Power Plant 1-3
What must be done to the connecting rods after a cylinder is removed?
They must be solvent washed and lubricated using fresh 10W30 oil
Nothing, they are just fine.
They must be supported using elastics or cardboard templates.
They must be lock-wired to the base studs to prevent movement.
What position is the piston supposed to be in when removing a cylinder from an engine?
TDC of the compression stroke
Any position
TDC on any stroke
. BDC of the exhaust stroke
When are the seals/packings on a cylinder replaced?
At annual inspections
At TBO
Every 500 hrs
Every time the cylinder is removed
What is ring stagger?
The spacing between the compression rings of a piston
The spreading out of the end gaps on the compression rings of a piston
When the rings don’t roll straight across the work bench
The waviness in the oil control ring
What needed to be done to get the piston into the cylinder when installing the cylinder on the Lycoming O235 engine?
Nothing, they slide in just fine
A ring compressor must be used
A pry-bar must be used
A hammer must be used to tap the cylinder down
What is the purpose of ring stagger?
To reduce leakage out of the combustion chamber
To prevent unwanted movement of the piston in the cylinder assembly
To scrape excess oil off the cylinder walls
To prevent sideways movement of the connecting rod on the crankshaft
What is used to seal the rocker covers to the cylinder head?
�OO” silk thread and sealant
RTV silicone
An o-ring
A cork gasket
What is used to seal the cylinder bases to the crankcase?
A silicone gasket
�00” silk thread sealant
An o-ring
A cork gasket
What needed to be done to get the piston into the cylinder when installing the cylinder on the Lycoming O235 engine?
A hammer must be used to tap the cylinder down
A pry-bar must be used
A ring compressor must be used
Nothing, they slide in just fine
How does oil get back to the crankcase from the cylinder head on the Lycoming O235 engine?
Through dedicated cylinder drain lines
Through the oil return manifold system and a scavenge pump
Through the pushrod shroud tubes
Through the pushrods
What tool is used to remove the Lycoming O235 cylinder base nuts?
Combination wrench
Vicegrips
A Ratchet & sockets
Ratchet & cylinder base nut wrench
When are the seals/packings on a cylinder replaced?
Every time the cylinder is removed
At TBO
Every 500 hrs
At annual inspections
What is the purpose of ring stagger?
To scrape excess oil off the cylinder walls
To prevent sideways movement of the connecting rod on the crankshaft
To reduce leakage out of the combustion chamber
To prevent unwanted movement of the piston in the cylinder assembly
What can cause low compression on a cylinder?
Compression rings, intake and exhaust valve seats, crack in the cylinder
Where are the seals/packings located on a cylinder?
Between cylinder head and rocker cover, between shroud tub I/O e and crankcase/cylinder head
What kinds of seals/packings are used on a cylinder (type, material, shape)?
Silicone gasket
When are the seals/packings on a cylinder replaced?
After every cylinder removal or on condition
What kinds of seals/packings are used on a cylinder (type, material, shape)?
Silicone gasket
When are the seals/packings on a cylinder replaced?
After every cylinder removal or on condition
How does the oil get from the cylinder head back to the crankcase?
Through the drain line (on lycoming engine)
Back through pushrods (on continental engine)
What adjustments are there on the cylinder? Why?
Valve Clearance, to ensure better compression
What must be done to the connecting rods immediately after cylinder removal?
Must be supported using elastics or cardboard template
What can happen if you do not support the connecting rod when the cylinder is removed?
Connecting rod can damage the crankcase or itself
Why do you “stagger the rings”?
To prevent airflow past the rings (not over the pin)
What tools did you need for this job?
Flathead screwdriver, torque wrench 300 inch pounds (25-35 ft. lbs.), cylinder base wrench, ratchet and sockets, valve adjustment tool, piston ring compressor
Where can leaks occur on a cylinder?
Around the intake/exhaust valves, piston’s oil rings, packings, seals, and any cracks in the cylinder case.
Where are seals/packings located on a cylinder?
Under the valve risers, cylinder flange, rocker box cover, and push rod shroud tube ends
What kinds of seals/packings are used on a cylinder (type, material, shape)?
Rocker box cover: Cork Cylinder base & push rod shrouds: Silicon Exhaust riser: Rubber Intake riser: Paper
When are seals/packings replaced?
Anytime the cylinder is disassembled and the seals are removed.
How does the oil get from the cylinder head back to the crankcase?
O200: Shroud tubes
O235: Oil drain tubes
What adjustments are there on a cylinder? Why?
O200: No valve adjustments thanks to its hydraulic lifters
O235: Adjust valve clearance with common screwdriver (necessary due to its solid lifters)
What must be done to the connecting rods immediately after cylinder removal?
Support the rods by securing them to the cylinder port to prevent them from scoring the crankcase.
Why would you “stagger the rings”?
It prevents compression loss due to warping of the rings.
What tools did you need to Re & Re the cylinder?
Cylinder base wrench, ring expander, screwdriver, ratchet, piston ring compressor.
When would you change a cylinder?
If the engine fails a differential compression test (low compression or cracked cylinder)
Obvious damage on cooling fins
Borescope finds corrosion
Cylinder is leaking
Cylinder doesn’t perform to specs
After extended time in storage
What is the torque for the cylinder base nuts?
3/8”: 300 in-lbs
7/16”: 420 in-lbs
What are the components of a cylinder assembly?
Cylinder head
Piston pin
Piston head
Valve Assembly
Piston rings
When are camshaft bearings replaced on the Lycoming O235 engine?
There are no camshaft bearings
How are the halves (outer halves on the O235 L2C) of a crankcase sealed?
By “00” silk thread and sealant
Why is it important to follow the correct torque pattern when reassembling a crankcase?
So the crankshaft is held and aligned properly in the case with its associated bearings
What lubrication methods are used for the camshaft journals?
Pressure
What is the correct torque pattern for the lycoming O235 case parting face bolt?
E,D,F,B,A,C
How are the halves of a crankcase aligned for assembly?
By dowel pins
When are camshaft bearings replaced on the Lycoming O235 engine?
Whenever the case is opened
When the camshaft is replaced, they are matched parts
Every 2000 hours of operation
There are no camshaft bearings
How is the accessory case aligned with the crankcase for assembly?
By the case bolts
By dowel pins
By the through bolts
By the crankshaft and camshaft
Why is it important to follow the correct torque pattern when reassembling a crankcase?
So the crankcase won't crack
So the camshaft bearings don't spin
So the Through bolts wont twist
So the crankshaft is held and aligned properly in the case with its associated bearings
What lubrication method is used for the camshaft lobes?
Immersion
Spray
Pressure
Splash
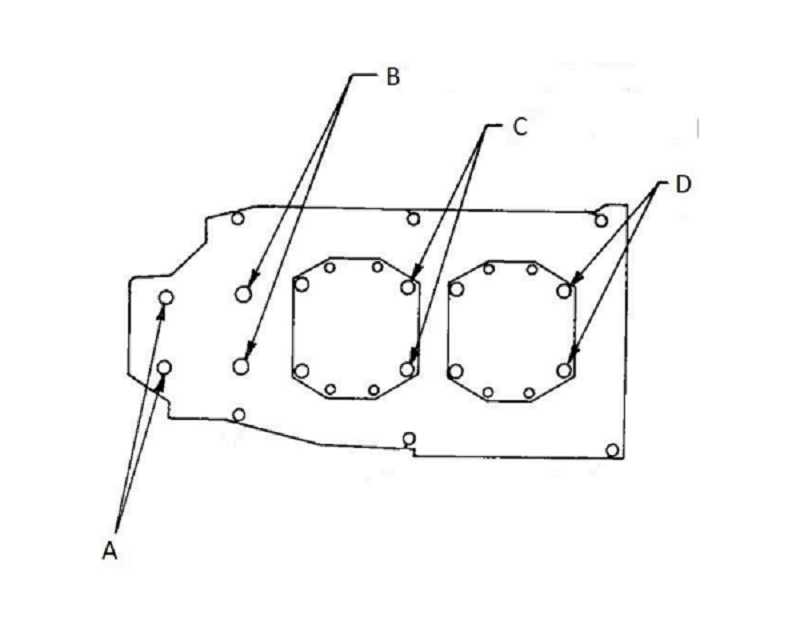
What is the correct torque pattern for the Lycoming O235 case through bolts?
B, A, D, C
C, D, B, A
A, B, C, D
C, D, A, B
Where can the crankcase leak?
Front and Back of the Crankcase, Rubber Sealings, Gaskets, Floating through Bolts.
How many through bolts hold cases together?
8
How often are the main bearings replaced?
Major Overhaul or Bulk Inspection (On condition)
Every 100 hours of operation
Once a year
When the engine reaches 10,000 hours of operation
How often are the camshaft bearings replaced?
There are no cam bearings.
Camshaft bearings are replaced every 10,000 miles
Camshaft bearings need to be replaced annually
Camshaft bearings typically last for 5 years before replacement
How is the crankshaft lubricated?
Pressure Lubrication
Splash Lubrication
Dry Lubrication
Air Lubrication
The crankshaft is lubricated by a network of tiny tubes
How are the camshaft journals lubricated?
Pressure Lubrication
Splash Lubrication
Dry Lubrication
Magnetic Lubrication
Air Lubrication
How are the camshaft lobes lubricated?
The camshaft lobes are lubricated via splash lubrication in the crank case
The camshaft lobes are lubricated by direct injection of oil
The camshaft lobes are lubricated by a pressurized air system
The camshaft lobes are lubricated by a magnetic field generated by the engine
The camshaft lobes are lubricated by a specialized gel coating
What is the torque pattern for torquing the crankcase through bolts?
1. Left side - middle 2. Left side - top 3. Left side - middle 4. Tightening right side - bottom case 5. Tightening crankcase fastening 6 to 13
3. Left side - middle 1. Left side - top 2. Left side - middle 5. Tightening right side - bottom case 4. Tightening crankcase fastening 6 to 13
2. Left side - middle 1. Left side - top 4. Left side - middle 5. Tightening right side - bottom case 3. Tightening crankcase fastening 6 to 13
Tightening crankshaft pulley
Torquing the oil pan bolts
What is the torque pattern for torqueing the crankcase parting face bolts?
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
What size nuts are used for the cylinder bases?
9/16
5/8
1/2
3/4
7/16
What can cause damage inside the crankcase?
Over tightening of the through bolt causing damage to the journals/spun bearing.
Excessive heat buildup
Lack of lubrication
Foreign objects entering the crankcase
Corrosion or rusting of internal components
How are the crankcase assembly halved and sealed?
POB seals and Silk thread.
Bolted together with rubber gaskets
Welded together using high heat
Secured with adhesive tape
Joined with metal clips
How are the crankcase assembly halved aligned?
1st - right half and 2nd -left half (Via Dowel Pins)
Top half and bottom half (Via Dowel Pins)
Front half and back half (Via Dowel Pins)
Inner half and outer half (Via Dowel Pins)
Upper half and lower half (Via Dowel Pins)
When would you open the crankcase for inspection?
Only if the repair is needed or any damage is found
During routine maintenance
After every 100 hours of operation
When the engine is running smoothly
If there is a change in oil pressure
What tools were needed for this job?
Telescopic gauge, micrometer, feeler gauge.
Wrench
Screwdriver
Hammer
Pliers
What is clearance?
The space between two parts.
The amount of money needed to purchase an item
A type of sale or discount
A form of permission or authorization
The process of removing unwanted items or clutter
What is interference?
Lack of clearance/two parts touching.
Interference is when two objects merge together seamlessly.
Interference occurs when there is a lack of communication between two parties.
Interference refers to the disruption of a signal or transmission.
Interference is the result of external factors affecting the performance of a system.
What tool is used to measure inside diameter?
Telescopic gauge (measured at three spots).
Caliper
Micrometer
Depth gauge
Feeler gauge
What tool is used to measure outside diameter?
Micrometer.
Caliper
Vernier gauge
Dial indicator
Gauge block
What tools are needed to measure a clearance?
Micrometer, bore gauge, feeler gauge, vernier calipers, etc.
Laser pointer
Thermometer
Screwdriver
Tape measure
How often will a micrometer be used for this kind of work?
All the damn time.
Rarely, only for special occasions
Occasionally, when other tools are not available
Never, micrometers are outdated and not used anymore
Only once in a blue moon, when precision is not important
How often will a vernier caliper be used for this kind of work?
Rarely, not as often a micrometer.
Only for very precise measurements
Occasionally, but not frequently
Only when measuring small objects
Not commonly used in modern industries
What is spark plug reach and how do you know what reach spark plug a cylinder requires?
The depth a spark plug threads in a cylinder. Thicker cylinder wall means more threads needed and therefore a longer reaching spark plug. .020 cylinders (yellow paint below spark plug) need longer reach.
Spark plug reach refers to the distance between the spark plug and the piston in a cylinder. It is determined by the size of the spark plug electrode.
The reach of a spark plug is the measurement of how far the spark plug protrudes into the combustion chamber. It is determined by the engine manufacturer's specifications.
Spark plug reach is the length of the metal shell of the spark plug. It is determined by the type of ignition system used in the vehicle.
The reach of a spark plug is determined by the compression ratio of the engine. Higher compression engines require longer reach spark plugs.
How do you know what treatment a cylinder wall has?
It’ll have painted fins below the spark plug (Lycoming)
The cylinder wall will have a rough texture
There will be visible scratches on the cylinder wall
The cylinder wall will have a glossy finish
There will be a distinct odor coming from the cylinder wall
When would you measure a cylinder?
During overhaul, bulk inspection, or repair.
During routine maintenance
When conducting a pressure test
After a cylinder has been painted
When checking for corrosion
How would you know if a cylinder is chrome plated?
Orange painted fins
The cylinder has a rough texture
The cylinder is magnetic
The cylinder has a strong odor
The cylinder reflects light differently
How would you know if a cylinder is nitrided?
Blue painted fins.
The cylinder has a rough texture
There are visible cracks on the surface of the cylinder
The cylinder emits a distinct odor when heated
The cylinder becomes magnetic after nitriding
How would you know if a cylinder is cermicrome plated?
Orange AND white painted fins.
The cylinder has a rough texture
The cylinder is magnetic
The cylinder has a strong odor
The cylinder is transparent
How would you know if a cylinder is .010” oversized?
Green marked.
The cylinder would have a noticeable increase in diameter.
There would be a slight decrease in the cylinder's internal volume.
The cylinder would have a smoother surface finish.
The piston would fit loosely inside the cylinder.
How would you know if a cylinder is .020” oversized?
Yellow marked.
The cylinder would have a noticeable increase in diameter
There would be a significant decrease in the piston clearance
The cylinder walls would show signs of excessive wear
The engine would produce more power due to increased compression
How often will the crankshaft bearings be removed?
At overhaul
Every 10,000 miles
Once a year
After 100 hours of operation
Only when there is visible damage
How often will the connecting rod bearings be removed?
At overhaul
Every 10,000 miles
Once a year
After 100 hours of operation
Only when there is visible damage
How often will the piston pin bushing be replaced?
On condition
Every 100,000 miles
Once every 5 years
Only when the engine is overheating
After every oil change
What is run out?
How far it rotates off the axis. Eccentricity/ like a skipping rope/ out centre.
It refers to the distance covered by a runner during a race.
Run out is a term used in cricket to describe when a batsman is dismissed by a fielder throwing the ball and hitting the stumps before the batsman reaches the crease.
Run out is a measurement of how much fuel is left in a vehicle's tank.
In gymnastics, run out refers to the distance a gymnast covers before executing a tumbling pass or vault.
What is a slinger flange?
A flange at the front end of the front journal which acts as an oil slinger. Helps to sling the oil back into the engine and there is a rubber seal
A slinger flange is a type of decorative accessory used in fashion design.
A slinger flange is a term used in the construction industry to describe a specialized tool for applying mortar.
A slinger flange is a slang term for a person who is skilled at throwing frisbees.
A slinger flange is a type of musical instrument commonly used in traditional folk music.
What kind of crankshaft was used in the O200 engine we inspected?
Nitrided. It can be re-grinded then a larger bearing insert can be used and then it has to be re-hardened.
The O200 engine we inspected used a forged steel crankshaft.
The crankshaft in the O200 engine we inspected was made of cast iron.
The O200 engine we inspected had a chrome-plated crankshaft.
The crankshaft in the O200 engine we inspected was made of aluminum.
What process is used to harden the O200 crankshaft?
Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface.
Tempering is a process used to harden the O200 crankshaft.
Galvanizing is a process used to harden the O200 crankshaft.
Annealing is a process used to harden the O200 crankshaft.
Quenching is a process used to harden the O200 crankshaft.
Describe the type of bearing used in the connecting rod at the crankshaft end
2 piece, semicircular split style bearing
Ball bearing
Needle roller bearing
Tapered roller bearing
Thrust bearing
What keeps the connecting rod bottom bearings and the crankshaft bearings from turning?
Notches and tangs. The crushing weight of the case
Magnetic force
Friction
Gravity
Lubrication
How do you know which cylinder a connecting rod will be installed in?
The number is found on the cap of the connecting rod where it connects to the crankshaft, there are two numbers: 1 on the bottom part and the other on the rod, these numbers line up to close the connecting rod onto the crankshaft to correspond with the correct cylinder
The connecting rod is randomly assigned to a cylinder during assembly.
The cylinder number is determined by the size of the connecting rod.
The connecting rod is labeled with the cylinder number on the piston head.
The cylinder number is determined by the position of the connecting rod in the engine block.
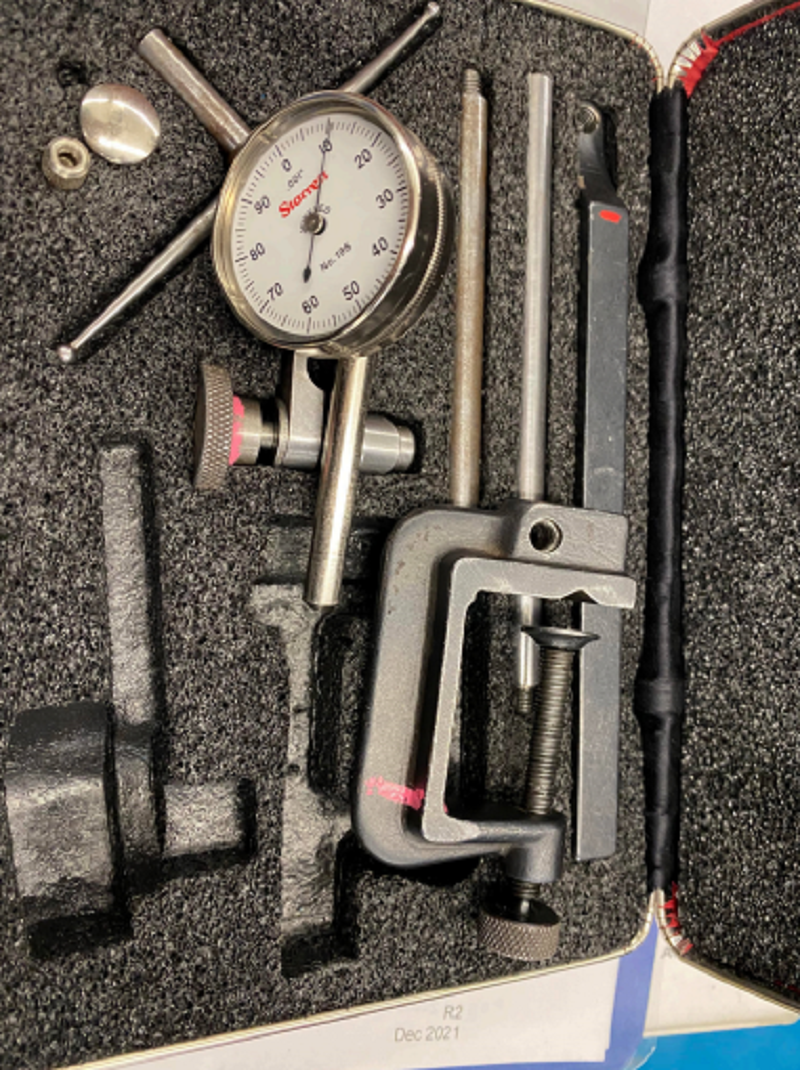

What is the name of this tool, and what does it measure?
Dial Indication - Run out (face of flange, centre journal)
Telescoping Gauge/ snap gauge/transfer gauge - Inside diameter
Micrometer - Outside diameter
Feeler gauge - End Clearance (rod on crankpin)
Depth Gauge - Depth
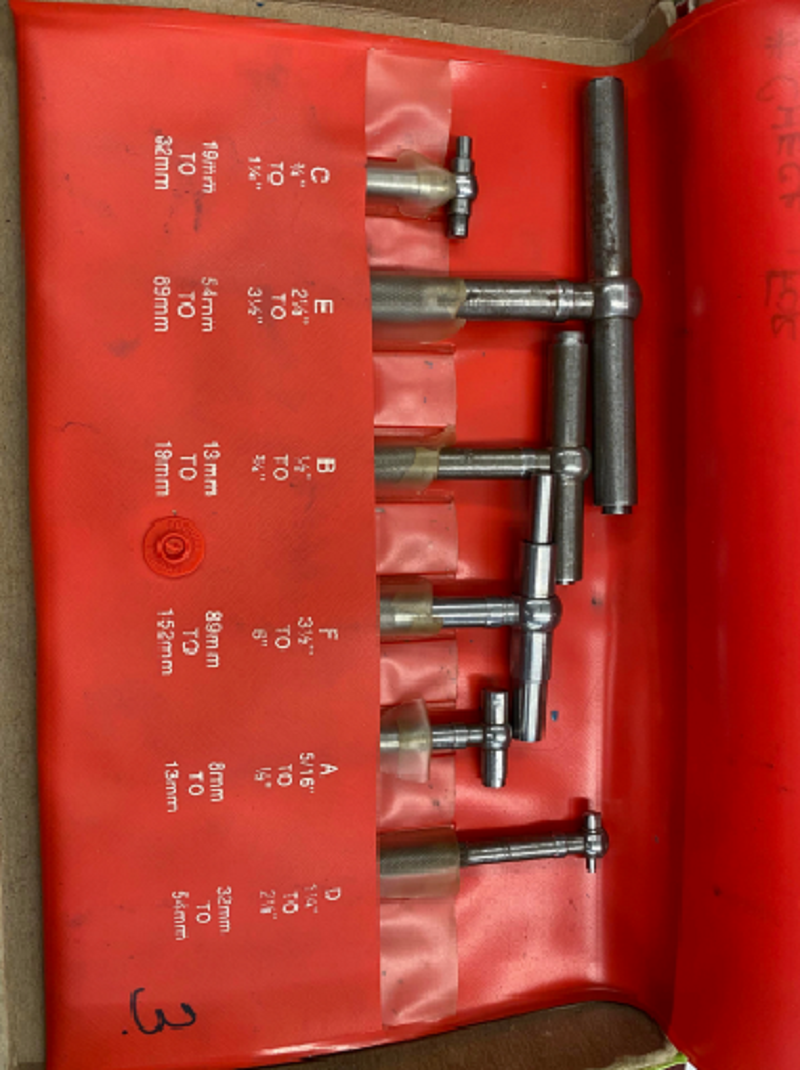

What is the name of this tool, and what does it measure?
Dial Indication - Run out (face of flange, centre journal)
Telescoping Gauge/ snap gauge/transfer gauge - Inside diameter
Micrometer - Outside diameter
Feeler gauge - End Clearance (rod on crankpin)
Depth Gauge - Depth
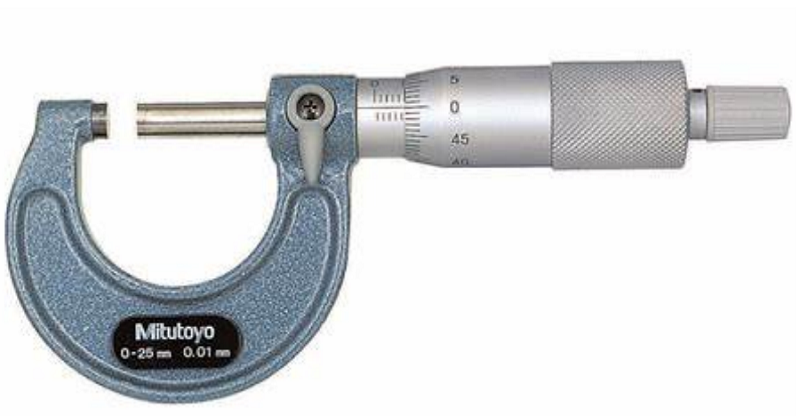

What is the name of this tool, and what does it measure?
Dial Indication - Run out (face of flange, centre journal)
Telescoping Gauge/ snap gauge/transfer gauge - Inside diameter
Micrometer - Outside diameter
Feeler gauge - End Clearance (rod on crankpin)
Depth Gauge - Depth
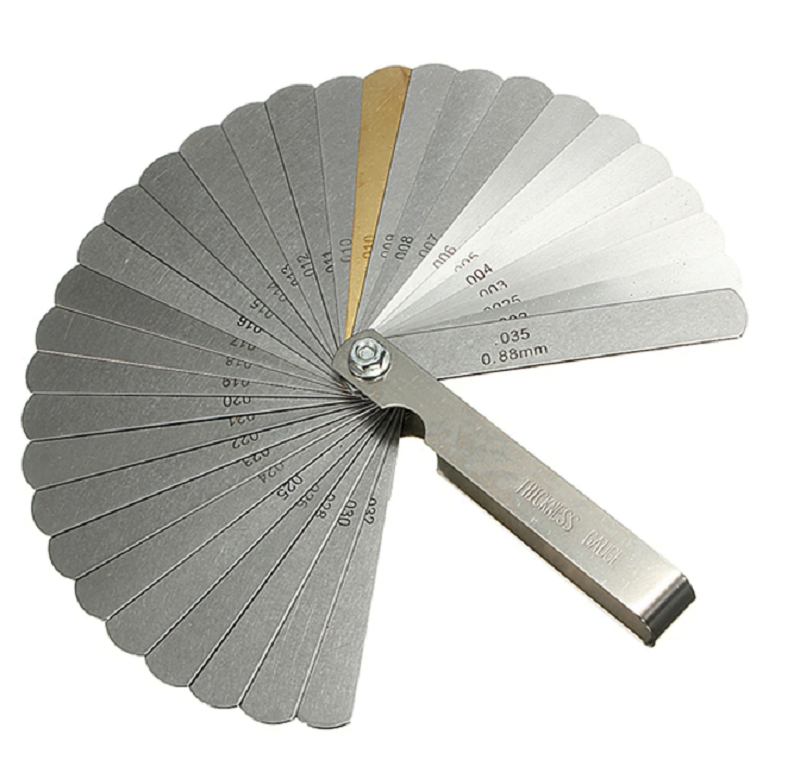

What is the name of this tool, and what does it measure?
Dial Indication - Run out (face of flange, centre journal)
Telescoping Gauge/ snap gauge/transfer gauge - Inside diameter
Micrometer - Outside diameter
Feeler gauge - End Clearance (rod on crankpin)
Depth Gauge - Depth
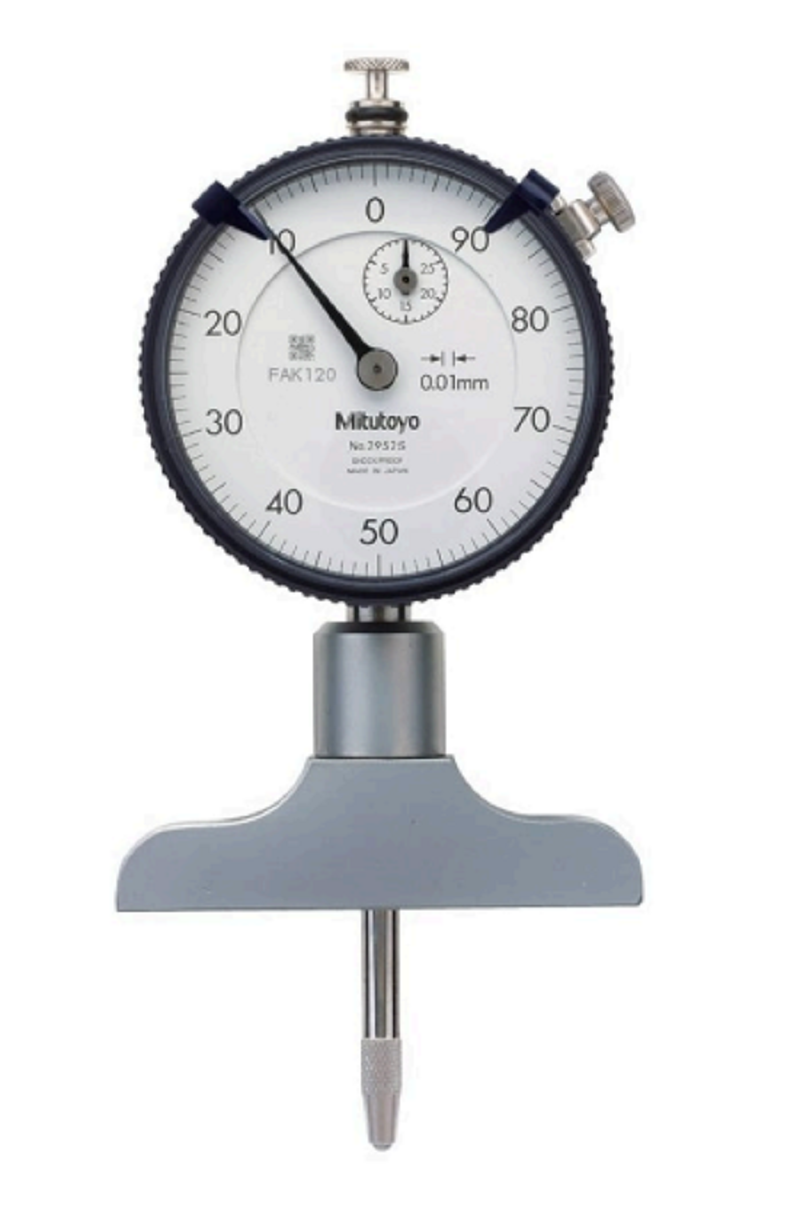

What is the name of this tool, and what does it measure?
Dial Indication - Run out (face of flange, centre journal)
Telescoping Gauge/ snap gauge/transfer gauge - Inside diameter
Micrometer - Outside diameter
Feeler gauge - End Clearance (rod on crankpin)
Depth Gauge - Depth
{"name":"Power Plant 1-3", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"What must be done to the connecting rods after a cylinder is removed?, What position is the piston supposed to be in when removing a cylinder from an engine?, When are the seals\/packings on a cylinder replaced?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/97-4789987/torque-pattern.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Movie round
12658
Who run the world? GIRLS.
10522
Metacognition
520
How to make money online
1050
Free Death of a Salesman
201025474
Think You Know Characteristics of Matter? Take the!
201027781
Free U.S. Government and Citizenship Knowledge
201026439
Free Perfect Competition: Spot the Exception
201021867
Free Project Management Staff Knowledge Test
201025945
Romeo Juliet Questions: Test Your Shakespeare IQ
201026189
Free Networking Fundamentals Chapter Assessment
201026695
Kesha IQ Test: Are You More Like Kesha or Taylor Swift?
201032211