DES 3 ep 8
167) A 50-year-old pale man comes to the office and says, "For the past year, I've been feeling very weak. I get tired early, and I feel that I've lost my sense of humor. I find it difficult to remember things now." When asked about his social history, he says, "I'm jobless and am living on social security benefits. I don't drink or smoke anymore, but I was charged with driving under the influence three times before." His parents died of old age. He shares his room with four friends. His vital signs are normal. CBC reveals: WBC 5,500 /mm3, Hemoglobin 7.0 mg/dl, Hematocrit 22%, Platelets 196,000/mm3, RBC count 1.7 million, MCV 119 fl, MCH 36, MCHC 28%, Reticulocyte count 04%. Peripheral smear shows anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, and basophilic stippling. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Iron studies
. Osmotic fragility test
Sugar water test
. Serum B12 and folate levels
. Bone marrow biopsy with prussian blue staining
168) A 45-year-old white male presented to his primary care physician due to easy fatigability. He is a pure vegetarian and a known alcoholic. Physical examination revealed significant pallor. His hemoglobin level was 10.8gm/dl, and serum iron studies were within normal limits. His physician placed him on folic acid (1 mg daily), and his hemoglobin level increased to 13gm/dl over a period of several months. The patient continued to take folic acid for the next two years. On his next follow-up visit, he complained of gradual memory loss and difficulty in maintaining his balance for the past six months. Which of the following is the most likely thing to consider at this point?
. He should be referred for CT of the abdomen with and without contrast
. He has been treated with subtherapeutic doses of folic acid
. The physician should have checked his vitamin B12 levels
. Order FTA-ABS to rule out syphilis
. The patient should have been started on pyridoxine
169) A 39-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of double vision. She feels "weak all over," especially at the end of the day. She had the same complaints 8 months ago that persisted for several weeks, but she didn't see a doctor because she had no insurance then. She has no past medical history. Her mother has rheumatoid arthritis, and her brother has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Her vital signs are normal. She has diplopia and mild ptosis. Her blood profile, CBC and thyroid tests are within normal limits. Electromyography and repetitive nerve stimulation reveals a decremental response in compound action potentials. Her acetylcholine receptor antibody test is positive. Which of the following tests should be ordered next?
. Edrophonium (Tensilon) test
. Muscle biopsy
. Anti-RNP antibodies
. Anti-Jo antibodies
. CT scan of chest
170) A 51-year-old man comes to you complaining of increased itching, especially after bathing. He also has occasional headaches and dizziness. There is no history of smoking or alcohol use. His sister has psychiatric problems and both parents died in a car accident, many years ago. His vitals are; Temperature: 36.7°C (98.2°F); BP 148/90 mm Hg; PR 77/min; RR 12/min. On examination, his spleen is enlarged and he appears plethoric. CBC was ordered and came back as: WBC 14,500/mm3, Hemoglobin 21.5, Hematocrit 64%, Platelets 521,000/mm3, RBC count 7.6 million, MCH 30, MCHC 36, MCV 92, ROW 15.1 (n=10.3-14.1). Which of the following is expected on further work up?
. Markedly elevated serum cortisol level
Absence of measurable erythropoetin in urine
. Elevated brain natriureteric peptide level
. Elevated ESR
. Hyponatremia and hyperkalemia
171) A 35-year-old white female slipped and fell on her side 2 days ago while she was going down the stairs from her house. Since that time, she has been having pain in her right shoulder. She describes this as an ache, which has been about the same over the last couple of days. She has tried ibuprofen, with only slight relief. She denies smoking and alcohol use. Examination suggests a shoulder sprain. You order an x-ray and see a normal shoulder but incidentally a 1.5cm coin-shaped lesion, in the outer side of right lung with well-aerated surrounding lung. She denies any respiratory complaints. What is the next best step regarding her lung lesion?
. Fine needle aspiration
. Ask for an old X-ray
. Bronchoscopy
. CT scan chest
. Open lung biopsy
172) A 74-year -old Caucasian man is evaluated for occasional palpitations and poor exercise tolerance. He has been living alone since his wife died two years ago. His diet consists mainly of precooked food that he heats up in the microwave oven. He has a history of degenerative joint disease and hypertension. He takes a daily aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide, and glucosamine. He quit smoking 20 years ago and occasionally drinks alcohol. His peripheral blood smear is shown below. Which of the following substances is most likely elevated in this patient's blood?
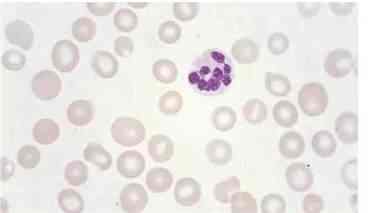

. Ferritin
. Methionine
. Homocysteine
. Haptoglobin
. Cobalamin
173) A 45-year-old male with Burkitt's lymphoma is being treated with combination chemotherapy and allopurinol. On the 3rd day of treatment, he is noted to have decreased urine output and increased levels of BUN and creatinine. The patient is started on vigorous hydration. EKG reveals prolonged QT intervals. The suspected diagnosis is tumor lysis syndrome. Complete metabolic profile is ordered. Which of the following sets of results are expected in this patient? (Calcium, Phosphate, Potassium, Uric Acid)
. Decreased, Decreased, Decreased, Decreased
. Increased, Increased, Increased, Increased
. Decreased, Increased, Increased, Increased
. Decreased, Decreased, Increased, Increased
. Decreased, Increased, Decreased, Decreased
174) A 55-year-old woman comes with complaints of episodes of night sweats and fever, for the last 6 weeks. She denies any cough or other respiratory complaints. She has lost 201b (9kg) and does not feel like eating anything. She denies smoking or alcohol use. Her brother was recently diagnosed with polycythemia vera. Physical examination reveals pallor and splenomegaly. Chest-X ray is within normal limits. Blood work is ordered and results are: WBC 66,100/cmm, Hemoglobin 8.70, Hematocrit 30%, Platelets 610,000/cmm. The leukocyte distribution on differential smear was: Promyelocyte 1%, Myelocyte 8%, Metamyelocyte 15%, Bands 35%, Segmented Neutrophils 25%, Lymphocytes 14%, Monocytes 2%. Further tests are ordered. Which one of the following is expected in this patient?
. Absence of measurable erythropoetin in urine
. Elevated leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
. Presence of auer rods
. Increased bone marrow iron
. Decreased leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
175) A 62-year-old man comes to the office and complains of increasing fatigue and weakness for the last 4 months. He also describes a dull pain in his back and arms, which gets worse with walking. He denies any numbness or paresthesia. On examination, he appears pale. There is tenderness around the lumbar spine. CBC reveals: WBC 8,600 mm3 with normal differential, Hemoglobin 8.6 g/dl, Hematocrit 27%, Platelets 164,000 mm3. The RBC morphology is significant for a rouleaux appearance. The ESR is 55mm/hr. Bence Jones proteins are identified in the urine. Which of the following is expected in this patient's bone marrow examination?
. Increased marrow cellularity with megakaryocytic hyperplasia
. Over proliferation of plasma cells
. Normocellular bone marrow
. Hypoplastic fat- filled marrow with no abnormal cells
. Hypocellular and fibrotic bone marrow
176) A 27 year-old African-American woman presents to the emergency room complaining of unilateral leg swelling, pleuritic chest pain and shortness of breath. She reports a rash on her face that worsens in the sun, two previous miscarriages, and complains of recent painful swelling in both knees. A CT angiogram confirms a pulmonary embolus. Which of the following is the most likely laboratory abnormality?
. Absent Von Willebrand's factor
. Decreased prothrombin time (PT)
. Increased bleeding time
. Prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
. Thrombocytosis
177) A 60-year-old man comes to office with persistent complaints of malaise and easy fatigability, for the past 8 months. On examination, he appears pale. PR 93/min; BP 127/84mm Hg; Temperature 37°C (98.6°F); RR 16/min. Fecal occult blood test is negative. Further testing is ordered that include CBC, serum electrolytes and colonoscopy. The results are: WBC 7,600/mm3, Hemoglobin 8.8 gm/dl, Hematocrit 30%, RBC count 3.6 million, Platelets 211,000/mm3. RBC Indices were:MCV 65 fl, MCH 16.5 pg, MCHC 26%, Reticulocyte count 0.5%. Which one of the following is expected on iron studies in this patient? (Serum Iron, Ferritin, TIBC, Transferrin Saturation)
. High,Normai,High,Normal to High
. Low,High,Low,Lowto normal
. Low,Low,High,Low
. Normal, Normal, Normal, Normal
. Low,Low,Low,Low
1) A 55-year-old woman comes to her primary care physician with complaints of pain, itching and red streaks in her left arm. She feels that her arm is "simply not the same". She had a similar episode in her chest almost 2 weeks ago, but it went away on its own. She has no other complaints, except for heartburn and some upper abdominal pain that has been there for a few months. She takes antacids for it, but has never got over it completely. She thinks that she has lost some weight but she feels happy about it, as she always wanted to lose weight. Her vitals are stable and there is mild epigastric tenderness. She has tender, erythematous, cord like veins palpable over left arm and some over the chest. She smokes 1-2pack/day for 15years and drinks alcohol, only on parties. What is the next best step in this patient?
. Antibiotics and reassurance
. Upper GI endoscopy with barium swallows
. CT scan abdomen
. Colonoscopy
. Spiral CT chest
2) A 51-year-old man comes to the office for his annual examination. He is apparently healthy, and does not have any complaints. His diet is normal, and he exercises regularly. He experiences some stress at work, but says that he is "strong and can fight it out." His father died of a heart attack 4 years ago, and his mother has Alzheimer's disease. His brother has recently been diagnosed with colonic polyps. His vital signs are stable. Hematology and chemistries are within normal limits, but the fecal occult blood test (FOBT) is positive. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Do colonoscopy
. Perform screening sigmoidoscopy
. Advise him to change his diet and examine him next week
. Perform double contrast barium enema
. Order abdomen radiograph for air under the diaphragm
3) A 35-year-old man presents with gastrointestinal complaints for the last 4 months. He currently has fever, bloody diarrhea, nausea, and severe abdominal cramps. He has lost 20 lb (9kg), and has also been feeling fatigued and anorexic. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1° F), blood pressure is 110/74 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination reveals tenderness in the right lower quadrant. Digital rectal examination is positive for occult blood. His blood work shows: WBC 11,600 /mm3, Hemoglobin 9.6 g/dl, Hematocrit 30%, Platelets 214,000 /mm3. Flexible sigmoidoscopy reveals larger areas of ulceration within the colon. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Dietary modification and reassurance
. Refer him for procto-colectomy
. Perform a biopsy of the colon lesion
. Give sulfasalazine
. Give a bolus of corticosteroids
4) A 34-year-old man presents to your office for a routine check-up. He has no current complaints except for being "a little stressed out." He works as an executive officer and travels a lot within the country. He does not smoke and consumes alcohol occasionally. He currently takes no medications. His family history is insignificant. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and heart rate is 80/min. Chest examination is unremarkable. The liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable. There is no cervical lymphadenopathy. Laboratory studies show: Erythrocyte count 5 million/mm3, Hemoglobin 14.0 g/dL, Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3, Platelet count 80,000/mm3. Which of the following is the best initial test for this patient?
. Rapid plasma reagin test
. Epstein-Barr virus titers
. Schilling test
. HIV antibody test
. Blood folate level
5) A 25-year-old female presents to your office complaining of exertional dyspnea and fatigue. Her past medical history is insignificant. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals pale conjunctiva. The laboratory values are: ESR 15 mm/hr, Hemoglobin 7.5 g/dL, MCV 70 fl, MCHC 29%, Leukocyte count 7,000/cmm, Segmented Neutrophils 55%, Bands 3%, Eosinophils 3%, Basophils 0%, Lymphocytes 32%, Monocytes 7%. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Serum folate level
. Bone marrow sampling
. Schilling test
. Iron studies
. HbA2 measurement
A 40-year-old male comes to the office because of progressive knee and shoulder pain, which he describes as 5/10 in intensity and started 6 months ago. He has no other medical problems, except for newly diagnosed diabetes. He admits to "chain smoking" for "all his life" and drinks 1-2 bottles of beer a night. He is faithful to his wife. His mother died of "blood cancer" when he was 3-years-old. His father also has diabetes mellitus. His temperature is 37°C (98.6° F), pulse is 86/min, blood pressure is 134/86 mmHg, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals slightly swollen and tender knee joints. Mild hepatomegaly is present on abdominal examination. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Serum iron studies
. HbA1C level
. Liver biopsy
. X-ray of the shoulder and knee
. Steroid injection of the joint
7) A 42-year-old male presents to your office complaining of fatigue. His past medical history is insignificant. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and heart rate is 85/min. Physical examination is insignificant. Laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 7.7 g/dL, MCV 72 fL, MCHC 28%, Leukocyte count 8,000/cmm, ESR 15 mm/hr. Serum iron and ferritin levels are decreased. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
. Test for occult blood in the stool
. Iron supplementation
. Work-up for malabsorption
. Dietary modifications
. Bone marrow sampling
8) A 35-year-old male is brought to the emergency room with headaches and confusion for the past 2 days. He denies any focal weakness or sensory symptoms. His past medical history is significant for HIV and hepatitis C infections for which he is not receiving therapy. The remainder of his medical history is unobtainable due to his mental status. On physical exam, he has a temperature of 37.9°C (100.2°F), a blood pressure of 140/86 mm Hg, a pulse of 96/min, and respirations of 16/min. Mild icterus is present. The patient's oropharynx is clear and his neck is supple and without rigidity. Examination of his chest and abdomen are unremarkable. Neurologic examination reveals no focal deficits. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count:Hemoglobin 7.6 g/L, MCV 85 fl, Reticulocytes 8.1%, Platelet count 80,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 3,500/mm3. Chemistry panel: Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 30 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.2 mg/dL, Serum calcium 10.0 mg/dL, Blood glucose 98 mg/dL. Liver studies:Total bilirubin 3.6 mg/dL, Direct bilirubin 1.0 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 120 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 178 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 255 U/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
. Right upper quadrant ultrasound
. Liver biopsy
. Lumbar puncture
. Peripheral blood smear
. CT scan of the head
9) A 46-year-old woman comes to the office and says, "I can't believe I've lost so much weight in the last 2 months because I seem to be eating much more than ever. I also find it odd that I drink lemonade all the time, and I have to rush to the bathroom regularly. It seems like everything in me is vanishing."Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 110/70mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 14/min .Physical examination reveals a lean woman with an erythematous, scaly plaques on her face, and on her buttocks. The laboratory studies reveal: WBC 6,400 /mm3, Hemoglobin 8.7 g/dL, Hematocrit 29%, Platelets 193,000/mm3, Sodium 144 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 21 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL, Glucose 245 mg/dL. Which of the following is expected in this patient?
. Increased glucagon level
. Increased thyroxine level
. Increased gastrin level
. Decreased insulin level
. Increased serotonin level
10) A 56-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of an ulcer on her left elbow. The ulcer is a persistent, scaly red patch with irregular borders, and it sometimes crusts or bleeds. She recalls the time when she badly burned her left elbow while learning how to cook pasta at thirteen years of age. She works as a public relations officer in a large marketing company. She is a social smoker, and does not like drinking alcohol. Physical examination of the left elbow reveals a big scar with a firm, nontender, reddened, non-healing indolent, 3cm ulcer in the center. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Punch biopsy
. Surgical excision
Chemotherapy
. Observation for 3 weeks with antibiotics
. Local radiation
11) A 56-year-old male is being evaluated for increased fatigability. His past medical history is significant for severe aortic stenosis that required aortic valve replacement, diabetes mellitus, and osteoarthritis. Peripheral blood smear findings are shown on the slide below. Which of the following laboratory findings would you most expect to find in this patient?
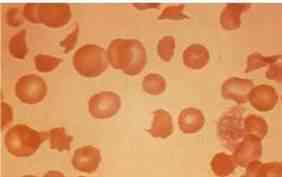
zzz

. Increased total serum iron level
. Decreased serum haptoglobin level
. Decreased reticulocyte count
. Increased mean corpuscular volume
. Decreased serum albumin level
12) A 64-year-old woman comes to the hospital due to an "irritating sore throat for 3 months." She admits to smoking 1 pack of cigarettes daily for the past 29 years, and continues to smoke. She was jailed twice for driving under the influence of alcohol, and went to Alcohol Rehabilitation last year. She currently denies any alcohol intake. She has no fever or any other complaints. She had a complete hysterectomy several years ago for symptomatic fibroids. Her vital signs are stable. Physical examination reveals a 1.5-cm right cervical lymph node. The rest of the examination is normal. Biopsy of the lymph node reveals metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. The CT scan of the chest is negative. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Repeat CT in 3 months
. Empirical chemotherapy
. Screening mammogram
. Pan-endoscopy
. Radical neck dissection
13) A 45-year-old white male comes to the emergency room with "all sorts of things going wrong with him", for the last few months. He has a severe headache, chest and abdominal pain. He is sweating profusely. He has lost weight recently, has diarrhea and palpitations. He is feeling hot all the time. Vital signs reveal BP: 190/100mm of Hg; PR 124/min; RR 18/min; Temperature 37.7° C (99.8°F). On physical examination he has enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Examination of the thyroid reveals multiple thyroid nodules. FNA biopsy reveals thyroid C-cell hyperplasia. Which of the following can also be found on laboratory results?
. Increased serum phosphorus
. Decreased serum calcitonin
. Decreased serum alkaline phosphatase
. Decreased urine metanephrine
. Increased serum calcium
14) A 24-month-old pale child is brought to the office by his mother, who says, "Doc, I think he is under some weird spell. He acts bizarre and always seems tired. He likes to eat wooden, painted toys." The child and her mother live in a relatively poor neighborhood. CBC reveals:WBC 8,600 /mm3, Hemoglobin 7.1 g/dl, Hematocrit 25%, Platelets 166,000 /mm3. His blood lead levels are elevated. Which of the following is most likely seen in this child's peripheral blood smear?
. Megaloblastic anemia and basophilic stippling
Tear-drop RBCs and hypochromic, microcytic anemia
. Basophilic stippling and microcytic, hypochromic anemia
. Loss of concavity of the RBC and basophilic stippling
. Normochromic, normocytic anemia and basophilic stippling
15) A 42-year-old white female, who has a long history of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, presented with exertional shortness of breath. On examination, she appears very pale and there is a pulmonic flow murmur heard over the second intercostal space. Her vitals are: BP: 130/80mm of Hg; HR: 80/min and regular; RR: 16/min; Temperature 36.7°C (98°F).Initial evaluation reveals hemoglobin of 8.2 gm/dL. WBC count is within normal limits. You are suspecting an iron deficiency anemia secondary to excessive bleeding. Which one of the following studies is most definite for the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia?
. A low serum iron concentration
. A low serum ferritin level
. Bone marrow iron staining
. Increased total iron binding capacity
. Total iron content of the gastric epithelial cells
16) A 60-year-old Hispanic laboratory technician presents with increasing fatigue and generalized weakness for the last 2 months. He also has chronic pain in the lower back and legs when he walks. He has been smoking 2-3 packs of cigarettes daily for 30 years, and drinks alcohol almost daily. His mother has diabetes, while his father died of a stroke. Physical examination reveals pallor. There is mild hepatomegaly. The neurological examination is completely normal. Complete work-up reveals: CBC: Hemoglobin 9.8 g/L, MCV 85 fl, Platelets 226,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3, Neutrophils 60%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 29%, Lvlonocytes 10%. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 138 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 28 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.1 mg/dL, Calcium 11.2 mg/dL, Blood glucose 98 mg/dL. Liver studies: Albumin 4.0 mg/dL, Total protein, serum 9.5 g/dL, Total bilirubin 1.0 mg/dL, Direct bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 110 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 58 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 25 U/L. ESR is 100 mm/h. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Serum immunoelectrophoresis
. ANA and anti-Smith antibodies
. Kidney biopsy
. Bone marrow biopsy
. Bone scan
17) A 57-year-old man comes to the office and complains of long-standing heartburn and chest pain. He describes the pain as burning in nature, and unrelated to eating. For the past week, his interest in things has decreased, and he has been more tired than usual. He has lost almost 40 lbs (18kg) in the last 6 months. He used to smoke 6-10 cigarettes daily, but he quit 4 years ago. He drinks alcohol occasionally. He takes ranitidine for his heartburn. His father died at the age of 67 from lung cancer. His vital signs are stable. Physical examination is unremarkable. The chest x-ray result is within normal limits. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
CT scan of the chest with and without contrast
. Bronchoscopy
. Give omepra zole and follow-up in 2 months
. Barium swallow followed by endoscopy
. Test and eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection
18) A 50-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of right shoulder pain which radiates to her hand. She has had cough for many weeks, and feels "more tired than the usual." In addition, her fingers are always swollen, and she now finds it difficult to walk because her knees give way. She has had rheumatoid arthritis for the past 10 years and is used to having pain in her joints; however, she believes that this pain is not due to her arthritis. She takes celecoxib for rheumatoid arthritis. She admits to smoking one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 25 years and to drinking one odd beer every night. All her family members have crippling rheumatoid arthritis. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. Physical examination reveals drooping of the right eyelid and miosis. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. X-ray of the shoulder
. CT scan of head and neck
. Chest x-ray
. Steroid therapy
. Nerve conduction study
19) A 54-year-old patient walks into a blood donation camp at a community hospital. His blood report shows an ELISA positive for HIV and HBsAg. He is notified of this finding, and a subsequent western blot test is also positive for HIV. Considering this new diagnosis of HIV, which of the following is indicated in this patient?
. Hepatitis B vaccine
. PPO skin test and anti-Toxoplasma antibody titer
. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis
. Serum transaminases and lipid profile
. Hepatitis C antigen
20) A 25-year-old female presents to her physician with a painful ulcerative lesion on her labia for the past 2 days. She also complains of dysuria. She admits to having sexual intercourse with multiple partners for the last 6 years. Tzanck preparations of one of her lesions reveal multi-nucleated giant cells. She is encouraged to undergo testing for HIV and other STDs. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening test for HIV infection?
. HIV serology by western blot
. HIV serology by ELISA
. Absolute CD4 count
. HIV viral load
. P 24 antigen assay
21) A 27-year-old, HIV-positive man comes to his physician with a two-day history of fever, profuse watery diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. He has been taking zidovudine, didanosine, and indinavir for the past eight months. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 102/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 105/70 mm Hg. He is started on fluid and electrolyte support. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
. Colonoscopy with biopsy of the colonic mucosa
Stop antiretroviral therapy and send stool for Clostridium difficile toxin assay
. Start empiric treatment for cytomegalovirus
. Stool examination for ova and parasites
. Loperamide and lactose-free diet until diarrhea subsides
Reports muscle aches. He has no cough or shortness of breath. He has a thirty pack-year history of cigarette smoking. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 120/76mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 16/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. Blood cultures reveal Streptococcus bovis. Echocardiogram reveals vegetations on the mitral valve. Other than antibiotic treatment, what further step is recommended in this patient?
. Bronchoscopy
. Cystoscopy
. Fecal occult blood testing
. Colonoscopy
. CT scan of the head
23) A 43-year-old male presents to a physician with an ulcer on the shaft of his penis. The ulcer is non-tender, with a raised border and a smooth base. There is bilateral inguinal adenopathy. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Dark field microscopy of a specimen from the ulcer base reveals spirochetes. Which of the following additional screening studies should be performed on this patient?
. VDRL
. FTA-ABS
. Proctosigmoidoscopy
. HIV antibodies by ELISA
. Serum prostate specific antigen
24) A 19-year-old man presents to your office with a one-week history of fever, fatigue, and sore throat. He denies diarrhea or rash. He has no significant past medical history. His brother died of cystic fibrosis at 14 years of age. He admits to occasional cigarette use and alcohol consumption. He has smoked marijuana several times but has never used injectable drugs. He is sexually active with one partner and uses condoms occasionally. Physical examination reveals enlarged tonsils with a whitish exudate and enlarged, slightly tender lymph nodes deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle bilaterally. The exam is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the best initial test in this patient?
. Heterophile antibody test
. Rapid plasma reagin (RPR)
. Lymph node biopsy
. HIV antibody determination
. Purified protein derivative
25) A 17-year-old man presents with new symptoms of fatigue, malaise, fever, and a sore throat. He has no significant past medical history and is not on any medications. Physical examination is entirely normal except for enlarged, palpable cervical, lymph nodes. He reports no weight loss or night sweats. Laboratory investigations include a normal chest x-ray, negative throat swab, but abnormal blood film with atypical lymphocytes. The hemoglobin is 15.5 g/dL; hematocrit 42%; platelets 290,000/mL; WBC 10500/mL, with 45% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 54% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Bone marrow
Lymph node biopsy
Heterophil antibody (sheep cell agglutination) test
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Hepatic biopsy
26) A 30-year-old male presents with right upper quadrant pain. He has been well except for an episode of diarrhea that occurred 4 months ago, just after he returned from a missionary trip to Mexico. He has lost 7 pounds. He is not having diarrhea. His blood pressure is 140/70, pulse 80, and temperature 37.5°C (99.5°F). On physical examination there is right upper-quadrant tenderness without rebound. There is some radiation of the pain to the shoulder. The liver is percussed at 14 cm. There is no lower-quadrant tenderness. Bowel sounds are normal and active. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation of the patient?
. Stool for ova and parasite
. Serology and ultrasound
. Diagnostic aspirate
. Blood cultures
. Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
27) A 30-year-old male with sickle cell anemia is admitted with cough, rusty sputum, and a single shaking chill. Physical examination reveals increased tactile fremitus and bronchial breath sounds in the left posterior chest. The patient is able to expectorate a purulent sample. Which of the following best describes the role of sputum Gram stain and culture?
. If the sample is a good one, sputum culture is useful in determining the antibiotic sensitivity pattern of the organism, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Sputum Gram stain and culture lack the sensitivity and specificity to be of value in this setting
. There is no characteristic Gram stain in a patient with pneumococcal pneumonia
Empirical use of antibiotics for pneumonia has made specific diagnosis unnecessary
. Gram-positive cocci in clusters suggest pneumococcal infection
28) A 25-year-old male student presents with the chief complaint of rash. He denies headache, fever, or myalgia. A slightly pruritic maculopapular rash is noted over the abdomen, trunk, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. Inguinal, occipital, and cervical lymphadenopathy is also noted. Hypertrophic, flat, wartlike lesions are noted around the anal area. Laboratory studies show the following: Hct: 40%, Hgb: 14 g/dL, WBC: 13,000/μL, Diff: 50% segmented neutrophils, 50% lymphocytes. Which of the following is the most useful laboratory test in this patient?
. Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test
. Weil-Felix titer
. Chlamydia titer
. Blood cultures
. Biopsy of perianal lesions
29) A previously healthy 19-year-old female university student develops myalgia, headache, fever, and malaise. Blood tests reveal lymphocytosis, with 20% of the lymphocytes being atypical. She remains tired and unwell for 6 weeks, but repeated tests for heterophil antibody are negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Human herpes virus type 7 (HHV-7)
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection
CMV infection
Primary HIV infection
Toxoplasmosis
30) A 20-year-old female college student presents with a 5-day history of cough, low-grade fever (temperature 37.8°C [100°F]), sore throat, and coryza. On examination, there is mild conjunctivitis and pharyngitis. Tympanic membranes are inflamed, and one bullous lesion is seen. Chest examination shows a few basilar rales. Sputum Gram stain shows white blood cells without organisms. Laboratory findings are as follows: Hct: 31, WBC: 12,000/μL, Lymphocytes: 50%, Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): 94 nL, Reticulocytes: 9% of red cells, CXR: bilateral patchy lower lobe infiltrates. Which of the following is the best method for confirmation of the diagnosis?
. High titers of IgM cold agglutinins or complement fixation test
. High titers of antibody to adenovirus
. Blood culture
. Methenamine silver stain
. Culture of sputum on chocolate media
31) A 20-year-old woman complains of headache and discomfort in both sides of her jaw. Physical examination reveals enlarged parotid glands that are slightly tender on palpation. There is reddening of the orifice of Stensen’s duct on intra oral examination; her temperature is 38.3°C, and the pulse rate is 80/min. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 14 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; WBC 11000/mL, with 33% segmented neutrophils, 7% monocytes, and 60% lymphocytes. Which of the following diagnostic tests will help to confirm the diagnosis of epidemic parotitis?
Blood cell count
Single blood sample for a specific immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Blood culture
Single blood test for a specific immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Serum amylase
32) A 19-year-old male presents with a 1-week history of malaise and anorexia followed by fever and sore throat. On physical examination, the throat is inflamed without exudate. There are a few palatal petechiae. Cervical adenopathy is present. The liver span is 12 cm and the spleen is palpable. Throat culture: negative for group A streptococci, Hgb: 12.5, Hct: 38%, Reticulocytes: 4%, WBC: 14, 000/μL, Segmented: 30%, Lymphocytes: 60%, Monocytes: 10%, Bilirubin total: 2.0 mg/dL (normal 0.2 to 1.2), Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) serum: 260 IU/L (normal 20 to 220), Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): 40 U/L (normal 8 to 20 U/L), Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): 35 U/L (normal 8 to 20 U/L), Alkaline phosphatase: 40 IU/L (normal 35 to 125). Which of the following is the most important initial test combination to order?
. Streptococcal screen and antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer
. Liver biopsy and hepatitis antibody
. Toxoplasma IgG and stool sample
. Peripheral blood smear and heterophile antibody
. Lymph node biopsy and cytomegalovirus serology
33) A 27-year-old man presents with diarrhea. He returned 3 weeks ago from a trip to rural South America. Over the past few days, he has gradually developed lower abdominal pain and diarrhea. Now the symptoms are much worse with eight stools a day consisting mostly of mucus and blood. He is afebrile, the abdomen is tender in left lower quadrant, and the remaining examination is normal. His stool is mostly comprised of blood and mucus. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Examination of a dried stool specimen
Stool culture
Immunofluorescence of stool specimen
Stool toxin assay
Examination of a wet stool specimen
34) A 60-year-old male complains of low back pain, which has intensified over the past 3 months. He had experienced some fever at the onset of the pain. He was treated for acute pyelonephritis about 4 months ago. Physical examination shows tenderness over the L2-3 vertebra and paraspinal muscle spasm. Laboratory data show an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 80 mm/h and elevated C-reactive protein. Which of the following statements is correct?
. Blood cultures will be positive in most patients with this process
. Hematogenous osteomyelitis rarely involves the vertebra in adults
. An MRI scan is both sensitive and specific in defining the process
. The most likely initial focus of infection was soft tissue
. Surgery will be necessary if the patient has osteomyelitis
35) A 40-year-old school teacher develops nausea and vomiting at the beginning of the fall semester. Over the summer she had taught preschool children in a small town in Mexico. She is sexually active, but has not used intravenous drugs and has not received blood products. Physical examination reveals scleral icterus, right upper quadrant tenderness, and a palpable liver. Liver function tests show aspartate aminotransferase of 750 U/L (normal < 40) and alanine aminotransferase of 1020 U/L (normal < 45). The bilirubin is 13 mg/dL (normal < 1.4) and the alkaline phosphatase is normal. What further diagnostic test is most likely to be helpful?
. Abdominal ultrasound
. Liver biopsy
Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
IgM antibody to hepatitis A
. Determination of hepatitis C RNA
36) A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 24-hour history of right flank pain, burning micturition and high-grade fever with chills. Her temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination shows costovertebral angle tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely urine dipstick finding in this patient?
. Positive for nitrites only
. Positive for nitrites and esterase
. Positive for esterase only
. Negative for both esterase and nitrites
. Negative for esterase and positive nitrites
37) A 27-year-old woman complains of fatigue, low-grade fevers, anorexia, headaches and skin rash over the past several weeks. She also notes new exertional dyspnea and an unintentional 5-pound weight gain over the past two weeks. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 190/110 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Which of the following is the most likely finding on this patient's urinary tests?
. High daily cortisol excretion
. High VMA excretion
. Glucosuria
. Red blood cells
. Uric acid crystals
38) A 70-year-old man comes to the physician because of nocturia. He states that over the past two years his urinary frequency has increased and he has to strain while passing urine. He also notes dribbling of a few drops of urine at the end of voiding. Sometimes he has to void again within two hours. He has no other symptoms. He has no history of diabetes mellitus, stroke or trauma. He does not take any medication. His father had surgery of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. He has a 15-pack-years history of cigarette smoking. Rectal examination shows smooth, firm enlargement of the prostate with no induration. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory study shows a serum creatinine of 0.7 mg/dl. Which of the following studies is indicated at this time?
. Ultrasound of kidney, bladder and ureter
. Blood urea nitrogen
. Serum prostate specific antigen
. Urinalysis
. Cystoscopy
39) A 65-year-old man comes to the physician because of increased urinary frequency and urgency, as well as suprapubic discomfort His temperature is 37C(98.6F), blood pressure is 130/75 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respirations are 14/min. Rectal examination shows prostatic induration; physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows no abnormalities. Expressed prostatic secretions show a leukocyte count of 20 WBCs/HPF (normal is less than 10 WBCs/HPF). They are sent for culture and sensitivity, and fail to grow any bacteria. Serum prostatic specific antigen is 2 ng/ml (normal value is less than 4ng/ml). A diagnosis of nonbacterial prostatitis is suggested. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Repeat culture of prostatic secretions
Perform urinary cytology and cystoscopy
. Treatment with oral erythromycin
. Repeat urinalysis
. Treatment with oral trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole
40) A 33-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a 4-day history of left-sided flank pain, nausea, vomiting, fevers and chills. Her temperature is 39°C (102°F) and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Examination shows significant left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urinalysis shows positive nitrites, many WBC and bacteria. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 17,000/cmm with 8% bands. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Blood cultures
. Intravenous pyelogram
. CT scan of the abdomen
. Intravenous antibiotics
. Ultrasound of the abdomen
41) A 14-year-old boy comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of fever and nasal discharge. He has also had malaise, fatigue and myalgia. His temperature is 38.8°C (101.9°F), blood pressure is 130/70mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Urine dipstick testing shows proteinuria but there is no hematuria or pyuria; urinalysis otherwise shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. BUN and serum creatinine
. Repeat dipstick testing
. Renal ultrasound
24-hour urinary collection for protein
. Reassurance
42) A 57-year-old man comes to the physician because of 2 episodes of hematuria. He also complains of cough fatigue and fever for several days. He has smoked two packs of cigarettes daily for 25 years. He does not use alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are stable. Examination shows a left-sided varicocele which fails to empty when the patient is recumbent; examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show Hb of 16.2 g/dl and platelets of 480,000/cmm. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic step in management?
. Abdominal CT scan
. Chest x-ray
. Serum alfa-fetoprotien levels
. Urinalysis
. Ultrasonogram of the testicles
43) A patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia has moderately severe symptoms and is started on finasteride. After six months of treatment with finasteride, his symptoms improve remarkably and his prostate has regressed in size. Which of the following histological patterns was most likely present at the time of initiation of treatment?
. Hyperplasia of prostate with predominance of muscular element
. Hyperplasia of prostate with predominance of epithelial components
. Hyperplasia of prostate with predominance of both collagen and smooth muscles
. Hyperplasia of prostate with predominance of collagen
. Hyperplasia of prostate with predominance of glandular tissue
44) A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a two-month history of fatigue and weight gain. She has rheumatoid arthritis and hypertension. She takes hydrochlorothiazide and naproxen. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows generalized edema; liver is palpated 2 cm below the costal margin. Urinalysis shows 4+ proteinuria. Ultrasound of the kidneys shows slight enlargement. Renal biopsy was performed. Which of the following is the most likely finding on renal specimen analysis?
. Deposits revealed under polarized light
Crescent formation on light microscopy
. Granular immunoglobulin deposits revealed on immunofluorescence microscopy
. Linear immunoglobulin deposits revealed on immunofluorescence microscopy
. Normal light microscopy findings
45) A 73-year-old man comes to the physician because of a one-year history of progressively worsening urinary urgency, hesitancy, nocturia, and weak urinary stream. He has no fever, abdominal pain, hematuria, malaise or weight loss. He takes atenolol for essential hypertension. He has no history of diabetes mellitus or ischemic heart disease. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Rectal examination shows a smooth, firm enlargement of the prostate with no induration or asymmetry. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show serum creatinine of 2.1 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Transurethral resection of prostate
Ultrasound of kidneys, ureters, and bladder
. Treatment with finasteride
. Watchful waiting
. Treatment with prazosin
46) A 30-year-old woman comes to the office due to the recent onset of fever, chills, and dysuria. Her temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), blood pressure is 110/70mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows tenderness at the right costovertebral angle. Laboratory studies show WBC count of 16,000/microl with left shift. Urinalysis shows bacteriuria and pyuria. Her urine and blood is collected for culture and sensitivity. She is prescribed oral ciprofloxacin and sent home. After three days, she returns for a follow-up visit. She is still febrile, and the physical examination is unchanged. The blood cultures have no growth after 72 hours of incubation. Results of the urine culture show. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
eee

. Continue oral ciprofloxacin for another 10 days
. Start intravenous ampicillin and gentamicin
. Perform renal ultrasound
. Start intravenous ciprofloxacin
. Renal CT scan
47) A 57 -year-old woman is admitted to the ICU after being involved in a highway motor vehicle accident. She was hypotensive at the scene and received 7 litters of fluids, which included crystalloids, blood, and fresh frozen plasma. She apparently had significant external blood loss from multiple fractures and skin loss. She undergoes surgery, after which she is transferred to the ICU and receives continuous IV fluids and vasopressors. Her laboratory studies 24 hours after the accident show the following: Hb 9.5 g/dl, WBC 15,000/cmm, Platelets 130,000/cmm, BUN 34 mg/dl, Serum Creatinine 2.2 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely microscopic finding on urinalysis?
. Muddy brown cast
. Broad cast
. WBC casts
. RBC casts
. Fatty casts
48) A 46-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of fever and chills. His fever was gradual in onset. He also complains of perineal and back pain, which is worse towards the sacral area. He has repeated urges to urinate, along with pain on micturition. Rectal examination shows a boggy, exquisitely tender prostate. Laboratory studies show: Hb 13 g/dl, Hct 40%, WBC 12,000/cmm, Platelets 329,000/cmm, Dipstick urinalysis:, Esterase +++, PH 5.0, Nitrite +++, WBC 50+, Protein +, Blood ++. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Send culture of mid-stream urine sample
Send culture of post-prostatic massage sample
. Administer alpha blocking agents
. Urethral catheterization
. Start empirical treatment on an outpatient basis
49) A 19-year-old man presents with malaise, nausea, and decreased urine output. He was previously well, and his physical examination is normal except for an elevated jugular venous pressure (JVP) and a pericardial rub. His electrolytes reveal acute renal failure (ARF). Which of the following findings on the urinalysis is most likely in keeping with acute glomerulonephritis (GN)?
White blood cell casts
Proteinuria
Granular casts
Erythrocyte casts
Hyaline casts
50) A 24-year-old woman presents with nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and gross hematuria. She had a sore throat 2 weeks ago that resolved on its own. On examination, her blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse 90/min, JVP is 7 cm, heart sounds are normal, there is 1+ pedal edema, and the lungs are clear. She has a renal biopsy. Which of the following electron microscopy findings on the renal biopsy is most likely in keeping with poststreptococcal GN?
Low potassium
High sodium
Low pH
High specific gravity
Osmolality > 500 mOsm/kg
52) An 85-year-old man who resides in a nursing home presents with a 3-day history of lower abdominal pain and increasing fatigue and lethargy. He is afebrile, his BP is 160/92 mm Hg, and RR 16/min. His lungs are clear and his heart examination normal. There is diffuse abdominal tenderness on palpation and a large area of fullness and dullness to percussion starting just below the umbilicus and extending to the suprapubic area. His serum sodium is 130 mEq/L, potassium 4.9 mEq/L, BUN 75 mg/dL, and creatinine is 3.5 mg/dL. His baseline BUN and creatinine were 25 and 1.3 respectively as recently as 1 month ago. A Foley catheter is placed and 1200 cc of urine is obtained. What will be the likely clinical course for this patient with regard to his renal function?
. His creatinine will return to 1.3 over the next week
His creatinine will continue to rise slowly for 2 to 3 more days
. He will produce minimal urinary output for at least 3 days
. He will require dialysis within 24 hours
. His renal function is unlikely to show any improvement in the future and 3.5 will be his new baseline
53) A 64-year-old man presents with symptoms of malaise, shortness of breath, edema, and no urine output for 24 hours. His past medical history is not significant, and his only medication is daily aspirin. On examination his JVP is 4 cm, heart sounds are normal, lungs are clear, and the abdomen is soft. A Foley catheter is inserted into his bladder for 200 cc of urine, which is sent for urinalysis. His urine output still remains low. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Urine cultures
Renal ultrasound
Inferior vena cavagram with selective renal venogram
Blood cultures
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)/creatinine ratio
54) A 46-year-old woman with nausea and vomiting presents to hospital because of light- headedness when standing and decreased urine output. She looks unwell; the blood pressure supine is 90/60 mm Hg and 80/60 mm Hg when standing. Her abdominal, heart, and lung examinations are normal. Which of the following laboratory values suggests prerenal azotemia in this patient?
Unchanged urea, elevated creatinine
Markedly elevated urea, unchanged creatinine
Urea/creatinine ratio of 10
Little change in either creatinine or urea for several days after oliguria develops
Urea/creatinine ratio of 25
Is 120/70 mm Hg without orthostatic change, and he is well perfused peripherally. The neurological examination is nonfocal. His laboratory values are as follows: Na: 138 mEq/L, K: 4.2 mEq/L, HCO3: 5 mEq/L, Cl: 104 mEq/L, Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL, BUN: 14 mg/dL, Ca: 10 mg/dL. Arterial blood gas on room air: PO2 96, PCO2 15, pH 7.02 Blood glucose: 90 mg/dL. Urinalysis: normal, without blood, protein, or crystals. Which of the following is the most likely acid-base disorder?
. Respiratory acidosis
. Pure normal anion-gap metabolic acidosis
Pure high anion-gap metabolic acidosis
Combined high anion-gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
. Combined high anion-gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory acidosis
56) A 17-year-old woman presents with peripheral and periorbital edema. She has previously been healthy and takes no medications. Her blood pressure is 146/92 mm Hg; she is afebrile. The patient has mild basilar dullness on lung examination; her cardiac examination is normal. She has periorbital edema and soft, doughy 3+ edema in her legs. Her serum creatinine is 0.6 mg/dL and her serum albumin is 2.1 g/L. Urinalysis shows 3+ protein, no RBC or WBC, and some oval fat bodies. What is the next best step to take in evaluating this patient?
. Order serum and urine protein electrophoresis
Request a nuclear medicine renal scan
. Order a 24-hour urine collection to quantitate the degree of proteinuria
Measure plasma aldosterone and renin activity
Ask a nephrologist or radiologist to perform a renal biopsy
57) A 56-year-old man is involved in a severe motor vehicle accident. He develops ARF after admission to hospital. One of the possibilities for his ARF is posttraumatic renal vein thrombosis. Which of the following findings is most likely to suggest renal vein thrombosis?
Heme-granular casts
White cell casts on urinalysis
Urine supernatant pink and tests positive for heme
Heavy proteinuria
Specific gravity >1.020
59) A 60-year-old male who emigrated from Russia comes to you with complaints of dizziness, fatigue and weight loss. A review of systems reveals that the patient experiences daily fevers and cough. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He does not take any medication. His blood pressure is 108/64 mmHg while standing. His respiratory rate is 14/min and is unlabored. Laboratory studies reveal the following: Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 130 mEq/L, Serum potassium 5.9 mEq/L, Chloride 102 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL, Blood glucose 58 mg/dL. Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 10.0g/L, Platelets 430,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3, NeutrophiIs 46%, Lymphocytes 45%, Eosinophils 9%. Chest x-ray shows a right upper lobe cavity. Which of the following acid-base disturbances is expected in this patient?
. Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis
. Elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis
. Respiratory acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory alkalosis
60) A 20-year-old white male is found to have an elevated calcium level on routine pre-employment screening blood tests. He denies any polyuria, polydipsia or constipation. He has no significant past medical history and does not take any medication. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. His pulse rate is 82/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, temperature is 37.0°C (99°F) and respirations are 14/min. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show the following: Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Chloride 103 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 18 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Calcium 11.2 mg/dl, Blood glucose 98 mg/dl, Serum PTH level 55 pg/ml (normal 10-65 pg/ml), Urine calcium/creatinine clearance ratio < 0.01. Which of the following conditions is most consistent with this patient's findings?
. Vitamin D overproduction
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Sarcoidosis
. Multiple myeloma
. Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia
61) A four-week-old male infant is brought to the emergency department because of persistent vomiting immediately after feeding for the past several days. Examination shows an emaciated infant with dry mucus membranes. An olive-shaped mass is palpated in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Which of the following acid-base abnormalities is most likely in this patient? pH, PaCO2 (mm Hg), HCO3- (mEq/L)
. 7.55, 46, 42
.7.10, 80, 24
. 7.62, 21, 21
. 740, 40, 24
. 7.62, 30, 30
62) A 35-year-old male with severe persistent bronchial asthma requiring multiple medications presents complaining of weight gain over the past several months despite no changes in appetite, diet, or activity level. He denies alcohol, tobacco, and drug use and has no other significant past medical history. On physical examination, he has a blood pressure of 143/92 mm Hg, a heart rate of 65/min, a temperature of 98.7°F, and a respiratory rate of 16/min. There is moderate supraclavicular fullness, and his skin is thin with areas of bruising and acne. Neurologic exam reveals decreased proximal muscle strength. Which of the following findings is most likely to also be present in this patient?
. Hypercalcemia
. Hyperkalemia
. Hyponatremia
Hypokalemia
. Hypomagnesemia
63) A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with multiple complaints. She reports that she had been feeling well until approximately one month ago, when she began to feel increasingly fatigued and weak. For the past two weeks, she has had anorexia, nausea, and abdominal pain. In the past three days, she has had two syncopal episodes. Her medical history is unremarkable and she takes no medications. She denies tobacco and drug use and drinks wine only occasionally. Physical exam reveals a temperature of 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure of 86/52 mmHg, heart rate of 90/min, and respiratory rate of 18/min. Her cardiac exam is normal and her lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. You note hyperpigmentation of the skin in the palmar creases. Which of the following additional findings is most likely to be present in this patient?
. Hypernatremia
. Hyperkalemia
. Hypochloremia
. Hypokalemia
. Hypomagnesemia
64) A 42-year-old male is found unconscious in a subway station. He is brought to the emergency department where cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is done and IV glucose and thiamine are given. His lab profile shows: Blood pH 7.20, PaO2 90mmHg, PaCO2 30mmHg, HCO3 12 mEq/L. Which of the following is the best next step in the diagnosis of this patient's acid-base status?
. Calculate the urine anion gap
. Calculate the plasma anion gap
. Calculate the urine osmolar gap
Calculate the plasma osmolar gap
. Obtain venous blood gas
65) A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of confusion. Her other complaints include increased thirst and "using the bathroom more frequently." She denies any fever, chills, headache, chest pain, shortness of breath, or cough. Her past medical history is significant for bipolar disorder that is well-controlled by medication. She does not drink alcohol, smoke cigarettes, or use illicit drugs. Her vital signs are stable, and physical exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies reveal the following: Sodium 154 mEq/L, Potassium 4.1 mEq/L, Chloride 116 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 28 mEq/L, Glucose 95 mg/dl, Urine osmolality 250 mOsm/L, Plasma osmolality 326 mOsm/L. What is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms and laboratory findings?
. Divalproic acid
. Dehydration
. Craniopharyngioma
. Lithium
. Head trauma
66) An 87-year-old female is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of altered mental status. Her medical history is significant for multi-infarct dementia, hypertension, stroke, coronary artery disease, severe degenerative joint disease, chronic atrial fibrillation, constipation and urinary incontinence. Her medications include aspirin, acetaminophen, atenolol, nitroglycerin, multivitamins, pravastatin, docusate, senna, digoxin and glucosamine. She lives in a local nursing home, and the people who brought her to the ED deny any history of new symptoms. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, respirations are 16/min and temperature is 36.1°C (97°F). Physical examination reveals dry mucus membranes and decreased skin turgor. There are no new focal neurologic deficits. Which of the following is most likely to be present in this patient?
. Hypokalemia
Hyponatremia
. Hyperkalemia
. Hypernatremia
. Hypocalcemia
67) A 56-year-old diabetic male is brought to the emergency department due to nausea and vomiting. While you are examining the patient, a nurse asks if determination of the patient's acid-base status will help ascertain the etiology and subsequent management of the patient's primary problem. Which of the following pairs of laboratory values will help get the best picture of the patient's acid-base status?
. PaO2 and PaCO2
. pH and PaCO2
. Urinary pH and PaCO2
PH and PaO2
. Urinary pH and HCO3-
68) A 45-year-old female with severe depression, migraine and rheumatoid arthritis is brought in after she was found to have nausea, fever and upper abdominal discomfort. The patient describes severe tinnitus and vertigo. She admits that she overdosed on one of her medications. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 24/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following acid-base statuses is most likely in this patient? pH, PaCO2 (mm Hg), HCO3- (mEq/L)
. 7.29, 50, 23
. 7.36, 22, 12
. 7.40, 40, 24
. 7.22, 35, 14
. 7.45, 30, 20
69) As you are walking across the hospital lobby, you stumble upon the arterial blood gas (ABG) results of a patient. The ABG (on room air) results are shown below: Blood pH 7.43, PaO2 100 mm Hg, PaCO2 25 mm Hg, HCO3- 16 mEq/L. Which of the following patients is most likely to have these laboratory values?
. 42-year-old patient with severe asthma exacerbation
42-year-old female with aspirin toxicity
. 36-year-old patient with pulmonary embolism
. 52-year-old female with persistent vomiting
. 64-year-old male with excessive diuresis
70) A 27-year-old man complains of difficulty in walking. He noticed leg weakness several days ago, and now he is barely able to walk. He also complains of mild back pain and foot numbness. Two weeks ago, he had an upper respiratory tract infection. Physical examination reveals lower extremity muscle weakness, absent knee and ankle reflexes, and minimal sensory loss. Spinal MRI shows no abnormalities. Which of the following findings would you expect on CSF analysis in this patient? (Protein, WBC, count RBC, count Glucose)
. high, increased, normal, low
. high, increased, normal, normal
. high, normal, normal, normal
. high, increased, increased, low
. normal, increased, increased, normal
71) A 27-year-old man complains of poor appetite, loss of interest in his daily activities, and impaired sleep. He has lost 10 pounds over the last two months. He says that he feels regretful about IV drug abuse in his past, but denies having suicidal or homicidal thoughts. He drinks alcohol occasionally but denies regular alcohol consumption or early morning drinking. He is sexually active with one partner and she uses oral contraceptives. On physical examination, his pulse is 76/min and his blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. His heart and lung exams are unremarkable and his abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 9 cm and the spleen is not palpable. He is fully oriented to person, place and time but performs poorly on memory tests. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
. HIV testing
. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
. Thyroid function testing
. Benzodiazepines
. Serum iron studies
72) A 23-year-old white man is brought to the emergency department (ED) by an ambulance due to an epileptic seizure. He fell on the sidewalk while going home from a pub, where he had two beers. A witness noted tonic-clonic movements of all four extremities for about one minute. This seizure was his first episode, and lasted 30 minutes. In the ED, he is in a state of partial confusion and disoriented to time, place and person. The physical examination does not reveal any focal neurologic pathology. His eye exam does not show any papilledema. His airway is secured, and his breathing is normal. CBC, serum electrolytes, EKG and chest x-ray are normal. Urine toxicology screen is ordered, and lorazepam is given. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
. Brain computed tomography with contrast
. Psychiatric consultation
. Lumbar puncture
. Brain computed tomography without contrast
. Electroencephalogram
73) A 35-year-old bank executive is brought to the emergency department after the sudden onset of a severe (10/10) headache, followed by a brief period of unconsciousness. His headache started while he was at a meeting and shortly thereafter, he vomited and lost consciousness. He regained consciousness soon afterwards, but was quite confused and irritable. His blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), and respirations are 16/min. The physical examination reveals a normal pupil size, no congestion or inflammation of the eye, and no focal neurological deficits. The ECG reveals nonspecific ST and T wave changes. The CT scan shows a subarachnoid hemorrhage. What is the most likely expected electrolyte abnormality with the patient's disease?
. Hyponatremia
. Hypokalemia
. Hypernatremia
. Hyperkalemia
. Hypercalcemia
74) A 68-year-old white male comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of right-sided hemiplegia, headache and impaired consciousness. There is no prior history of transient ischemic attacks. His medical problems include hypertension, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, tobacco abuse, benign essential tremor, gout, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. His medications include amlodipine, simvastatin, colchicine, propranolol, and doxazosin. The neurological exam shows right-sided weakness and hemi-sensory loss. There is a carotid bruit on his left side. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CT scan of head without contrast
. Anticoagulate with heparin
. CT scan of head with contrast
. Give aspirin
. Perform MRI scan of head
75) A 76-year-old male with a history of mild dementia, hypertension and diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department by his daughter because of two days of confusion, disorientation and decreased oral intake. She says that he has been talking to people who are not there and wandering around the house in the middle of the night. His current medications are metoprolol, valsartan and metformin. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. Which of the following initial evaluations is most important for this patient?
. CT scan of the head
. Complete blood count and iron studies
. EKG and serum troponin T level
. Serum electrolytes and urinalysis
. Brain MRI
76) A 69-year-old patient is brought to the office by his daughter because his behavior changed progressively for the past several months. He roams in the apartment at night, and forgets his grandchildren's names. Three days ago, he was found by the doorman urinating by the building's gates. His wife died three years ago. He insists that there is nothing wrong with him, and tries to give excuses for what his daughter is reporting. He does not feel particularly fatigued and has a good appetite. He does not smoke, has no history of alcohol abuse, and no history of diabetes. His blood pressure is 155/85 mm Hg, pulse is 90 /min, and respirations are 15/min. Although the neurologic exam was difficult to assess, there were no abnormalities found. The Babinski sign is negative bilaterally. There is no evidence of rectal or bladder incontinence. The mini-mental state examination (MMSE) score is 15/30 (normal > 24). The laboratory studies show: Hb 13.5 g/dl, RBC 4.5 million/mm3, Hct 45%, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3, Platelet count 230,000/mm3, MCV 83 um3, MCHC 32% Hb/cell, S. calcium 9.0 mg/dl, S. sodium 137 mEq/dL, S. potassium 4.0 mEq/dL, S. creatinine 1.1 mg/dl, S. glucose 100 mg/dl, TSH 3 uU/mL, Total cholesterol 180 mg/dl. CT scan is done. Which of the following abnormalities would you expect to see on the CT scan?
. Hypodense images involving different brain regions
. Normal appearance
. Enlargement of the ventricle without cortical atrophy
. Diffuse cortical and subcortical atrophy
. Marked atrophy of the frontal and temporal cortices
77) A 34-year-old Caucasian man presents to your office with a several day history of difficulty walking. He also describes some "funny" sensations in his feet. He denies any recent skin rash, diarrhea, or joint pain. His past medical history is significant only for a recent mild respiratory infection. He visited his friends in Connecticut one month ago. He smokes one pack of cigarettes a day and admits to occasional IV drug use. He is not sexually active. His temperature is 36°C (98°F), heart rate is 90/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg. Chest examination is unremarkable. Abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable. Cranial nerves II-XII are intact. Muscle strength is reduced in the lower extremities but well preserved in the upper extremities. Lower extremity sensation is decreased. Stroking the soles of the feet elicits extension of the great toe. Which of the following is most likely to diagnose this patient's condition?
. CT scan of the brain
. Electromyography
. Serologic tests for B. burgdorferi
. MRI of the spine
. Lumbar puncture
78) An 18-year-old girl comes to the office due to a three-week history of headaches that has been disturbing her daily activities, including her sleep. She describes these headaches as pulsatile, diffuse, and occasionally results in vomiting. Her school grades have deteriorated over the past 3 months. She complains of double vision when she looks sideways. Her family history is significant for migraine. She is afebrile. Her neurologic examination is significant for sixth cranial nerve palsy. The pupils are equal, and reactive to light and accommodation. There is no sinus tenderness. Fundoscopy reveals bilateral papilledema. MRI of the brain reveals an empty sella. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
. Refractive testing of the eye
. Lumbar puncture
. Trial of prednisone
. Sinus imaging
. Start sumatriptan
79) A 30-year-old white female presents with an attack of common migraine. This is her fourth attack of migraine over the last 4 months. Her attacks previously responded well to aspirin and ibuprofen; however, her current headache is very severe and not relieved by NSAIDs. She has been trying to conceive for the past 2 months. Six years ago, she was treated with isoniazid due to a positive PPD test. Her father died at the age of 45 from an acute myocardial infarction. Before starting therapy with serotonin agonists (e.g., sumatriptan), which of the following tests should be performed in this patient?
. Liver function tests
. Stress echocardiogram
. Pregnancy test
. PPD and chest x-ray
. Visual field testing
80) A 72-year-old male comes to the emergency department (ED) due to a sudden onset of right-sided weakness, aphasia and incontinence. He did not lose consciousness. All his symptoms started suddenly, 1 hour ago. He was previously diagnosed with hyperlipidemia, and is on simvastatin. He is a known smoker and alcoholic. He is taking aspirin as prophylaxis for heart attacks and strokes. His family history is not significant. His blood pressure is 160/88 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, respirations are 18/min, and temperature is 37.8°C (100°F). He is admitted to the ED, and a patent airway is secured. The cardiac examination and EKG findings are normal. CT of the brain shows no acute hemorrhage. Which of the following interventions will result in the best outcome in this patient?
. Tissue plasminogen activator within 3 hours
. IV nitroprusside to reduce blood pressure
. Streptokinase and heparin combination
. Nimodipine
IV high dose corticosteroids
81) A 17-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to weakness of her hands and legs. The weakness has been progressively worsening over the past 24 hours, and she now feels that the weakness is affecting her hips. Her mother says she was a bit unwell a couple of weeks ago, but otherwise her past medical history is unremarkable. The physical examination reveals 1/5 power in ankle and knee flexion/extension and 2/5 power in hip flexion. Reflexes are absent in her lower extremities bilaterally. She is admitted to the hospital. Spinal fluid analysis shows albumino-cytologic dissociation. Which of the following tests is the most appropriate for monitoring her respiratory function?
. FEV1/FVC ratio
. Arterial blood gas
. Peak expiratory flow rate
. Vital capacity
. Chest x-ray
82) A 29-year-old female is brought to the emergency department due to paraplegia, urinary incontinence and urgency. She denies any trauma. She has a history of trigeminal neuralgia. The neurological examination shows spasticity and hyperreflexia in the lower extremities, and impaired vibration and proprioception in her left forearm. Which of the following is the most likely finding in this patient's cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination?
. Albumino-cytologic dissociation
. Oligoclonal bands
. Increased cell count
. Increased pressure
. Increased total protein concentration
83) A 28-year-old Caucasian female presents to the emergency department (ED) appearing very anxious. She is accompanied by her boyfriend. She woke up this morning with severe weakness over the right side of her body. The weakness came on all of a sudden, but gradually resolved during the day. She denies any sensory symptoms. Her boyfriend reports that her speech was "weird, almost as if she was stuttering or struggling to get her words out." This too has resolved. The patient denies any other symptoms. The only other history of note is that she returned from a holiday in Italy 2 days ago. Vitals signs are unremarkable. The neurological examination is normal. Her chest x-ray is within normal limits. EKG shows normal sinus rhythm with a rate of 82/min. An urgent head CT scan is within normal limits. Which of the following investigations is most likely to reveal the underlying cause of this episode?
Psychiatric referral
. Carotid Doppler ultrasonography
. Transthoracic echocardiogram
. MRI head
. Cerebral angiography
84) A 76-year-old Caucasian female is brought to the hospital with a one-hour history of confusion. Her husband says that she started to complain of occipital headaches two hours ago and took some acetaminophen; an hour later, he found her confused on the couch and called an ambulance. She has no recent history of fever, chills, ear pain, or upper respiratory infection. Her past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and atrial fibrillation. She had triple vessel coronary artery bypass five years ago. Her current medications include warfarin, metoprolol, diltiazem and lisinopril, plus 25 units of long-acting insulin at bedtime. She lives with her husband and is independent in her activities of daily living. On examination, her blood pressure is 160/90 mmHg and her heart rate is 80/min and irregular. She is unable to follow simple commands or speak. She moves all four extremities. Deep tendon reflexes are symmetric and Babinski reflexes are downgoing bilaterally. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluating this patient?
. Electroencephalogram
. Brain MRI
. Nerve conduction studies
. CT scan of the head without contrast
. Lumbar puncture
85) A 26-year-old white female presents with worsening weakness of her right upper extremity, left lower extremity and ataxia. She also complains of unilateral eye pain and visual loss. The eye pain is worsened by ocular movements. On eye examination, there is a central visual field defect in her right eye. Fundoscopy is normal. Neurological examination shows spastic paraparesis in the right upper extremity and the left lower extremity. What is the most appropriate next step in this patient's management?
. Lumbar puncture
. CT scan with contrast
. Brain biopsy
MRI of the brain
. PET scan
86) A 52-year-old male comes to the office due to a sudden onset of photophobia, redness around the eye and pain in his right eye. He also has nausea and a terrible headache, which has not responded to ibuprofen. He denies any trauma, and has never had such an episode before. He was watching TV when the event started. The physical examination reveals a non-reactive mid-dilated pupil. The eye appears red with conjunctival flushing. What is the best diagnostic test for this patient's condition?
. CT scan of the head
. Tonometry
. Lumbar puncture
. Fluorescein staining of eye
. Duplex studies of carotid artery
87) A 32-year-old female is brought to the clinic by her husband because he believes she is a malingerer and is "just being difficult." Sometimes, she appears confused and disoriented. Over the past year, she has complained of visual loss, eye pain and inability to do any household chores. Two months ago, she claimed to have lost control of her bladder. Interestingly, she is "her normal self" when it is time to go for summer trips. The wife insists that she does not understand what is happening to her, and adds that she occasionally loses the ability to move her right hand. The physical examination is basically normal. The patient appears, alert, oriented, and is in no distress. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Tonometry
. MRI of the brain
. Serum immunoglobulins
. Lumbar puncture
. Nerve conduction studies
88) A 45-year-old Caucasian male presents in the office with a movement disorder and behavioral disturbance. For the past month, he has been having frequent, sudden, jerky and irregular movements of his upper extremities. He has become irritable, and does not visit his family or friends. He is a business executive, and co-workers have commented on the serious decline in his performance. His father had similar problems and died in a nursing home CT scan is ordered. Which of the following is a typical CT finding in such patients?
. Diffuse atrophy of the cerebral cortex
. Atrophy of the caudate nucleus
. Atrophy of frontal lobes
. Atrophy of lenticular nucleus
Atrophy of temporal lobes
89) A 69-year-old comatose man is brought to the emergency department by an ambulance. His wife says that he has been hypertensive for the past twenty years, and he is not compliant with his medication. His pulse is 80/min and blood pressure is 240/140 mm Hg. The physical examination reveals reactive pupils, no oculocephalic reflexes, no nystagmus, positive conjugate gaze deviation to the left, and reflexes of 3/4 on the right and 2/4 on the left side. Which of the following is most likely to be seen on computed tomography?
. Ruptured aneurysm
. Bleeding into brain tumor
. Basal ganglia haemorrhage
. Normal brain
. Brain abscess
90) A 75-year-old male comes to the office for the evaluation of a two-month history of intermittent right eye visual loss. Each episode is "painless, lasts a few seconds, and feels like a curtain coming over the eye." He denies any other symptoms. He has never had any trauma to his eye, and does not use any medications. His past medical history is significant for hypertension. He quit smoking 20 years ago, but had smoked for 25 years. On examination, the patient is alert and without neurologic findings. His blood work and chest x-ray are normal. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Echocardiography
. CT head
Duplex study of neck
Lumbar puncture
. MRI brain
91) A 60-year-old, obese, diabetic woman comes to the office and complains of "balance problems while walking." She also has tingling and paresthesias in her feet, decreased sensation below the knees, and burning and aching sensations in both legs. She has been very fatigued lately. The neurological examination reveals diminished proprioception peripherally on her feet, "stocking" distribution of hypesthesia from her knees distally, and positive signs of spinal ataxia. What is the best diagnostic test for this patient's condition?
. Electroencephalography
Evoked potentials
. Regular checking of blood sugar and diabetic diet
. Repetitive stimulation electromyography
. Electromyography and conduction studies
{"name":"DES 3 ep 8", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"167) A 50-year-old pale man comes to the office and says, \"For the past year, I've been feeling very weak. I get tired early, and I feel that I've lost my sense of humor. I find it difficult to remember things now.\" When asked about his social history, he says, \"I'm jobless and am living on social security benefits. I don't drink or smoke anymore, but I was charged with driving under the influence three times before.\" His parents died of old age. He shares his room with four friends. His vital signs are normal. CBC reveals: WBC 5,500 \/mm3, Hemoglobin 7.0 mg\/dl, Hematocrit 22%, Platelets 196,000\/mm3, RBC count 1.7 million, MCV 119 fl, MCH 36, MCHC 28%, Reticulocyte count 04%. Peripheral smear shows anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, and basophilic stippling. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?, 168) A 45-year-old white male presented to his primary care physician due to easy fatigability. He is a pure vegetarian and a known alcoholic. Physical examination revealed significant pallor. His hemoglobin level was 10.8gm\/dl, and serum iron studies were within normal limits. His physician placed him on folic acid (1 mg daily), and his hemoglobin level increased to 13gm\/dl over a period of several months. The patient continued to take folic acid for the next two years. On his next follow-up visit, he complained of gradual memory loss and difficulty in maintaining his balance for the past six months. Which of the following is the most likely thing to consider at this point?, 169) A 39-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of double vision. She feels \"weak all over,\" especially at the end of the day. She had the same complaints 8 months ago that persisted for several weeks, but she didn't see a doctor because she had no insurance then. She has no past medical history. Her mother has rheumatoid arthritis, and her brother has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Her vital signs are normal. She has diplopia and mild ptosis. Her blood profile, CBC and thyroid tests are within normal limits. Electromyography and repetitive nerve stimulation reveals a decremental response in compound action potentials. Her acetylcholine receptor antibody test is positive. Which of the following tests should be ordered next?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
Fun Quiz (RANDOM)
1890
ÖRGÜTSEL DAVRANIŞ VİZE SORULARI
20100
Shall I break up with Rayan?
100
Diagnostico Filenet
1780
Urban Planning Research
15820915
Introduction to Engaged and Public Anthropology
15825798
Ultimate TV Doctor Trivia: Hospitals & Hit Medical Shows
201029404
Ultimate Dog Lovers Trivia: 201+ Tail-Wagging Questions
20010019879
Free DevOps/Linux Command-Line Proficiency
201023121
Ace Your Learners Permit with Practice Permit Test MA
201036559
Free Roles and Responsibilities Knowledge Test
201026532
Fart: What Does Your Fart Say About You? Take the Test
201026037