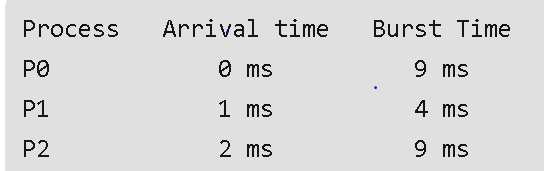Operating Systems Quiz CTS Students CLub
{"name":"Operating Systems Quiz CTS Students CLub", "url":"https://www.supersurvey.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of operating systems with our engaging quiz designed specifically for CTS students! Dive into 16 challenging questions that cover a range of topics, including deadlock prevention, scheduling algorithms, and memory management.Participate now to see how well you understand the complexities of operating systems:Multiple choice questionsFocus on key OS conceptsPerfect for students and enthusiasts","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Surveys
Entity Relationship Lecture
10539
Quiz Poll, Lecture 1
8471
Programming Background Knowledge
6318
9-Basic Programming
331624
Tech-Cult : The CSEian's Club
4255
Subject Preferences
3231
Computer Science
6350
Is extra python training needed/wanted?
6319
Mivane
8418
Video Game Development Club Team Interests After Workshops
9417
Using flashcards in studying vocabularies in reading skill
9418
What does each letter stand for that can help you remember its use? E.g. A for Aliens
943