Strategy Quiz- CSCA (Certified in Strategy & Competitive Analysis) - All Sections

Strategy determines
The direction and scope of an organization over the long term
How resources should be configured to meet the needs of markets and stakeholders
Organizational resources, skills, and competencies should be combined to create competitive advantage
All Options

A corporate strategy establishes the big picture. Each business unit within the organization then has a business unit strategy, which its leaders use to determine how they will compete in their individual markets.
True
False

Individual teams should not have its own strategy tied to day-to-day activities help move the organization in the right direction.
True
False

At the corporate level, which are not examples of how can strategy be supported?
Sharing technologies and resources between business units
Raising capital cost-effectively
Developing and nurturing a strong corporate brand
Developing a new product
Identify new customers

What type of strategy would be described by the following approach? Good research, development and innovation. The ability to deliver high-quality products or services. Effective sales and marketing, so that the market understands the benefits offered by the differentiated offerings.
Differentiation
Focus
Cost Leadership
Generic

Strategy at the ____________ level is concerned with competing successfully in individual markets, and it addresses the question, "How do we win in this market?" However, this strategy needs to be linked to the objectives identified in the corporate level strategy.
Business unit
Funtional
Board
Executive

For smaller businesses, corporate and business unit strategy may overlap or be the same thing. However, if an organization is competing in different markets, then each business unit needs to think about its own strategic direction.
True
False

Mission, vision and values help people working within each unit should be able to draw direct links between this strategy and the work that they're doing.
True
False

Apple, Harley-Davidson, Nespresso, LEGO, Nike and Starbucks follow which strategy?
Differentiation
Cost Leadership
Focus

Southwest Airlines, Wal-Mart, McDonald’s, EasyJet, Costco and Amazon follow which strataegy?
Differentiation
Cost Leadership
Focus

Rolls Royce, Omega, Prada and Razer follow which strategy?
Differentiation focus
Cost focus
Cost Leadership
Differentiation

Claire’s, Home Depot and Smart follow which strategy?
Differentiation focus
Cost focus
Cost Leadership
Differentiation

The fundamental goal of a company is
Superior long-term return on invested capital (ROIC)
A record high stock price
Employee engagement
Profitability

Business-level strategy defines what set of businesses to compete in, while business unit strategy describes how to compete in each distinct business or industry.
True
False

Which statement is false?
In diversified companies, corporate leaders can enhance competitive advantage by capturing synergies across business units within the corporate portfolio.
Competitive advantage is won or lost at the business unit level. To achieve competitive advantage, companies must position themselves strategically within their industries.
The terms “business unit strategy,” “business strategy” and “competitive strategy” are often used interchangeably in Porter's work.
The fundamental goal of a company is superior short-term return on invested capital (ROIC)
Profitability
Market share
Business growth
Brand equity
Level of differentiation
Firm resources
Efficiency and effectiveness of internal linkages
Customer loyalty
Syngergy
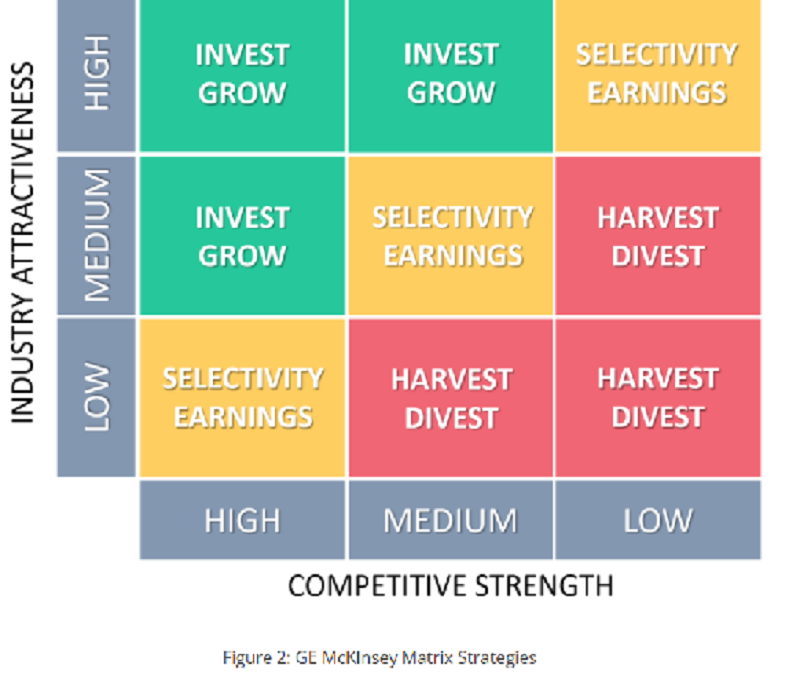
The GE McKinsey Matrix is a good alternative for the BCG Matrix and has the advantage that the two variables used consist of multiple factors combined.
True
False
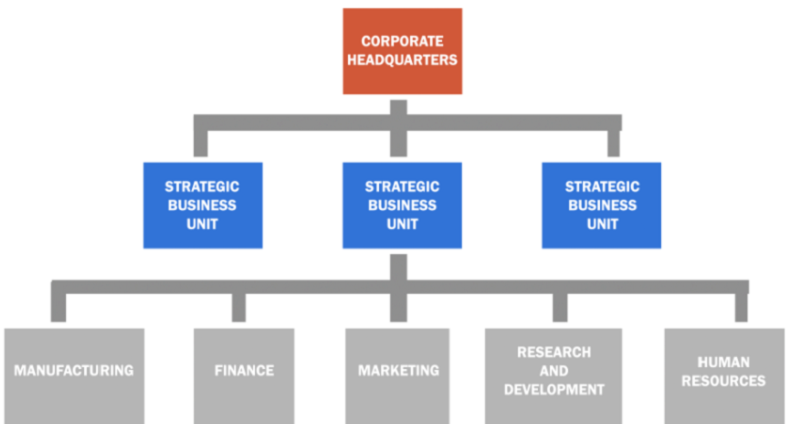
Which level of strategy is indicated by the grey squares?
Functional-level strategy
Corporate-level strategy
Business-level strategy
Board-level strategy
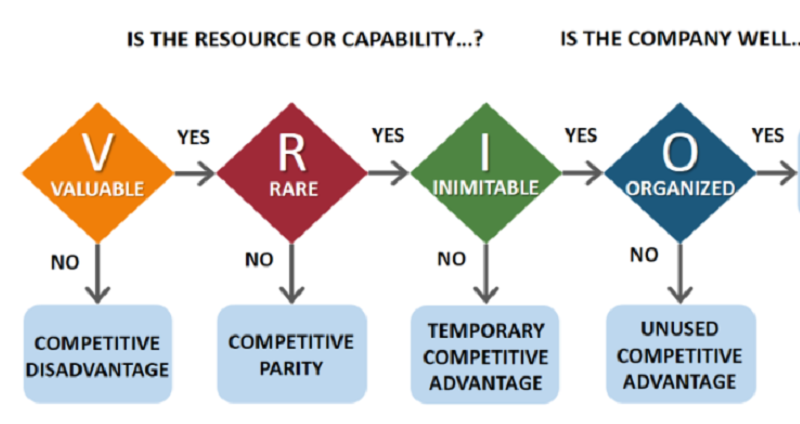
The VRIO framework leads to
Sustained competitive advantage
Higher short-term profitability
Synergies
Executive bonuses
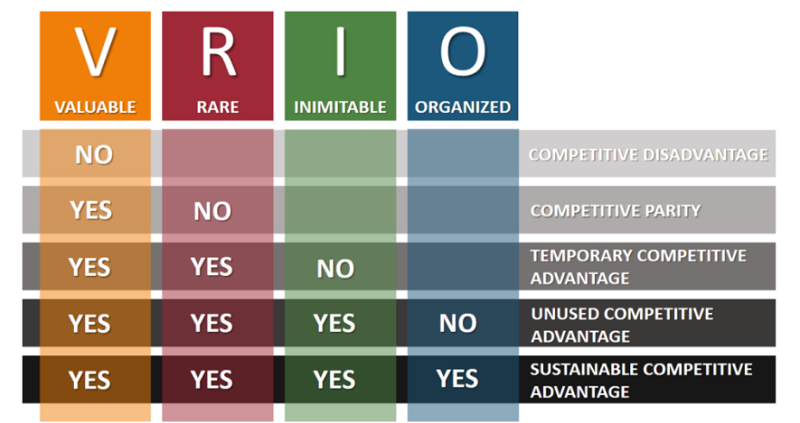
Even without the correct organization to acquire, use and monitor the resources involved, companies with valuable, rare and imperfectly imitable resources will be able to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
True
False
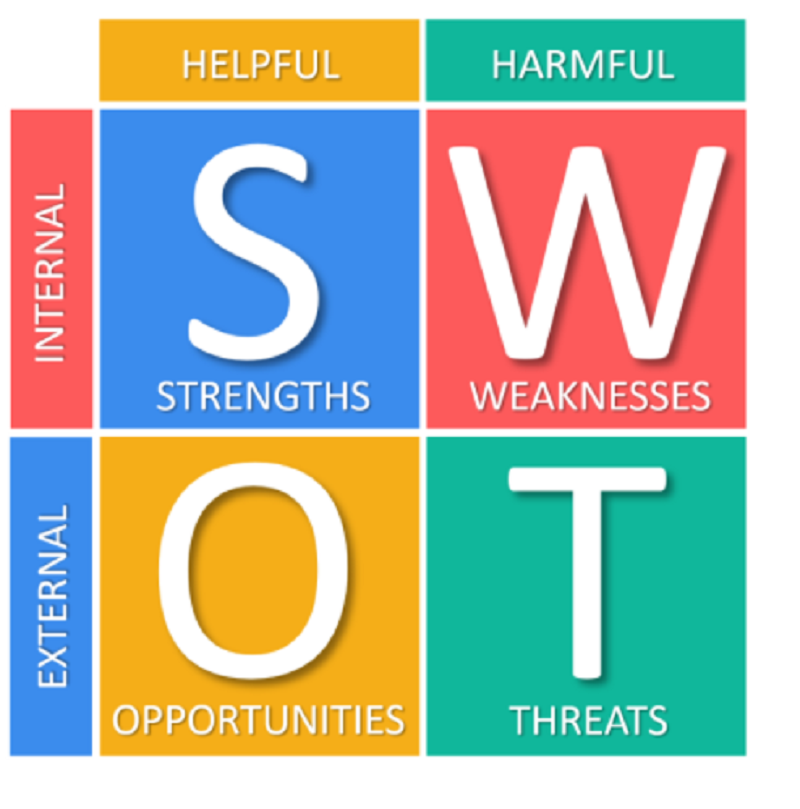
Both internal and external factors will have to be taken into account of course to improve a company’s chances for success.
True
False
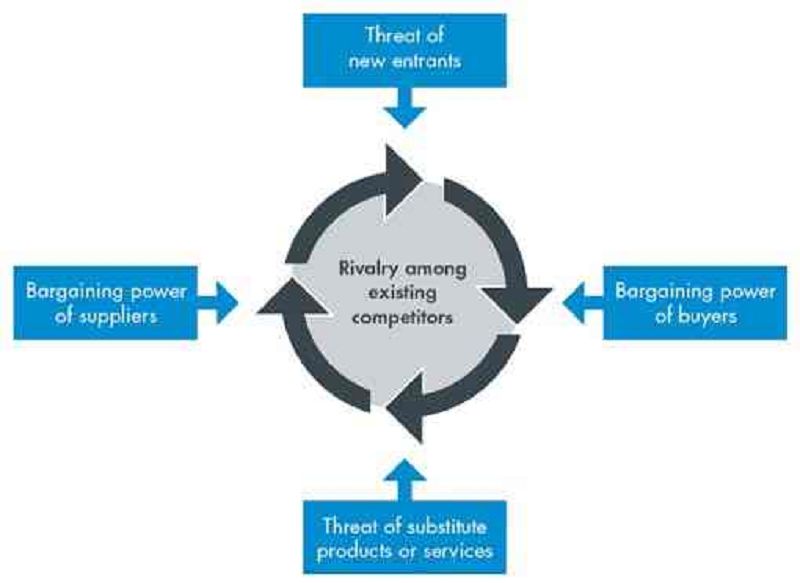
The number of customers,size of each customer order, differences between competitors, price sensitivity, buyer's ability to substitute, buyer's information availability, and switching costs influence which factor?
Rivalry among existing competitors
Threat of new entrants (potential competitors)
Threat of substitute products (alternatives)
Bargaining power of suppliers
Bargaining power of buyers

What does the following statement describe? Company A and Company B combine their respective resources, capabilities, and core competencies to generate mutual interests in designing, manufacturing, or distributing goods or services.
Strategic competition
Strategic alliances
Synergies
Corporate dissodance

Which option is false? Strategic alliances create value by
Improving current operations
Changing the competitive environment
Ease of entry and exit
Borrowing ideas from peer R&D

How do strategic alliances not improve operations?
Economies of scale from successful strategic alliances
The ability to learn from the other partner(s)
Risk and cost being shared between partner(s)
Lower accountability leads to lower risk

Strategic alliances may face which challenge(s)
Partners may misrepresent what they bring to the table (lie about competencies that they do not have).
Partners may fail to commit resources and capabilities to the other partners.
One partner may commit heavily to the alliance while the other partner does not.
Partners may fail to use their complementary resources effectively.
All choices are correct

To maximize the value of the entire firm, leaders must determine how to allocate these resources to the various businesses or business units to make the whole greater than the sum of the parts. Key factors related to the allocation of resources are:
Identifying core competencies and ensuring they are well distributed across the firm
Moving leaders to the places they are needed most and add the most value (changes over time, based on priorities)
Ensuring an appropriate supply of talent is available to all businesses
Allocating capital across businesses so it earns the highest risk-adjusted return
Analyzing external opportunities (mergers and acquisitions) and allocating capital between internal (projects) and external opportunities
Determining how much autonomy to give business units
Determining the extent of vertical integration the firm should have

Portfolio management looks at the way business units complement each other, their correlations, and decides where the firm will “play” (i.e. What businesses it will or won’t enter). Corporate Strategy related to portfolio management includes:
Deciding what business to be in or to be out of
Determining the extent of vertical integration the firm should have
Managing risk through diversification and reducing the correlation of results across businesses
Creating strategic options by seeding new opportunities that could be heavily invested in if appropriate
Monitoring the competitive landscape and ensuring the portfolio is well balanced relative to trends in the market
Developing centers of excellence
Setting governance structures

Barriers to international trade,Changes in government regulation, Tax policy, Employment laws, Country-specific political risk relate to _________?
Political Factors
Economic Factors
Socio-Demographic (Social) Factors
Technological Factors
Research & development (R&D) investment, Scientific advances, emerging technologies, Diffusion of technologies relate to __________ ?
Political Factors
Economic Factors
Socio-Demographic (Social) Factors
Technological Factors
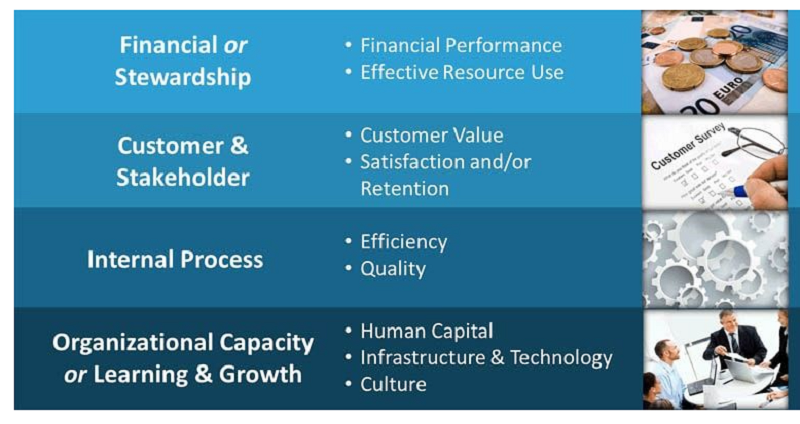
The BSC suggests that we examine an organization from four different perspectives to help develop objectives, measures (KPIs), targets, and initiatives relative to those views.
Financial (or Stewardship): | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Financial (or Stewardship): | Customer/Stakeholder: | Internal Process: | Organizational Capacity (or Learning & Growth): | |
Views an organization’s financial performance and the use of financial resources | ||||
Views organizational performance from the perspective of the customer or key stakeholders the organization is designed to serve | ||||
Views the quality and efficiency of an organization’s performance related to the product, services, or other key business processes | ||||
Views human capital, infrastructure, technology, culture, and other capacities that are key to breakthrough performance | ||||

____________ strategy focuses the entire organization on strategy and creating line-of-sight between the work people do and high level desired results
Cascading
Business
Synergistic
Profit

The ________ is a strategic planning and management system. Organizations use ________ to:
- Communicate what they are trying to accomplish
- Align the day-to-day work that everyone is doing with strategy
- Prioritize projects, products, and services
- Measure and monitor progress towards strategic targets
Balanced Scorecard
Business Stock Conference
Business KPI Index
Business Scorecard
A plan of action used by an organization is called
Strategy
Management
Report
Summary

Strategic alliances allow a company to rapidly extend its strategic advantage and generally require less commitment than other forms of expansion. A key motivator is sharing resources or activities, although there may be less obvious reasons as well. There are four types of alliance: scale, access, complementary, and collusive.
Scale alliances | Access alliances | Complementary alliances | Collusive alliances | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Involve companies combining to achieve necessary scale. The capabilities of each partner may be quite similar, but together they can achieve advantages that they could not easily achieve on their own. Thus, combining together can provide economies of scale in the production of outputs (products or services). Combining might also provide economies of scale in terms of inputs—for example by reducing purchasing costs of raw materials or services. | ||||
Involve a company allying in order to access the capabilities of another company that are required to produce or sell its own products and services. For example, in countries such as Mexico a Western company might need to partner with a local distributor to access effectively the national market for its products and services. The local company is critical to the international company’s ability to sell. Access alliances can also work in the opposite direction, with a local company seeking a licensing alliance to access inputs from an international company—for example technologies or brands. | ||||
Involve companies at similar points in the value network combining their distinctive but complementary resources so that each partner is bolstered where it has particular gaps or weaknesses. The Renault-Nissan Alliance is a great example of two companies combining their strenghts to overcome their individual weaknesses. | ||||
Involve companies colluding secretly to increase their market power. By combining into cartels, they reduce competition in the marketplace, enabling them to extract higher prices from customers or lower prices from suppliers. Such collusive cartels among for-profit businesses are discouraged by regulators. For instance, mobile phone and energy companies are often accused of collusive behavior. |

Strategy involves creating a
Model
Approach
Both
None

Objectives are the_____________ milestones?
Measurable
Qualitative
Quantifiable
All

Objectives make strategy
Actionable
Clear
Complex
Powerful
Plans
Initiatives
Strategy
Goals

_____________ are generally stated long-term aims?
Objectives
Purpose
Goals
All

The strategic plan is comprised of _________goals and objectives?
Short-term
Long-term
Permanent
Temporary

The ongoing sustainability of the organization, however, requires it to focus on _____________long-term goals?
Financial
Non-financial
Both
None

The strategic management and strategic planning process generate
Recommendations
Profits
Unncessary work
Referals

Nonprofit organizations compete for
Profit
Fame
Member Subscriptions
Owner Benefits

Effective implementation of a plan involves _________________support?
Leadership
Business
Consultant
Middle management

The challenge of developing or reestablishing a clear strategy is often primarily an organizational one and depends on ___________________?
Goals
Aims
Leadership
Competitors

The purpose of ___________ is to exploit and create new and different opportunities for the future?
Strategic Goals
Strategic Implementations
Strategic Management
Strategic Planning

Strategic planning can be thought of as the _______________?
Scientific Plan
Game Plan
Business Plan
Management Plan

Strategies are usually for a time span of ______________?
2 to 3 years
3 to 5 years
4 to 5 years
1 to 2 years

Strategic implementation is a term used to describe the ___________ within an organization?
Activities
Methods
Techniques
Rules

During the implementation process, a trusted, visible leader such as the __________will communicate the organization’s vision with passion?
HOD
CEO
CFO
COO

Sharing the plan of action is also known as a ____________________?
Strategy Plan
Strategy Map
Strategy Action
Strategy Protocol

Strategic plans are subject to future modifications because ______________factors are constantly changing?
Internal
External
Internal and External
Competitive
Market
Competitive and Market

Strategic ______________is a process for assessing an organization’s programs, projects, and activities.
Evaluation
Implementatio
Assumption
Planning

CSF stands for________________?
Complex Success Factors
Complete Success Factors
Critical Success Factors
Clear Success Factors

KPI means____________________?
Key Performance Identifier
Key Power Indicators
Kaleen Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators

Once a strategy has been implemented, its ________must be managed?
Implementation
Execution
Employees
Consultants

Large vs. Small companies also differ in their approach to ___________?
Strategic Mapping
Strategy Protocols
Strategic Planning
Strategic Methods

The size of an organization is very relevant to organizational ______________?
Strategy
Structure
Compensation
Strategy & Structure
Moral
Compensation & Morale

Domestic companies can typically have _______predominant strategic plan/plans?
1
2
3
4 or more

The focus of growth plans of domestic companies is to create new ____________?
Clients
Customers
Markets
Business

Nearly _______ of financial professionals work in business as management accountants?
60%
65%
70%
75%

Change the mind-set on your____________, and cultivate the right behaviors.
Team
Customer
CEO
Manager

Nearly ____________of controllers believe that the finance fun
70%
75%
80%
85%

Management accountants are increasingly being asked to provide ___________data?
Operational
Management
Statistical
Economical

To perform an external analysis, an organization must examine its _______________?
Worth
Branding
Competition
Plan

___________analysis, is used to assess the macro environmental factors?
STEEP
STEP
PTEES
TSEEP

STEEP analysis tool has evolved into a more commonly used tool known as _____________analysis.
TESTEP
ESPTES
PESTEL
LETEP

The components of STEEP analysis include ___________ forces?
Sociocultural
Technological
Economic
All

Global warming and climate change, weather, and changes in temperature are___________ factors?
Political
Technological
Ecological
Economic

Changes in the _________environment normally require a firm to reassess the industry?
Macro
Micro
Global
Domestic

Every company should already know what the average ______________of its industry is and how that has been changing over time?
Profitability
Growth
Brand VRIO
Compensation

Porter's ___________forces reveal why industry profitability is what it is?
4
5
6
7

The stronger the ____________________is, the more competition there is in the industry?
Threat Of Entry
Profitability
Growth
Economy

_________________create demand in the industry?
Buyers
Sellers
Marketing Efforts
Value chains

Bargaining power gives ____________________the ability to influence the price of goods or services?
CEOs
Buyers
Suppliers
Managers

_______________products are the products of different companies that can satisfy similar customer needs?
Substitute
Disposable
Incongruous
Redundant

When substitute products are very similar to one another, companies may be forced to charge __________________prices?
Higher
Lower
Flat
All options

The __________________among established companies is a fun
Intensity Of Reason
Intensity Of Competitors
Increment of Rivalry
Intensity Of Rivalry

_______________demand conditions moderate the competition among established companies and create opportunities for expansion?
Strong
Weak
Average
Changing

When demand is________________ intensive competition can develop?
Strong
Weak
Average
All

Rivalry affects the tactical actions of competing firms by driving down ______________?
Margins
Profits
Both
None

There are also competition-related issues that impact an organization and its strategy. Some of the most important include:
Industry life cycle
Industry competitive structure
Segmentation
All

Members of a company’s strategic group constitute its __________________?
Business Team
Immediate Competitors
Executive Board
Compensation Commitee

____________competition structure consists of many sellers producing identical products?
Internal
External
Pure
All

__________competition structure involves many companies selling products that are similar but not perfect substitutes
Monopolistic
Internal
External
Pure

An oligopoly structure is one where a _____________number of sellers control the entire industry but fun
Large
Small
Average
Constant

A Single firm produces a product or a service that has no close substitutes is called__________?
Monopoly
Pure Monopoly
Proprietorship
Pure Proprietorship

________________is defined as the process of subdividing a market into clearly identifiable groups of customers with similar needs, desires, and demand characteristics
Segmentation
Classification
Filtration
Partitioning

Identifying the industry the organization is in and who its competitors are, is called_____________?
Competitor Classification
Competitor Segmentation
Competitor Identification
Competitor Industry

____________is a industry where no single enterprise has large enough market share to be able to influence the industry’s direction?
Fragmented industry
Rich Industry
Independent Industry
Dependent Industry

Factors that lead to a fragmented industry include
Low Market Share
Low Economies Of Scale
Local Brand
All

The primary activity of competitive intelligence is to monitor _________________?
Customers
Rivals
Start-ups
Market conditions
The collection of data points that one can use to understand something is called_______________?
Data Analysi
Information
Reporting
Variance Analysis
All intelligence information must be ______________because using data from unreliable sources can lead to ethics issues?
Checked
Evaluated
Implemented
Validated

The uncertainties and untapped opportunities embedded in your strategy are ________________?
Strategic Risks
Management Risks
Implementation Risks
Business Risks

Market introduction phase is known as__________________?
The Growth phase
The Shakeout phase
The Mature phase
The Embryonic phase

A time of rapid increase in demand is known as______________?
The Growth phase
The Shakeout phase
The Mature phase
The Embryonic phase

_________________is when demand approaches saturation levels ?
The Growth phase
The Shakeout phase
The Mature phase
The Embryonic phase

The process of looking inward at the resources, capabilities, and competencies in order to recognize an organization’s strengths and weaknesses is called_________________?
Internal Analysis
External Analysis
Business Analysis
Market Analysis

_____________are essential internal activities that organizations have mastered ?
Pure competencies
Core competencies
Business competencies
All

Set of activities that an organization can carry out to identify efficiencies to create value for its customers is known as________________?
Value Chain
Customer Chain
Business Chain
Activity Chain
____________include the processes related to receiving and distributing?
Inbound logistics
Outbound logistics
Activity Logistics
Customer Logistics
{"name":"Strategy Quiz- CSCA (Certified in Strategy & Competitive Analysis) - All Sections", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Strategy determines, A corporate strategy establishes the big picture. Each business unit within the organization then has a business unit strategy, which its leaders use to determine how they will compete in their individual markets., Individual teams should not have its own strategy tied to day-to-day activities help move the organization in the right direction.","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/US/72-3288078/photo-1503551723145-6c040742065b-v2.jpg?sz=1200-00000000001000005300"}
More Quizzes
Vocabulary Quiz 3/19/21
10545
Discover Me Quiz
10525
Anatomie quiz 1
30150
Do you have any recommendations in new papers today?
100
Which Hannah Montana Character Are You? Discover Your Match!
201029707
Can You Ace the 2A656 Vol 1 URE Aircraft?
201078459
Advanced Operating Systems
15832709
Free Family Trivia: 15 MCQs
201024236
Is My FWB Catching Feelings? Free to Find Out
201028437
Free on Prime Factorization
201024650
Applied Food Microbiology
15825083
Free Corporate Knowledge
201028437









