BU2-Fire alarms-Ohm's law-wires

Fire Alarm Systems Knowledge Quiz
Test your knowledge on fire alarm systems with this comprehensive quiz! Challenge yourself with 25 questions that cover various aspects including components, types of systems, and relevant terminology.
Topics include:
- Fire Alarm Control Panels
- Alarm-initiating Devices
- Supervised and Non-supervised Systems
- Notification Methods
A system consisting of components and circuits arranged to monitor and annunciate the status of fire alarm or supervisory signal-initiating devices and to initiate the appropriate response to those signals.
The “brain” of any fire detection and alarms system is referred to as the
Control unit
Heat sensor
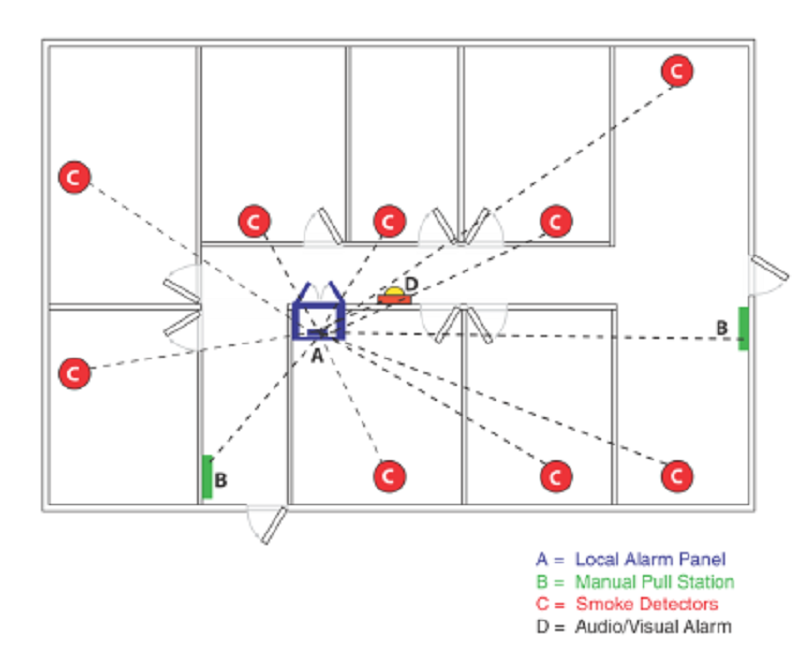
Sound an alarm only in the protected premises. Manually or automatically. For privately owned facilities. When building is unoccupied, notification to the fire dept. Is incidental
Protected Premises (Local) systems
Propriety fire alarm system
Remote-station protective signaling system
Supervising Station (Off- premises) systems
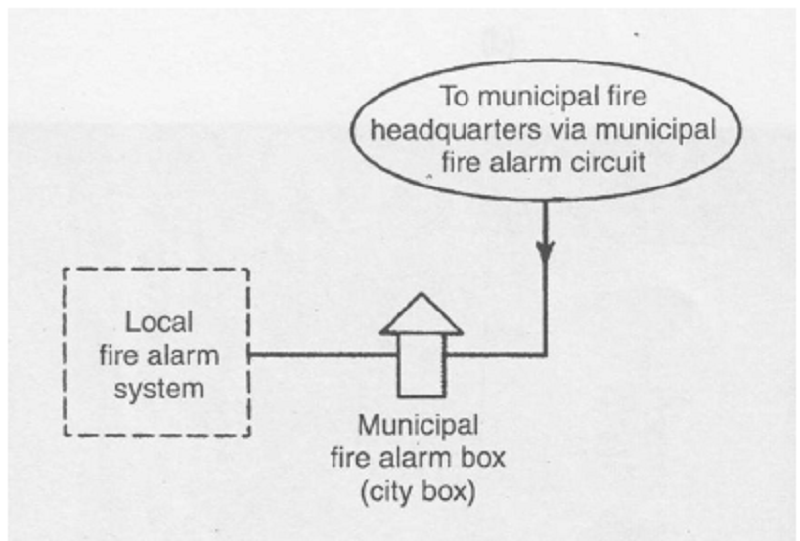
Receives signals from a protected premises fire alarm system.signal is processed by personnel. Direct connection to a municipal/city fire alarm box. Applied to public buildings, such as schools, government offices, museums and the like.
Supervising Station (Off- premises) systems
Remote-station protective signaling system
Central station fire alarm system
Protected Premises (Local) systems
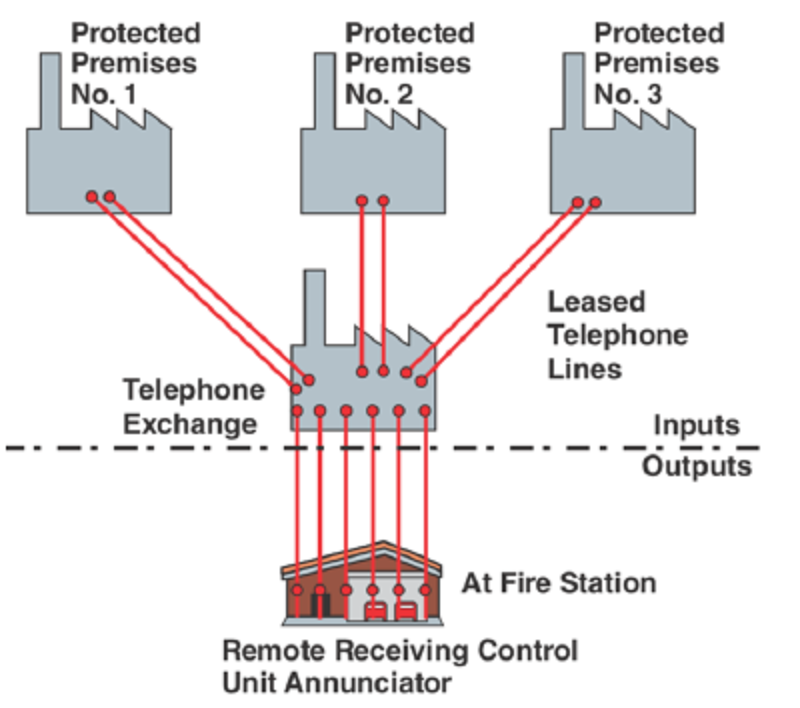
Used in unoccupied private bldgs. for PERIODS. Alarm is transmitted through a leased telephone line to a remote location that is manned 24/7 at the fire dept.
Propriety fire alarm system
Remote-station protective signaling system
Supervising Station (Off- premises) systems
Central station fire alarm system
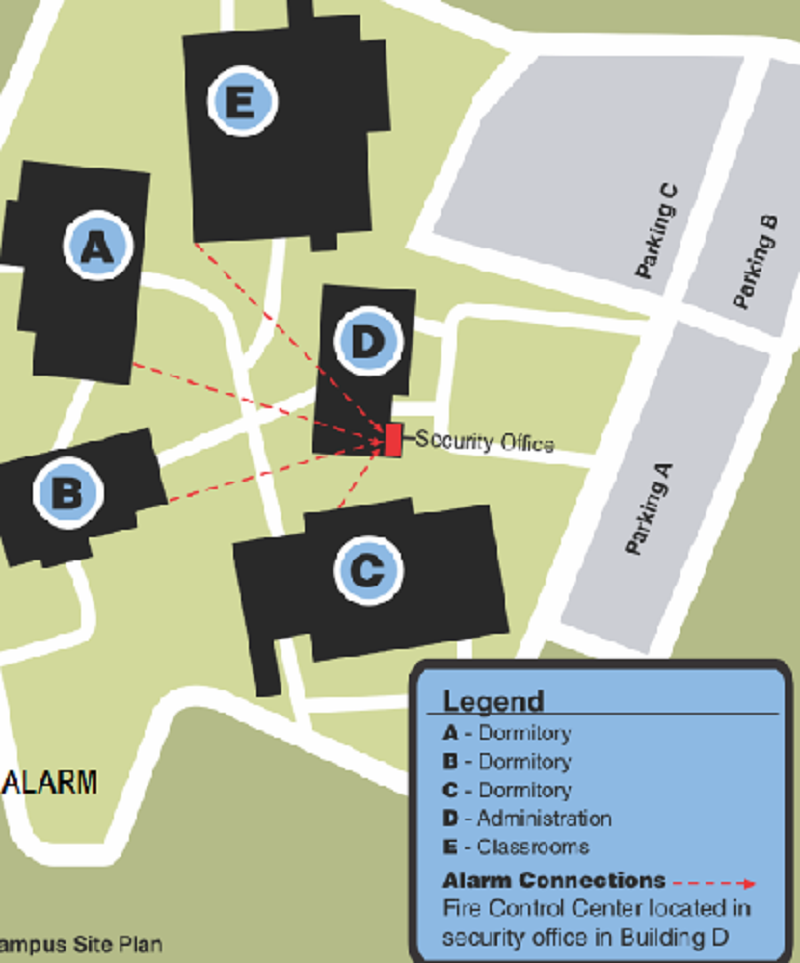
Central supervisory station that's on the site where it receive signals from all bldgs. Used in very large multi-bldgs. (universities, manufacturing facilities) site is locatedin a guard house where alarms will be sent manually to a fire dept.
Propriety fire alarm system
Central station fire alarm system
Remote-station protective signaling system
Supervising Station (Off- premises) systems

its equipment are owned and operated by a service company.supervises many individual unrelated local systems w/ fee. Receive all signals from individual users. Supervise access control, intrusion alarms, and related systems
Central station fire alarm system
Propriety fire alarm system
Remote-station protective signaling system
Supervising Station (Off- premises) systems
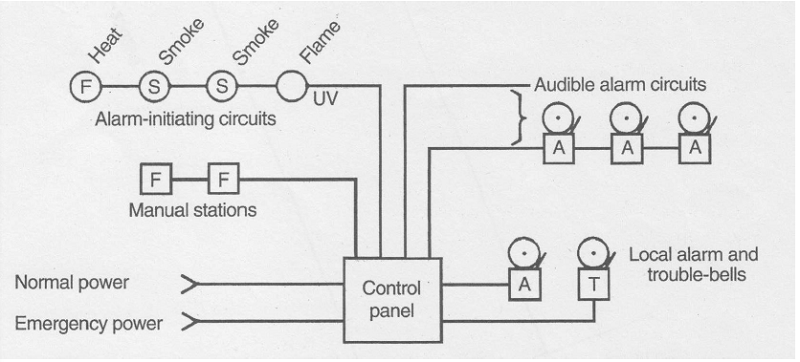
When alarm signal is received there is no way of knowing which of the devices alarmed and whether the signal represents an actual fire condition or caused by malfunction of a detector. Simplest and the oldest system. Require continual maintenance and field sensitivity checks. These regular checkups are rather an expensive and time-consuming procedure.
CONVENTIONAL SYSTEMS
Addressable/ non-addressable system
Manual/ automatic system
Coded / non-coded
Each fire detection or signaling device is assigned a unique coded frequency. Useful for a tenant-occupied building. Offers speed detection. Only zone can be identified
Addressable
Non-addressable system
Manual/ automatic system
Coded / non-coded
Includes a fire alarm control panel (FACP). Tend to be economical
Addressable
Non-addressable system
Automatic system
Manual
For building use groups that involve the public and for residential buildings over three stories in height. Thisdevice is mandatory. Signals are initiated by automatic detection devices, as well as from manual alarm stations
Manual
Automatic system
Non-addressable system
Addressable
Placed in the normal path of egress from a building so that an alarm may be turned in by a person as he/she exits. It is easily found
Manual
Automatic system
Non-coded
Addressable
A fire alarm system may provide the alarm signal continuously until the system is manually shut off.
Coded
Non-coded
Manual
Automatic system
Designed to produce four rounds of signals. If the signal is intermittent in duration or frequency, then the system is said to be
Coded
Non-coded
Automatic system
Non-addressable system
The signal notifies the building management of the problem until it is fixed. Minimally, an open circuit or a ground in any of the devices will cause a trouble signal.
Supervised
Non-supervised
Coded
Non-coded
System, accidental grounding or breaking of the wiring or contacts will unknowingly disable the system until the problem is discovered.
Supervised
Non-supervised
Manual
Coded
May divide the alarms into two or more zones according to the locations of the alarm devices. All alarms are activated at once
Single/zoned system
Pre-signal system/General alarm
Pre-signal system/General alarm
Single/ 2-stage system
All alarms within each zone will be activated to signal that the building should be evacuated.
Single-stage
Two-stage system
Zoned system
Single-zoned system
May provide a preliminary warning or alert to the occupants during the first stage and a signal to evacuate the building only when the second stage is energized.
Single-stage
Two-stage system
Single-zoned system
Zoned system
With this system, detection devices or manual alarm stations will send the signal only to limited locations so that management can determine whether and when a general alarm is to be activated. This is prohibited in the hospitals unless approved by code officials.
Pre-signal system/General alarm
Single/zoned system
Stand-alone or integrated system
Single-stage/two-stage system
The primary disadvantages are the complexity of the system and the mutual dependence among its components.
Stand-alone or integrated system
Pre-signal system/General alarm
Single/zoned system
Single or two-stage system
O Modern fire-signaling systems can also include public-address systems to provide instructions to the occupants by the building management, and in later stages, by the fire department. o The public address system may also be supplemented by twoway communication devices, such as telephones, intercoms, radio frequency modules, etc. o Speakers may be used to generate a tone in lieu of bells or horns. Required in all high-rise buildings and public assembly use groups.
Voice communication system
Single/zoned system
Single or two-stage system
Stand-alone or integrated system
Most basic alarm-initiating device in the system and does not include detection. Placed within reach. Coded or non-coded pull stations. Single-action and double-action pull stations, coded/non-coded
MANUAL ALARM-INITIATING DEVICES
AUTOMATIC ALARMINITIATING DEVICES
Commonly called detectors,
AUTOMATIC ALARMINITIATING DEVICES
MANUAL ALARM-INITIATING DEVICES
VISUAL ANNUNCIATION DEVICES
Consist of single or multiple lights with marked messages.used in places of public assembly, such as theaters, auditoriums, sports arenas, airplanes, schools, etc. − Intended for hearing-impaired persons
VISUAL ANNUNCIATION DEVICES
AUTOMATIC ALARMINITIATING DEVICES
MANUAL ALARM-INITIATING DEVICES
{"name":"BU2-Fire alarms-Ohm's law-wires", "url":"https://www.supersurvey.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on fire alarm systems with this comprehensive quiz! Challenge yourself with 25 questions that cover various aspects including components, types of systems, and relevant terminology.Topics include:Fire Alarm Control PanelsAlarm-initiating DevicesSupervised and Non-supervised SystemsNotification Methods","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}