Energy Conversion
1. What is the dc output voltage of an unfiltered half- wave rectifier whose peak output voltage is 9.8 V?
A. 6.23 V
B. 19.6 V
C. 9.8 V
D. 3.1 V
2. What is the frequency of the capacitor ripple voltage in a full wave rectifier circuit if the frequency of the transformer secondary voltage is 60 Hz?
A. 60 Hz
B. 50 Hz
C. 120 Hz
D. It cannot be determined
3. In a full-wave rectifier, the dc load current equals 1 A. How much dc current is carried by each diode?
A. 0.5 A
B. 1 A
C. 2 A
D. 0 A
4. The output from an unfiltered half-wave or full-wave rectifier is a
A. Pulsating dc voltage
B. Steady dc voltage
C. Smooth dc voltage
D. None of the choices
5. A diode is a
A. Unidirectional device
B. Linear device
C. Nonlinear device
D. both “unidirectional device” and “nonlinear device”
6. What is the approximate dc output voltage from a filtered bridge rectifier whose peak output voltage is 30 V?
A. 19.1 V
B. 9.5 V
C. 30 V
D. None of the choices
7. If the ac supply is 60 Hz, what will be the ripple frequency out of the half-wave rectifier?
A. 30 Hz
B. 50 Hz
C. 60 Hz
D. 120 Hz
8. If the ac supply is 50 Hz, what will be the ripple frequency out of the full-wave rectifier?
A. 50 Hz
B. 60 Hz
C. 100 Hz
D. 120 Hz
9. A silicon diode in a half-wave rectifier has a barrier potential of 0.7 V. This has the effect of
A. Reducing the peak output voltage by 0.7 V.
B. Increasing the peak output voltage by 0.7 V.
C. Reducing the peak input voltage by 0.7 V.
D. No effect.
10. In a regulated supply, what term describes how much change occurs in the output voltage for a given change in the input voltage?
A. Load regulation
B. Voltage regulator
C. Line regulation
D. Ripple voltage
11. In a regulated supply, what term describes how much change occurs in the output voltage over a certain range of load current values, from minimum to maximum current?
A. Line regulation
B. Voltage regulator
C. Current regulator
D. Load regulation
12. PIV is which of the following?
A. Peak input voltage
B. Peak inverse voltage
C. Peak immediate voltage
D. Positive input voltage
13. The output frequency of a half-wave rectifier is _____ the input frequency.
A. one-half
B. twice
C. Equal to
D. None of the above
14. Each diode in a center-tapped full-wave rectifier is _____ -biased and conducts for _____ of the input cycle.
A. forward, 90o
B. reverse, 180o
C. forward, 180o
D. reverse, 90o
15. The output frequency of a full-wave rectifier is _____ the input frequency.
A. one-half
B. Equal to
C. twice
D. one-quarter
16. What is the PIV for each diode in a full-wave center- tapped rectifier? Note: Vp(out) = peak output voltage.
A. Vp(out) – 0.7 V
B. Vp(out) + 0.7 V
C. 2Vp(out) – 0.7 V
D. 2Vp(out) + 0.7 V
17. In the operation of a half-wave rectifier with a capacitor-input filter, the ripple factor can be lowered by _____ the value of the filter capacitor or _____ the load resistors.
A. decreasing, decreasing
B. decreasing, increasing
C. increasing, decreasing
D. increasing, increasing
18. The maximum rectification efficiency in case of full wave rectifier is
A. 100%
B. 81.2%
C. 66.6%
D. 40.6%
Use this statement to answer the next 5 questions. A power supply using a half wave rectifier has a turns ratio of 2:1, the primary voltage is 170Vp.
- Determine the Vp(sec).
A. 340V
B. 240V
C. 60V
D. 85V
20. Find the Vp(out).
A. 0.7 V
B. 1.4 V
C. 84.3 V
D. 170 V
21. Find the minimum PRV.
A. 170 V
B. 85 V
C. 60 V
D. 340 V
22. Find the average output voltage.
A. 26.81 V
B. 53.61 V
C. 61.53 V
D. 42.15 V
23. Find the rms output voltage.
A. 26.81 V
B. 53.61 V
C. 61.53 V
D. 42.15 V
Use this statement to answer the next 6 questions. A power supply using a full wave rectifier has a turns ratio of 2:1, the primary voltage is 100Vp and the secondary is center tapped.
- Determine the Vp(sec).
A. 100 V
B. 200 V
C. 50 V
D. 25 V
25. Determine the Vp across each half of the secondary with respect to ground.
A. 100 V
B. 200 V
C. 50 V
D. 25 V
26. Find the Vp(out).
A. 24.3 V
B. 1.4 V
C. 84.3 V
D. 23.6 V
27. Find the minimum PIV.
A. 100 V
B. 200 V
C. 49.3 V
D. 24.3 V
28. Find the average output voltage.
A. 11.81 V
B. 19.61 V
C. 15.45 V
D. 17.18 V
29. Find the rms output voltage.
A. 11.81 V
B. 19.61 V
C. 15.45 V
D. 17.18 V
Use this statement to answer the next 5 questions. A bridge rectifier has and rms secondary output of 12V.
- Find the Vp(sec).
A. 12 V
B. 16.97 V
C. 15.57 V
D. 120 V
31. Find the Vp(out).
A. 12 V
B. 16.97 V
C. 15.57 V
D. 16.27 V
32. Find the minimum PIV.
A. 12 V
B. 16.97 V
C. 15.57 V
D. 16.27 V
33. Find the average output voltage.
A. 11 V
B. 6.5 V
C. 4.95 V
D. 9.9 V
34. Find the rms output voltage.
A. 11 V
B. 6.5 V
C. 4.95 V
D. 9.9 V
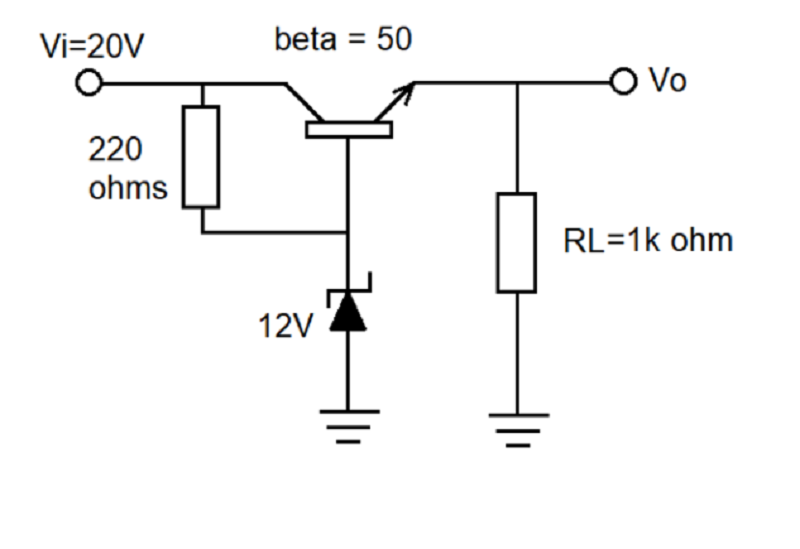
Use the figure below to answer the next 8 questions.
- Determine the circuit.
A. amplifier
B. filter
C. rectifier
D. regulator
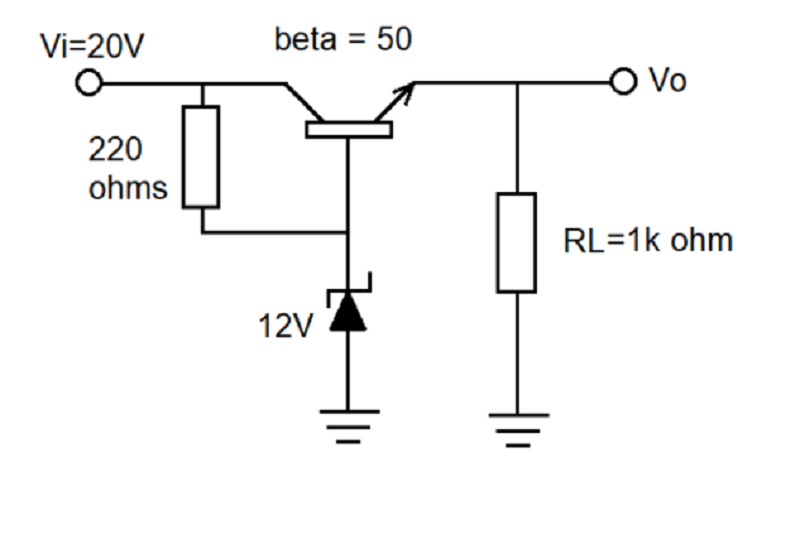
36. Determine the type of voltage regulator.
A. shunt
B. parallel
C. series
D. series-shunt
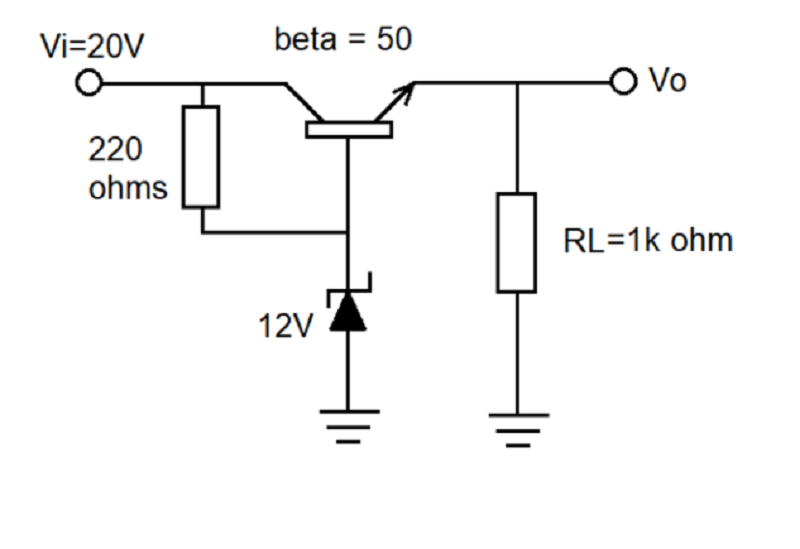
37. Solve for the output voltage.
A. 11.3 V
B. 12 V
C. 20 V
D. 8.7 V
38. Determine the VCE.
A. 11.3 V
B. 12 V
C. 20 V
D. 8.7 V
39. Determine the I at 220Ω.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 36.36 mA
C. 47 mA
D. 7.43 mA
40. Determine the IL.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 36 mA
C. 47 mA
D. 226 mA
41. Determine IB.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 36.13 mA
C. 47 mA
D. 226 uA
42. Determine IZ.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 36.13 mA
C. 47 mA
D. 226 mA
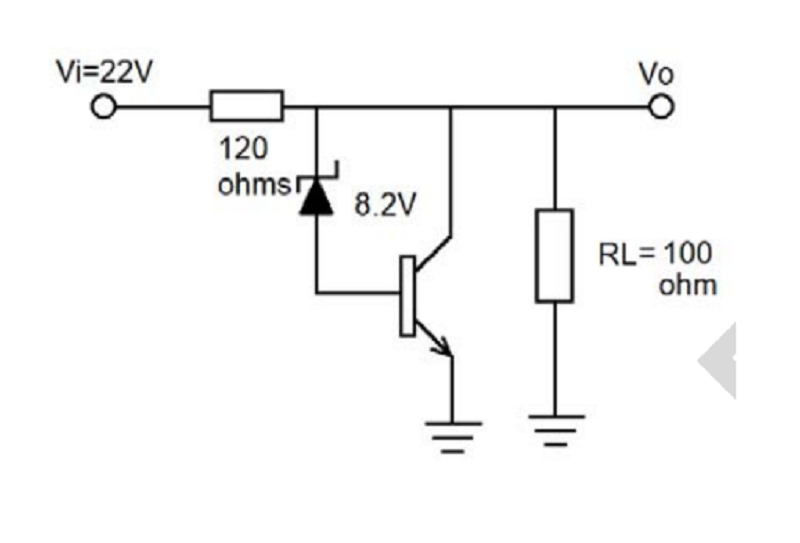
Use the figure below to answer the next 6 questions.
- Determine the circuit.
A. amplifier
B. filter
C. rectifier
D. regulator
44. Determine the type of voltage regulator.
A. shunt
B. parallel
C. series
D. series-shunt
45. Solve for the output voltage.
A. 13.1 V
B. 12.67 V
C. 21.5 V
D. 8.9 V
46. Determine the IL.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 20 mA
C. 89 mA
D. 109 mA
47. Determine the IS.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 20 mA
C. 89 mA
D. 109 mA
48. Determine the IC.
A. 11.3 mA
B. 20 mA
C. 89 mA
D. 109 mA
Use the statement below to answer the next 8 questions.A shunt-wound DC machine is running at “n” rev/s and has a shaft torque of “T” Nm. The supply current is “I” A when connected to DC bus-bars of voltage “V” volts. The armature resistance of the machine is “Ra” ohms, the armature current is “Ia” A and the generated voltage is “E” volts.
49. The input power when running as a generator
A. VI
B. E – IaRa
C. T(2πn)
D. V + IaRa
50. The output power when running as a motor
A. VI
B. E – IaRa
C. T(2πn)
D. V + IaRa
51. The input power when running as a motor
A. VI
B. E – IaRa
C. T(2πn)
D. V + IaRa
52. The output power when running as a generator
A. VI
B. E – IaRa
C. T(2πn)
D. V + IaRa
53. The generated voltage when running as a motor
A. V – IaRa
B. E + IaRa
C. VI
D. E – IaRa
54. The terminal voltage when running as a generator
A. V – IaRa
B. E + IaRa
C. VI
D. E – IaRa
55. The generated voltage when running as a generator
A. VI
B. E – IaRa
C. T(2πn)
D. V + IaRa
56. The terminal voltage when running as a motor
A. V – IaRa
B. E + IaRa
C. VI
D. E – IaRa
57. A four-pole generator having wave-wound armature winding has 51 slots, each slot containing 20 conductors. What will be the voltage generated in the machine when driven at 1500 rpm assuming the flux per pole to be 7.0 mWb?
A. 537 V
B. 735 V
C. 357 V
D. 223 V
58. Which of the following statements is false?
A. A DC motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
B. The efficiency of a DC motor is the ratio input power to output power
C. A DC generator converts mechanical power to electrical power
D. The efficiency of a DC generator is the ratio output power to input power
59. Which of the following statements is false?
A. A commutator is necessary as part of a DC motor to keep the armature rotating in the same direction
B. A commutator is necessary as part of a DC generator to produce unidirectional voltage at the terminals of the generator
C. The field winding of a DC machine is housed in slots on the armature
C. The field winding of a DC machine is housed in slots on the armature
60. If the speed of a DC machine is doubled and the flux remains constant, the generated emf.
A. Remains the same
B. Is doubled
C. Is halved
D. It cannot be determined
61. If the flux per pole of a shunt-wound DC generator is increased, and all other variables are kept the same, the speed
A. decreases
B. Stays the same
C. increases
D. It cannot be determined
62. If the flux per pole of a shunt-wound DC generator is halved, the generated emf at constant speed
A. Is doubled
B. Is halved
C. Remains the same
D. It cannot be determined
63. In a series-wound generator running at constant speed, as the load current increases, the terminal voltage
A. increases
B. decreases
C. Stays the same
D. It cannot be determined
64. Which of the following statements is false for a series-wound DC motor?
A. The speed decreases with increase of resistance in the armature circuit
B. The speed increases as the flux decreases
C. The speed can be controlled by a diverter
D. The speed can be controlled by a shunt field regulator
65. Which of the following statements is false?
A. A series-wound motor has a large starting torque
B. A shunt-wound motor must be permanently connected to its load
C. The speed of a series-wound motor drops considerably when load is applied
D. A shunt-wound motor is essentially a constant- speed machine
66. The speed of a DC motor may be increased by
A. Increasing the armature current
B. Decreasing the field current
C. Decreasing the applied voltage
D. Increasing the field current
67. The armature resistance of a DC motor is 0.5Ω, the supply voltage is 200V and the back emf is 196V at full speed. The armature current is:
A. 4A
B. 8A
C. 400A
D. 392A
68. In DC generators iron losses are made up of:
A. Hysteresis and friction losses
B. hysteresis, eddy current and brush contact losses
C. Hysteresis and eddy current losses
D. hysteresis, eddy current and copper losses
69. The effect of inserting a resistance in series with the field winding of a shunt motor is to:
A. Increase the magnetic field
B. Increase the speed of the motor
C. Decrease the armature current
D. Reduce the speed of the motor
70. The supply voltage to a DC motor is 240V. If the back emf is 230V and the armature resistance is 0.25Ω, the armature current is:
A. 10A
B. 40A
C. 960A
D. 920A
71. With a d.c. motor, the starter resistor:
A. Limits the armature current to a safe starting value
B. Controls the speed of the machine
C. Prevents the field current flowing through and damaging the armature
D. Limits the field current to a safe starting value
72. Which of the following cells is not a primary cell?
A. Carbon-zinc
B. Alkaline
C. Zinc-chloride
D. Lead-acid
73. The dc output voltage of a C-size alkaline cell is
A. 1.2 V
B. 1.5 V
C. 2.1 V
D. about 3 V
74. Which of the following cells is a secondary cell?
A. Silver-oxide
B. Lead-acid
C. Nickel-Cadmium
D. Both b and c
75. What happens to the internal resistance, ri, of a voltaic cell as the cell deteriorates?
A. It increases
B. It decreases
C. It stays the same
D. It usually disappears
76. The dc output voltage of a lead-acid cell is
A. 1.35 V
B. 1.5 V
C. 2.1 V
D. about 12 V
77. Cells are connected in series to
A. Increase the current capacity
B. Increase the voltage output
C. Decrease the voltage output
D. Decrease the internal resistance
78. Cells are connected in parallel to
A. Increase the current capacity
B. Increase the voltage output
C. Decrease the voltage output
D. Decrease the current capacity
79. Five D-size alkaline cells in series have a combined voltage of
A. 1.5 V
B. 5.0 V
C. 7.5 V
D. 11.0 V
80. The main difference between a primary cell is that
A. A primary cell can be recharged and a secondary cell cannot
B. A secondary cell can be recharged and a primary call cannot
C. A primary cell has an unlimited shelf life and a secondary cell does not
D. Primary cells produce dc voltage and secondary cells produce ac voltage
81. A constant-voltage source
A. Has very high internal resistance
B. Supplies constant-current to any load resistance
C. Has a very low internal resistance
D. None of the above
82. A constant-current source
A. Has very low internal resistance
B. Supplies constant current to a wide range of load resistances
C. Has very high internal resistance
D. Both b and c
83. The output voltage of a battery drops from 6.0 V with no load to 5.4 V with a load current of 50 mA. How much is the internal resistance, ri ?
A. 12 Ω
B. 108 Ω
C. 120 Ω
D. This is impossible to determine
84. Maximum power is transferred from a generator to load when
A. RL = ri
B. RL is maximum
C. RL is minimum
D. RL is 10 or more times the value of ri
85. What is the efficiency of power transfer for the matched load condition?
A. 100%
B. 0%
C. 50%
D. This is impossible to determine
86. The internal resistance of a battery
A. Cannot be measured with an ohmmeter
B. Can be measured with an ohmmeter
C. Can be measured indirectly by determining how much the output voltage drops for a given load current
D. Both a and c
{"name":"Energy Conversion", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. What is the dc output voltage of an unfiltered half- wave rectifier whose peak output voltage is 9.8 V?, 2. What is the frequency of the capacitor ripple voltage in a full wave rectifier circuit if the frequency of the transformer secondary voltage is 60 Hz?, 3. In a full-wave rectifier, the dc load current equals 1 A. How much dc current is carried by each diode?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/98-4823138/1231.png?sz=1200"}