It is the time when all body systems are fully grown and reach their physical peak from 18 to 30 years of age. – The person stops growing in height.
It is responsible for producing sperm cells and hormones. A sperm cell is needed to fertilize an egg cell.
What are the mature sperm cells' size compared to other cells in the human body?
Smaller
Larger
Same size
Varies
Where are the mature sperm cells produced in the male reproductive system?
Seminiferous tubules
Urethra
Vas deferens
Epididymis
How long are the seminiferous tubules in total?
More than 450 meters
Less than 100 meters
Around 250 meters
Varies
What is the name of the larger tube that sperm cells enter before leaving the testis?
Vas deferens
Seminiferous tubules
Urethra
Epididymis
Where do the two sperm ducts (vas deferens) lead to?
Urethra
Seminiferous tubules
Epididymis
Testis
What happens as sperm cells pass from the sperm ducts through the urethra?
They are mixed with fluids from three types of glands
They become smaller in size
They multiply rapidly
They exit the body
What is the function of the fluids mixed with sperm cells as they pass through the urethra?
They protect the sperm cells
They provide color to the semen
They remove excess heat from the body
They store the sperm cells
What is the final product formed when sperm cells are mixed with fluids?
Semen
Blood
Lymph
Urine
This is the outer component of the male reproductive system. It serves as the organ through which urine exits the body and transfers sperm into the female's body for reproduction.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It serves as a protective pouch for the testes, maintaining them at the necessary temperature, which is slightly lower than the body's temperature. This is crucial because sperm is sensitive to heat and requires a cooler environment.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
They are two small, egg-shaped structures found inside the scrotum. Their primary functions are to produce sperm and secrete a hormone.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
Are tiny cells that can fertilize an egg, leading to the formation of a baby.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It is a coiled tube attached to the back of each testis. It's where the sperm mature and get ready to leave the body.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It is a tube that connects the bladder to the penis. It carries both urine and sperm out of the body but not at the same time, of course!
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It is a long tube that connects the epididymis to the urethra. It's like a highway for sperm, allowing them to travel from the testes to the urethra.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It is also an important part of the male reproductive system. It produces a slippery fluid that helps to clean and prepare the urethra for the sperm's journey.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It is a small part of the male body, located near the bladder. Its job is to make a special liquid that mixes with sperm. This special liquid is called "prostate fluid," and it's important because it helps protect the sperm and gives them the energy they need to swim.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
Two small pouches that produce a sugary fluid that mixes with sperm and the prostate's fluid to create semen. This sugary fluid provides energy for the sperm so they can swim better.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
It refers to the organs and structures in a girl or woman's body that are involved in the process of reproduction, or the creation of new life.
It is a hormone produced by the testes in the male reproductive system. It plays a crucial role in the development of male characteristics, such as facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and muscle growth.
Penis
Scrotum
Testes
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas Deferens
Prostate Gland
Cowper’s Gland
Seminal Vesicles
Testosterone
Sperm
Are similar to two small passageways that link the ovaries to the uterus. This is where an egg can meet sperm
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Vagina
Ovary
Cervix
These are two small organs that produce egg cells.
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Vagina
Ovary
Cervix
It is a hallow, pear-shaped organ with muscular walls. It is where a fetus grows and develops.
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Vagina
Ovary
Cervix
The lower end of the uterus. It connects the uterus to the vagina.
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Vagina
Ovary
Cervix
It is a special part of a girl's or woman's body. It's like a flexible tube that connects the outside of the body to the inside.
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Vagina
Ovary
Cervix
This is when the lining of the uterus, which is a special part in a person's body where a baby can grow, is shed. This happens because the body gets ready for a possible pregnancy every month, and if there's no pregnancy, the extra lining is not needed. So, the body gets rid of it through the vagina.
MENSTRUAL PHASE
FOLLICULAR PHASE
OVULATION PHASE
LUTEAL PHASE
It starts on the first day of the menstrual period and lasts for 13-14 days. The pituitary gland in the brain releases a hormone to stimulate the production of the follicles in the ovary. One of the follicles will then form into a mature egg. While this happens, the inside lining of the uterus, called endometrium, develops and thickens in preparation for pregnancy.
MENSTRUAL PHASE
FOLLICULAR PHASE
OVULATION PHASE
LUTEAL PHASE
Happens when the pituitary gland releases a hormone that causes the ovary to release the mature egg cell. The mature egg cell moves along the fallopian tube toward the uterus.
MENSTRUAL PHASE
FOLLICULAR PHASE
OVULATION PHASE
LUTEAL PHASE
After ovulation, cells in the ovary called corpus luteum, release progesterone and estrogen. This causes the endometrium to thicken in preparation to pregnancy.
MENSTRUAL PHASE
FOLLICULAR PHASE
OVULATION PHASE
LUTEAL PHASE
What is the common term for the discharge of blood and tissue from the uterus during the menstrual phase?
Fertilization
Ovulation
Menstruation
Implantation
How long does menstruation typically last?
2-3 days
5 days
7 days
10 days
What causes abdominal cramps during menstruation?
Release of a mature egg
Thickening of the endometrium
Contraction of the uterus and abdominal muscles
Corpus luteum formation
When does the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle begin?
After ovulation
During menstruation
On the 14th day of the cycle
Before implantation
What is the role of the pituitary gland during the follicular phase?
Releases hormones for ovulation
Stimulates follicle production in the ovary
Thickens the endometrium
Causes the uterus lining to shed
When does ovulation typically occur in the menstrual cycle?
5th day
10th day
14th day
20th day
What happens during the luteal phase after ovulation?
Release of a mature egg
Thickening of the endometrium
Corpus luteum releases progesterone and estrogen
Contraction of the uterus
What happens during the luteal phase after ovulation?
5th day
10th day
14th day
20th day
What is the primary function of progesterone during the luteal phase?
Thickening the endometrium
Stimulating follicle production
Initiating ovulation
Shedding the uterine lining
What occurs if the egg is fertilized and implants into the uterus?
Menstruation begins
Corpus luteum dies
Progesterone levels drop
Pregnancy occurs
If pregnancy does not occur, what happens to the corpus luteum and the menstrual cycle?
Corpus luteum continues to produce hormones
Menstrual cycle restarts
Ovulation occurs again
Endometrium thickens for another cycle
Where are mature sperm cells produced in the human body?
Vas Deferens
Seminiferous Tubules
Urethra
Prostate Gland
Which is responsible for the production of primary female sex hormones?
Ovary
Testis
Uterus
Cervix
Which is not true about the female reproductive system?
The female reproductive system is a simple system.
Estrogen is produced by the ovaries.
The ovaries release one egg for each month.
Vagina is an internal female reproductive organ.
Which is true about the two statements below?
Statement 1: A male’s internal reproductive organs are the testes, epididymis, seminal vesicle, and prostate gland.
Statement 2: The male reproductive organs are designed to carry out several reproductive functions.
Statement 2 agrees with the idea expressed in Statement 1.
Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
Statement 2 does not explain Statement 1.
Statement 1 contradicts Statement 2.
Which describes the function of the ovary?
I. It houses the egg cells.
II. It nourishes the developing fetus.
III. It produces egg cells.
IV. It produces estrogen.
I, III and IV
I, II, and III
II and III
I and II
Which is the correct pathway of sperm cells before they are released from the body?
Testes – epididymis – vas deferens – seminal vesicle - prostate gland
Seminal vesicle – prostate gland – testes – epididymis – vas deferens
Vas deferens – epididymis – testes – prostate gland – seminal vesicle
Prostate gland – epididymis – vas deferens – testes – seminal vesicle
Choose the word that is related to the third word in the same way that the second is related to the first.
testes : sperm ; ovary : _____
Egg cell
Cervix
Zygote
Fimbriae
Choose the word that is related to the third word in the same way that the second is related to the first.
pregnancy: 36 weeks ; menstruation: ____
1 week
4 weeks
14 weeks
16 weeks
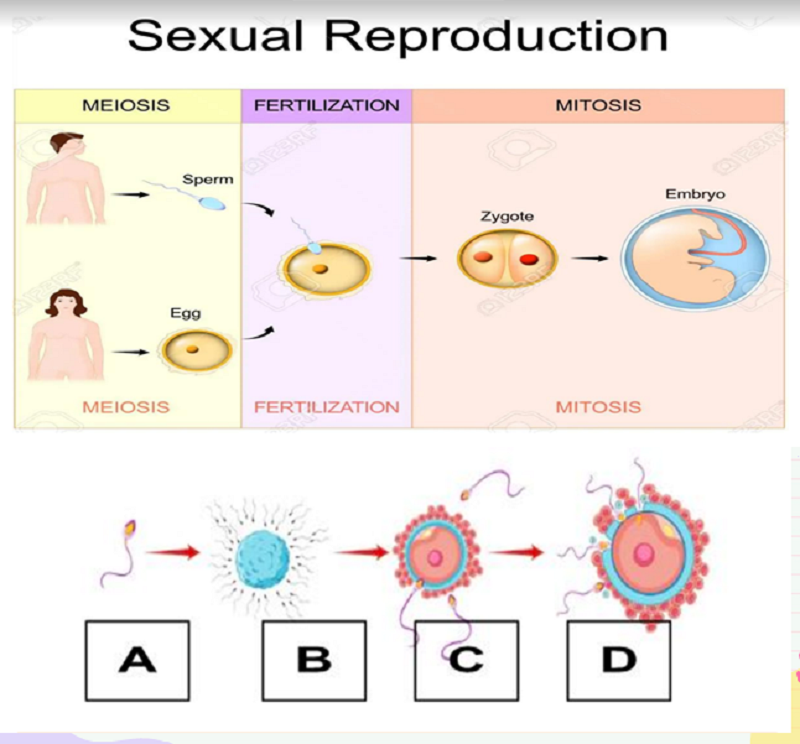
A -
Sperm
Journey through the Female Reproductive
Fertilization
Zygote development

B
Sperm
Journey through the Female Reproductive
Fertilization
Zygote development

C -
Sperm
Journey through the Female Reproductive
Fertilization
Zygote development

D -
Sperm
Journey through the Female Reproductive
Fertilization
Zygote development
What is the primary function of the ovaries?
Store mature egg cells
Produce hormones
Connect the uterus to the vagina
Facilitate ovulation
What happens to the eggs as a female matures into puberty?
They are released during ovulation
They decrease in size
They become inactive
They multiply rapidly
What is puberty?
A time when the body transforms from being a kid to becoming an adult
A time when eggs are released
A process of egg production
A stage after menopause
What is the size of a mature egg cell released from the ovary during ovulation?
About the size of a small dot on a piece of paper
Smaller than a dot on a piece of paper
About the size of a pea
The largest cell in the human body
What is the tube that leads from the ovary to the uterus called?
Fallopian Tube
Vagina
Uterus Tube
Ovarian Tube
Where does a fetus grow and develop in the female reproductive system?
Uterus
Ovary
Fallopian Tube
Vagina
What is the lower end of the uterus called?
Cervix
Ovary
Fallopian Tube
Vagina
What is the function of the cervix in the female reproductive system?
Connects the uterus to the vagina
Produces hormones
Releases eggs during ovulation
Connects the ovaries to the fallopian tubes
What is the vagina in the female reproductive system?
A tube connecting the outside of the body to the inside
A muscular organ where a fetus grows
The largest cell in the human body
A sac-like structure that stores eggs
What happens to a woman's uterus when she is not pregnant
It folds almost flat
It expands
It remains the same size
It contracts
What occurs starting at puberty in preparation for pregnancy?**
Uterus lining thickens
Uterus shrinks
Fallopian tube expands
Ovaries release fewer eggs
What is fertilization
The process of sperm and egg combining
The thickening of the uterus lining
The folding of the uterus
The growth of the zygote
What is a zygote?
The first cell formed when sperm fertilizes an egg
A type of hormone produced by the ovaries
A structure that connects the fetus to the placenta
The final stage of the menstrual cycle
What is a zygote?
A developing fetus
A thickened uterus lining
A mature egg cell
A fertilized egg
Where does fertilization occur in the female reproductive system?
Fallopian Tube
Vagina
Ovary
Uterus
What happens to the zygote after fertilization?**
It moves down the fallopian tube and embeds in the uterus lining
It stays in the fallopian tube
It disintegrates
It moves to the ovary
How long does a fetus typically develop inside the uterus?
38 weeks
9 weeks
18 weeks
48 weeks
What does the fetus eat while developing inside the uterus?**
Special nutrients supplied by the mother
The uterine lining
It doesn't eat
The mother's blood
How is a baby born when the time comes?**
Through the vagina
Through the abdomen
Through the fallopian tube
Through the cervix
What is the vagina's role in the female reproductive system during sexual activity?**
Receives sperm cells
Produces eggs
Releases hormones
Nourishes the fetus
What is the menstrual cycle's first phase, commonly known as the period?**
Menstrual Phase
Follicular Phase
Ovulation Phase
Luteal Phase
How long does the menstrual phase usually last?**
3-7 days
1-2 days
8-10 days
11-14 days
What causes abdominal cramps during menstruation?**
Contraction of the uterus and abdominal muscles
Thickening of the uterus lining
Release of mature egg cells
Hormonal changes in the fallopian tube
When does the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle begin?**
On the first day of menstruation
After ovulation
During the luteal phase
During pregnancy
What happens during the follicular phase?**
Development of the follicles in the ovary
Thickening of the uterus lining
Release of mature egg cells
Implantation of the fertilized egg
What hormone helps the follicles grow during the follicular phase?**
Estrogen
Progesterone
Testosterone
Oxytocin
When does ovulation typically occur in a 28-day menstrual cycle?**
Day 14
Day 7
Day 21
Day 28
What is released during the ovulation phase?**
Mature egg cell
Menstrual fluid
Progesterone
Estrogen
What is the corpus luteum, and what hormones does it release?**
It's the structure that forms after ovulation; it releases progesterone and estrogen.
It's the first phase of the menstrual cycle; it releases estrogen.
It's the lining of the uterus; it releases testosterone.
It's another name for the fallopian tube; it releases oxytocin.
What happens if the egg is not fertilized during the luteal phase?**
Menstrual cycle begins again
The corpus luteum continues to produce hormones
Ovulation occurs
Follicles develop in the ovary
What is the MENSTRUAL PHASE commonly known as?**
Menstrual cycle begins again
The corpus luteum continues to produce hormones
Ovulation occurs
Follicles develop in the ovary
{"name":"It is the stage of life after birth.", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"It is the stage of life after birth., Also know as a newborn baby, depends on his\/her parents for food, clothes, protection, and love., It is a time of mental and emotional development.","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/95-4660935/3.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which Canada child are you?
10521
Que tanto sabes de Thais o su Familia
6329
Surprise Bitch
20108
Ok
100
Condensed Matter Physics I
15833315
Free Japanese Lesson Review
201022131
Which Statement About Stigma Is True? Free Challenge
201026100
Free Legal Code Knowledge Assessment
201023715
Discover Your Capricorn Character Traits - Free
201024945
Free Intrapartum NCLEX Questions - Challenge Yourself
201044315
Which Alien Stage Character Are You? Free Reveal
201023910
Ultimate Engine Lubrication & Cooling: Test Your Skills
201044315