Biology Midterm 2
Select all of the following that correlates with Prokaryotes
Lack a membrane-bound nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelle
Lack a mitochondria
Have lysosomes
All bacteria and arcahae
Prokaryotes are distinguished by their cell shape, cell wall, and projections
True
False
Match the following cell shapes with their definitions
Cocci
Spiral, Usually alone
Spirochete
Rod, Most occur alone, Some occur in pairs or chains
Bacilli
Spherical (round), Forms chains, Forms clusters
Match the following cell shapes with their infections/diseases/symptoms etc.
Spirochete
Escherichia coli (E. Coli), Causes food poisoning
Bacilli
(Chains): Streptococci and Strep Throat. (Clusters) Staphylococci and Staph infection
Cocci
Lyme disease, Syphilis
Match the cell wall bacteria with their definitions
Peptidoglycan
Gram negative
Lipids and carbs
Gram positive
Many bacteria in cells walls have a capsule that allows them to stick to things or each other
True
False
Match the projections with their definitions
Fimbriae
Hair like projections (helps them stick to other things)
Flagella
Whip like structure that enables swimming
Match the following with their definitions (nutrition)
Chemoheterotrophs
Capture energy from inorganic chemical, Obtain carbon from organic sources, Largest and most diverse group, Eats almost anything
Photoautotrophs
Capture energy from inorganic chemical, Use CO2 for carbon, Can live in extreme or regular environments
Photoheterotrophs
Capture energy from sunlight, Obtain carbon from organic sources (complex molecules), Purple non-sulfur bacteria (found in aquatic sediments)
Chemoautotrophs
Capture energy from sunlight, Use CO2 for carbon, Cyanobacteria (blue green algae)
Match the four key groups of bacteria with their definitions
Proteobacteria
Gram negative, photoautotroph
Gram-positive bacteria
Gram positive, nutritionally diverse, pathogens
Cyanobacteria
Gram negative, chemoheterotrophs, pathogens, spiral shaped
Spirochetes
Gram negative, nutritionally diverse, pathogens, symbiosis
Archaea thrive in extreme environments. Select all of the following that is true about Archaea
Halophiles: salt loving
Thermophiles: heat loving
Methanogens: live in anaerobic (no oxygen) conditions and produce methane as waste
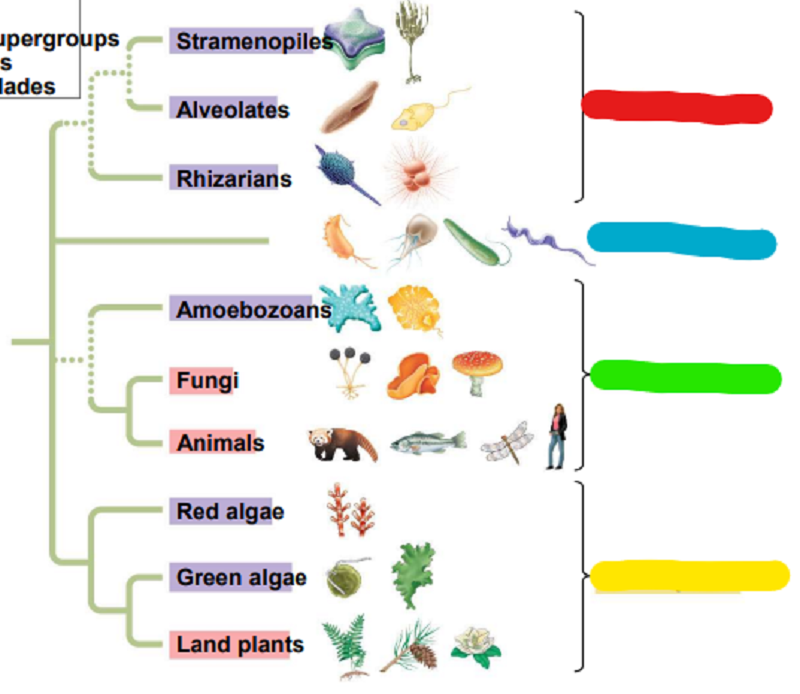
Match the following protists with their group by color
Blue
Archaeplastida
Green
Excavata
Yellow
SAR
Red
Unikonta
Protists have diverse nutrition. Match the following with their definitions
Mixotrophs
Both
Heterotrophs
Photosynthesize
Autotrophs
Eat other things
Match the SAR protists with their defintions
Alveolata
Dinoflagellates, ciliates
Rhizarians
Forminiferans, radiolarians
Stramenopiles
Diatoms, brown algae, water molds
Match the following protist super groups with their definitions
Excavata
Amoebozoans (heterotrophic, slime molds, free-living and parasitic amoebas)
Unikonta
Autotrophic, mostly multicellular, red algae, green algae (alternation of generations)
Archaeplastida
"Excavated" feeding groove, parasites, all nutrition (autotrophs, heterotrophs, mixotrophs)
The alternation of generations are multicellular haploid and diploid individuals
True
False
Match the following multicellular individuals with their definitions
Gametophyte
Produces spores
Sporophyte
Produces gametes
How do Fungi perform absorption?
Their roots eat away at plants and animals in small amounts once they've sunk into the ground
They secrete enzymes that digest plants and animals and then absorb the small nutrients
They produce a specific type of bacteria that eats the plants and animals for them, allow the original fungi to decay and new fungi to be born
They smell so bad that things just decompose around them. Like really bad.
Fill in the blanks in order: A fungus usually consists of a mass thread-like filaments called ______, which branch repeatedly as they grow, forming a ______
Hyphae; mycelium
Mycelium; hyphae
Fungi have asexual AND sexual lifecycles
True
False
Match the five groups of fungi with their definitions
Zygomycetes
Decomposers, plant pathogens, lichens
Basidiomycetes (club fungi)
Characterized by mycorrhizae which invade plant cells
Ascomycetes (sac fungi)
Mostly terrestrial, mostly decomposers (bread mold), have zygosporangium
Chytrids
Characterized by basidium (mushrooms!), decomposers, parasites
Glomeromycetes
Only fungi with flagellated spores, decomposers and parasites, causing amphibian mass extinction
Match the following with their definitions
Mycorrhizae
Helped plants colonize land, trade (plants get nutrients, fungus gets carbon)
Lichens
A symbiosis between an ascomycete and a cyanobacteria or green algae
Select the four key events that occurred in the history of the plant kingdom
Origin of land plants
Origin of vascular plants
Origin of sea plants
Origin of seed plants
Origin of vegetation plants
Origin of flowers
For plants that originated in water, what challenges were presented when living on land? Select all that apply
Drying out
Obtaining resources from two sources
Support (not falling over)
Reproduction and Dispersal
Select all of the following things that plants developed to keep them from drying out
Waxy cuticle
Roots
Stems
Stomata
What does a waxy cuticle do?
Keeps plants shiny
Keeps plants moist
Prevents gas exchange
Prevents predators from their scent
Select all of the following things that plants developed to obtain resources from two sources
Roots
Stems
Leaves
Vascular Tissue
Fill in the blank: To solve the issue with reproduction, all plants have alternation of ______
Transfigurations
Generations
Symbiosis
Photosynthesis
Match the follow dispersal methods for plants with their definitions on how they're dispersed
Gymnosperms (cone bearing plants)
Wind, gravity, animals
Angiosperms (flowering plants)
Water
Moss and ferns
Wind, ants, mammals, birds, water, gravity, etc.
What were the first plants? (moss, liverworts, hornworts)
Bryophytes
Pteridophytes
Tracheophytes
What are the characteristics of bryophytes? Select all that apply
Do not have true roots (have rhyzoids)
Has true roots
Do not have true leaves (phyllid)
Has leaves
Do not have lignin for structural support
Has lignin for structural support
Grows upright
Grow flat in dense mats
Must have water for fertilization
Non-vascular
Vascular
What are the characteristics of seedless vascular plants? Select all that apply
Do not have true roots (have rhyzoids)
Has true roots
Do not have true leaves (phyllid)
Has leaves
Do not have lignin for structural support
Has lignin for structural support
Grows upright
Grow flat in dense mats
Must have water for fertilization
Non-vascular
Vascular
Match the vascular tissues with their definitions (PAIR THEM BY NUMBER)
1 Xylem
2 Vessel walls consists of cells that are connected at their ends to form porous sieve plates
1 Pholem
3 Vessels are composed of dead tissues and are hollow
2 Pholem
2 Vessel walls consits of fused cells that create a continuous tube
3 Xylem
3 Vessels are composed of living tissue, however sieve tube elements lack nuclei and have few organelles
2 Xylem
1 Transports food and nutrients to storage organs and growing parts of the plant (bidirectional transport)
3 Pholem
1 Transports water and minerals from the roots to aerial parts of the plant (unidirectional transport)
Match the seed plant groups with their definitions
Gymnosperms
Cone bearing plants (naked seeds)
Angiosperms
Flowering plants (enclosed seeds)
Seed plants need water to reproduce
True
False
Select all the characteristics of confiers
Leaves in "needles"
Seeds in cones
Evergreen (mostly)
Have ovaries
All woody (secondary growth)
Have flowers
Select all the characteristics of angiosperms
Have flowers
Evergreen (mostly)
Have ovaries
Symbiosis with pollinators
Leaves in "needles"
Adaptations for dispersal
Match the following floral morphology with its purpose
Petals
Often attract animal pollinators
Carpels
Male reproductive structures (anther: contains pollen)
Stamens
The female reproductive structures (stigma, style, ovary)
Sepals
Enclose the flower before it opens
Match the dispersal method with its adaptation to move
Buoyancy
Bird and mammal dispersal
Fruits
Water dispersal
Burs
Ant dispersal
Elaiosomes
Mammals dispersal
Wings
Wind dispersal
Pollination syndromes are similarities among flowers that share the same pollinators. Match the animal with its pollination syndrome
Bees
Bright red and orange flowers, no scents
Bats and months
White flowers, highly scented, bloom at night
Birds
Marked with guides that lead to nectar
Match the word with its definition
Eudicots
Two cotyledons in seed leaves, branched leaf veins, vascular bundles in rings, flowers in multiples of four or five, taproot
Monocots
One cotyledon in seed leaves, parallel leaf veins, scattered vascular bundles, flowers in multiples of three, fibrous root system
Match the following words with its definitions (or characteristics)
Blade
Between stem and leaf, usually dormant
Stems
Primary growing point for getting taller
Petiole
Organ that has the leaves and buds on it, can photosynthesize
Nodes
Points at which leaves are attached
Terminal Bud
Increase surface area
Ancillary Bud
The leaf
Root hairs
Joins blade to the stem at a node
Plants are comprised of three systems. Match the following system and modified systems to its characteristics
Modified leaf
Primary site for photosynthesis, consists of blade and petiole
Modified roots
Stems (can photosynthesize and has nodes), buds (terminal and ancillary bud), and flower
Shoot
Spines (protects the plant from being eaten) and tendrils (modified leaves that help vines "climb")
Leaf
Large taproots that store food (carrots, turnips, sweet potatoes)
Modified shoot
Stolon, rhizome, tuber, succulence
Root
Anchors the plant to the soil, absorbs and transports minerals and water (facilitated by root hairs), taproots store carbohydrates
Growth is limited by lifespan, physics, and environmental conditions
True
False
Match the following with its definition
Meristems
Growing up (lengthens), meristems, apical meristems
Apical Meristems
Meristems at the tips of roots, in the terminal bud
Secondary growth
Growing out (thickens), meristems, lateral meristems
Lateral Meristems
Divided into two tissues (vascular cambium and cork cambium)
Primary growth
Unspecialized tissues that divide with conditions are right
Match the following with its plant reproduction definition
Sexual
Flowers, pollen, etc.
Asexual (cloning)
Fragmentation, rhizomes, stolons, used in agriculture
Transpiration is...
The process of condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull and flourishes wildlife plants
The process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers
There are three ways plants can do photosynthesis. Match the following with its definisions
C3
Take CO2 directly from the air
C4
Take in CO2 at night, stores it and does photosynthesis during the day
CAM
Converts CO2 to a 4C compound and then sequestered to a deeper tissue layer where less oxygen is present
Match the following with its definitions
Epiphytes
An adaptation to low nutrient conditions, kill insects and animals and digest them, often found in areas with low nitrogen
Parasitic plants
Grows on other plants, no a symbiosis, the host plant provides support (elevation toward more sunlight)
Carnivorous plants
Grown on (or near) other plants and steal nutrients, hemiparasites, holoparasites, modified roots (haustorium) attached to host plant and takes water/nutrients
Select the following that are characteristics of animals
Cells have cell walls
Eukaryotes
Multicellular heterotrophs
Use ingestion
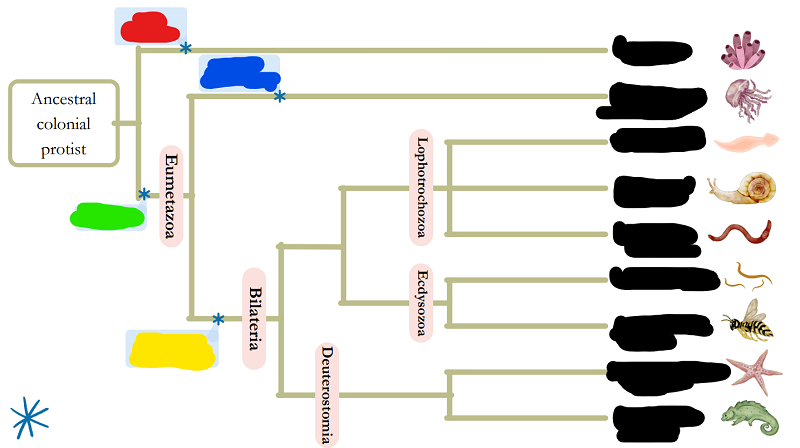
Match the following words with its place on the chart (by color; ignore things in black)
Blue
Bilateral symmetry
Red
Radial symmetry
Green
Tissues
Yellow
No tissues

Match the following words with its place on the chart (by color; ignore things in black)
Green
Molluscs
Purple
Arthropods
Brown
Nematodes
Red
Annelids
Pink
Flatworms
Blue
Cnidarians
Yellow
Echinoderms
Gray
Chordates
Orange
Sponges
Match the following characteristics of sponges with its definitions
Sessile
Use flagellum to move water and trap food
Amoebocytes
Produce skeletal fibers (yellow) and digest food
Choanocytes
Do not move
Suspension feeders
Collect food particles by passing water through a "trap"
Match the following with its definitions
Tissue
Mirror image right and left sides
Radial symmetry
Body parts radiate from center
Bilateral symmetry
Integrated group of cells with a common function or structure
Match the following with its characteristics
Arthropods
Have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, a body cavity, digestive tract with two openings, pseudococelom
Echinoderms
Radial symmetry, two true tissue layers, gastrovascular cavity, polyp and medusa body forms
Nematodes
Bilateral symmetry as larvae but radial as adults, three tissue layers, a body cavity, endoskeleton
Annelids
Have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, a body cavity, segmentation, closed circulatory system, cocelom
Flatworms
Have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, a body cavity, exoskeleton, open circulatory system
Cnidarians
Have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, a body cavity, open circulatory system
Molluscs
Have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, no body cavity
Sponges
No tissues, no nerves, no muscles, lack symmetry
Match the following with an animal from its category
Echinoderms
Hydra, Sea jelly
Sponges
Crayfish, Lobsters, Crabs
Molluscs
Snails, Slugs, Oysters, Clams
Nematodes
Segmented worms
Flatworms
Sea urchins, Sea stars
Arthropods
Planarians, Flukes, Tapeworms
Annelids
Roundworms
Cnidarians
...Sponges
Match the following characteristics of Chordates with its definition
Phalangeal Slits
A tail
Dorsal, hollow nerve cord
Cartilage rod; becomes disk in backbone
Post-anal tail
Used for filter feeding; becomes gills in fish
Notochord
Becomes the central nervous system
Match the following animal adaptations to living on land with its defintion
Amniotic egg
Moving on land
Lobed fins
Catch and eat food
Jaws
Babies out of water
Four limbs
Protection for spinal cord, attachment for muscles
Vertebral column
Breathing air
Milk
Nourishment for babies
Lungs
Walking
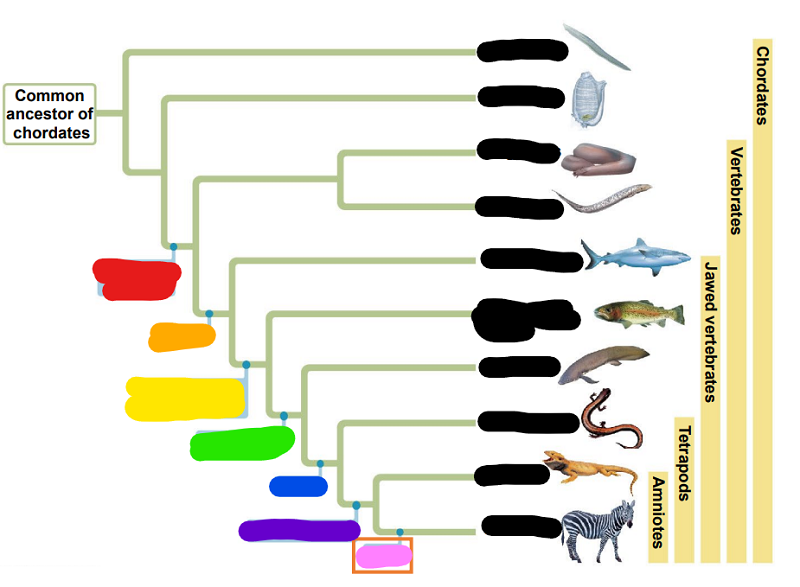
Match the following words with its place on the chart (by color; ignore things in black)
Green
Milk
Pink
Lobed finned fish
Blue
Legs
Red
Jaws
Yellow
Lungs or lung derivatives
Purple
Vertebral column
Orange
Amniotic Egg
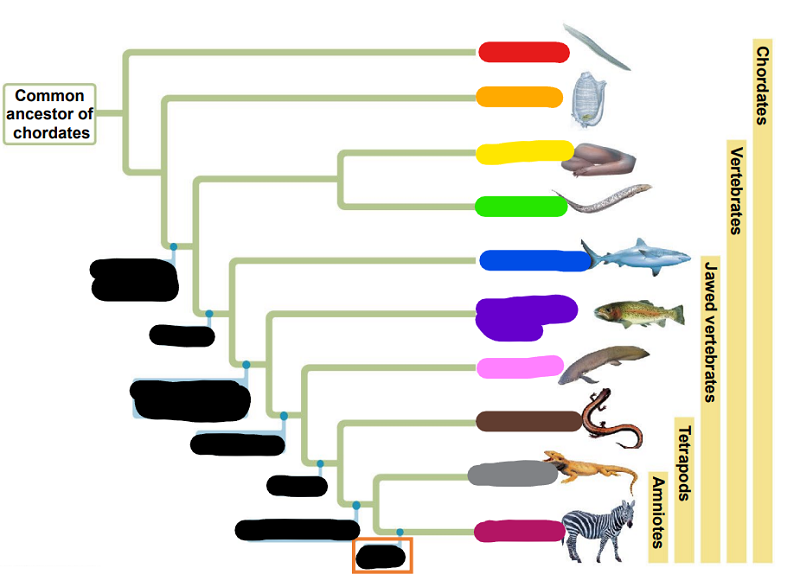
Match the following words with its place on the chart (by color; ignore things in black)
Orange
Hagfishes
Yellow
Amphibians
Green
Tunicates
Magenta (the last color since I ran out of colors)
Mammals
Brown
Ray-finned fish
Purple
Lobe-fins
Pink
Sharks, Rays
Gray
Reptiles
Blue
Lampreys
Red
Lancelets
Match the following with its characterists
Ray-finned fish
Fins and Jaws (sharks, rays, ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish)
Lobed-fin fish
Endothermic amniotes, hair, produce milk
Reptiles
Rudimentary vertebrae, notochord, NO hinged jaws nor paired fins
Mammals
Bony, operculum, swim bladder, lobed fins
Amphibians
Amniotes (amniotic egg), ectothermic (except birds, which are endothermic)
Sharks and Rays
Lay eggs in water, first tetrapod to colonize lands
Jawed vertebrates with gills and paired fins
Bony, operculum, swim bladder
Hagfishes and Lampreys
Cartilaginous fish, filter feeders
Match the following with its definition
Eutherian (placental mammals)
Nutrients from the mother's blood diffuse into the embryo's blood
Placenta
Have a brief gestation and give birth typically tiny, embryonic offspring that complete development in a pouch
Marsupials
Bear fully developed live young
Monotremes
Egg-laying mammals
Match the following with its definition
Intestines
A digestive tube with two openings
Crop
Breakdown (with chemicals) and store food
Stomach
Absorb nutrients
Alimentary Canal
Where food is softened and stored (animals without teeth)
Gizzard
Breakdown (with rocks and sand) and store food
Match the digestive system with the type of animal
Carnivores
No cecum, intermediate length
Herbivores
Long digestive tract (more time for plants), cecum (home to microbes that break down plants)
Omnivores
Expandable stomach, short digestive tract
Match the four main approaches to gas exchange with its characteristcs
Skin
Absorb O2 dissolved in water
Lungs
Must live in damp places, small animals
Tracheal System
Internal sacs lines with a moist epithelium, gas carried to cells via circulatory system
Gills
Has respiratory surfaces at the tips of tiny branching tubes in body, transports O2 direct to body cells and moves CO2 away from them
Match the following with its definition on the subject of thermoregulation
Thermoregulation
How animals maintain a internal temperature despite variation in external temperature
Endothermic
Using heat generated by metabolism to maintain a warm, steady body temperature
Ecothermic
Absorbing external heat rather than generating much of their own
Match the following with its definition on the subject of specialized sensory receptors
Pain receptors
Special nerve cells that are tuned to the conditions of the environment
Thermoreceptors
Sensed dangerous stimuli (harmful pressure, temperatures, or chemicals)
Merchanoreceptors
Respond to chemicals
Chemoreceptors
Receptors respond to electricity, magnetism or light
Electromagnetic
Respond to mechanical energy, such as touch
Sensory receptors
Detect heat or cold
{"name":"Biology Midterm 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Select all of the following that correlates with Prokaryotes, Prokaryotes are distinguished by their cell shape, cell wall, and projections, Match the following cell shapes with their definitions","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/98-4842110/screenshot-2024-02-19-135346.png?sz=1200-00000000001000008680"}