrasound waves through the skin so pictures can be obtained of the heart’s blood flow.
What complications can develop from uncontrolled atrial fibrillation that the nurse should monitor for? Select all that apply
A. Hypertension
B. Stroke
C. Heart failure
D. Hyperglycemia
True or False: If a patient has been in atrial fibrillation for more than 48 hours, anticoagulation is needed prior to a cardioversion due to blood clot risks
True
False
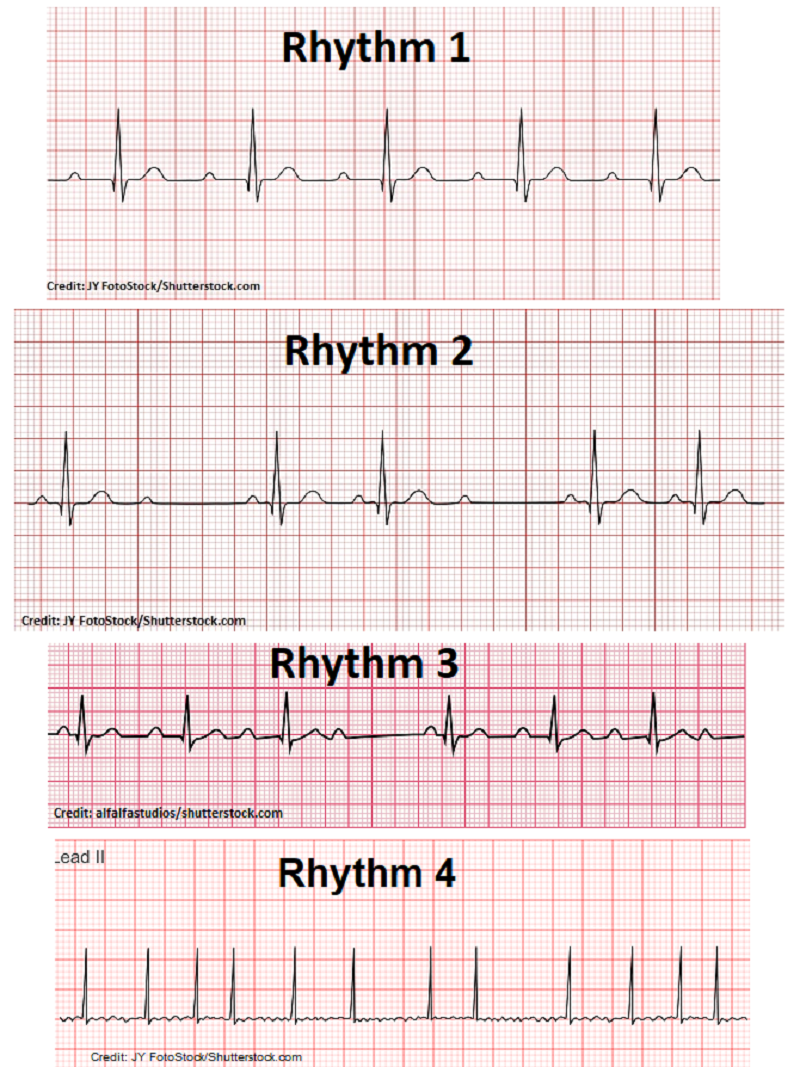
Which rhythm above is atrial fibrillation?
A. Rhythm 1
B. Rhythm 2
C. Rhythm 3
D. Rhythm 4
{"name":"Critical Nursing Arrhythmias Quiz Part 1 By:Mohamed Mamdouh", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Select the options below that describe the rhythm above, TRUE or FALSE: Torsades de pointes is known as a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia., Your patient is unresponsive and the cardiac monitor shows Torsades de Pointes as the patient’s rhythm. As the code team is attempting to resuscitate the patient, you look through the patient’s electronic health record to try to determine a potential cause for this rhythm. What found in the patient’s record is a cause of this rhythm?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/100-4920380/ventricular-tachycardia-monomorphic.jpg?sz=1200-00000000000442205300"}