RHM 3 ESAT PART 2
Which address could be the beginning address of a block of 32 classless addresses?
A. 2.4.6.5
B. 2.4.6.16
C. 2.4.6.64
D. None of the above
Which address could be the beginning address of a block of 16 classless addresses?
A. 2.4.6.5
B. 2.4.6.15
C. 2.4.6.62
D. None of the above
What is the first address of a block of classless addresses if one of the addresses is 12.2.2.76/27?
A. 12.2.2.0
B. 12.2.2.32
C. 12.2.2.64
D. None of the above
The____ mode provides synchronization for the entire stream of bits must. In other words, it guarantees that the data arrive at a fixed rate.
A. synchronous
B. asynchronous
C. isochronous
D. None of the above
Which of the following is not a type of cable generally used in LANs?
A. Coaxial cable
B. Ribbon cable
C. Twisted pair
D. fiber-optic cable
A ___ digital signal includes timing information in the data being transmitted.
A. self-synchronizing
B. self-modulated
C. self-transmitted
D. None of the above
For an 8-PSK modulator with an input data rate (fb), equal to 10 Mbps and a carrier frequency of 70 MHz, determine the minimum double-sided Nyquist bandwidth (fN) and the baud.
A. 1.11 MHz, 1.11 Mbaud
B. 2.22 MHz, 2.22 Mbaud
C. 3.33 MHz, 3.33 Mbaud
D. 4.44 MHz; 4.44 Mbaud
In decoding a digital signal, the receiver calculates a running average of the received signal power, called the .
A. baseline
B. base
C. line
D. None of the above
One of the oldest and most widely used local-area network is
A. token-ring
B. Ethernet
C. wireless WAN
D. fiber-optic SAN
The______rate defines the number of data elements sent in 1s; the____ rate is the number of signal elements sent in 1s.
A. data; signal
B. signal; data
C. baud; bit
D. None of the above
Determine the baud and minimum bandwidth necessary to pass a 10 kbps binary signal using amplitude shift keying.
A. 500 baud
B. 5,000 baud
C. 10,000 baud
D. 1,000,000 baud
In IPv6_____ address defines single computer.
A. A unicast
B. A multicast
C. An anycast
D. None of the above
In IPv6, _____address defines a group of computers with addresses that have the same prefix.
A. A unicast
B. A multicast
C. An anycast
D. None of the above
In IPv6,____group of computers. Address defines a
A. A unicast
B. A multicast
C. An anycast
D. None of the above
The signal rate is sometimes called the_____rate.
A. baud
B. bit
C. signal
D. None of the above
A network that is connected as a node on a network and performs bi-directional communication between two LANs is a
A. bridge
B. hub
C. switch
D. modem
The data rate is sometimes called the rate.
A. baud
B. bit
C. signal
D. None of the above
A digital communication scheme uses DQPSK to transmit a compressed PCM audio signal which has a bit rate of 16 kb/s. The chipping rate is 10 to 1. Calculate the number of signal changes (symbols) which must be transmitted each second.
A. 60 kbaud
B. 70 kbaud
C. 80 kbaud
D. 90 kbaud
In a ____ scheme, all the signal levels are on one side of the time axis, either above or below.
A. polar
B. bipolar
C. unipolar
D. All of the above
If the bit rate for an FSK signal is 1200 bps, the baud rate is____ .
A. 300
B. 400
C. 600
D. 1200
____conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in the digital data.
A. Digital-to-analog
B. Analog-to-analog
C. Analog-to-digital
D. Digital-to-digital
A frequency-hopping spread-spectrum system hops to each of 100 frequencies every 10 seconds. How long does it spend on each frequency?
A. 0.1 sec/hop
B. 0.01 sec/hop
C. 1000 sec/hop
D. 10 sec/hop
In___, the phase of the carrier is varied to represent two or more different signal elements. Both peak amplitude and frequency remain constant.
A. ASK
B. PSK
C. FSK
D. QAM
Although MANs are primarily fiber-optic networks, a wireless contender for metropolitan-area networking is known as
A. wirelessMAN
B. WiMAN
C. WiMAX
D. WiMIN
A constellation diagram shows us the of a signal element, particularly when we are using two carriers (one in-phase and one quadrature).
A. Amplitude and phase
B. Amplitude and frequency
C. Frequency and phase
D. None of the above
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a combination of____.
A. ASK and FSK
B. ASK and PSK
C. PSK and FSK
D. None of the above
During the busy hour, 1200 calls were offered to a group of trunks and six calls were lost. The average call duration was 3 minutes. Find the traffic offered, the traffic carried, and the traffic lost.
A. 60 E, 59.7 E, 0.3 E
B. 0.3 E, 60 E, 59.7 E
C. 6 E, 1994 E, 0.2 E
D. 1994 E, 0.2 E, 6 E
A wireless PAN will not link to which of the following?
A. Nearby laptop
B. PC across a room
C. PC in an adjacent room
D. nearby PDA
_____is an analog multiplexing technique to combine optical signals
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
The ability of IP to move fast audio and video data over the Internet from a single source to multiple destinations is called
A. multiplexing
B. multitasking
C. multicasting
D. multi-transmitting
In ___ schemes, the voltages are on the both sides of the time axis. For example, the voltage level for 0 can be positive and the voltage level for 1 can be negative.
A. polar
B. bipolar
C. unipolar
D. All of the above
In , the level of the voltage determines the value of the bit.
A. NRZ-I
B. NRZ-L
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
Unwanted ads and solicitations via email fall into the category of
A. spam
B. A virus
C. spyware
D. A smurf attack
In one's complement arithmetic, if positive 7 is 0111, then negative 7 is ____.
A. 1111
B. 1101
C. 1000
D. None of the above
In , the change or lack of change in the level of the voltage determines the value of the bit.
A. NRZ-I
B. NRZ-L
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
The idea of RZ and the idea of NRZ-L are combined into the___scheme.
A. Manchester
B. differential Manchester
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
Protecting data from interception and protecting the sending and receiving parties from unwanted threats such as viruses and spam on the Internet is referred to as
A. Internet protection
B. Spam busting
C. security
D. anti-virus protection
During the busy hour, 1200 calls were offered to a group of trunks and six calls were lost. The average call duration was 3 minutes. Find the grade of service and the total duration of the periods of congestion.
A. 0.004, 26s
B. 0.005, 18s
C. 0.002, 14s
D. 0.004, 14s
____ is designed to use the high bandwidth capability of fiber-optic cable.
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
The idea of RZ and the idea of NRZ-I are combined into the____scheme.
A. Manchester
B. differential Manchester
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
In _____encoding, the duration of the bit is divided into two halves. The voltage remains at one level during the first half and moves to the other level in the second half. The transition at the middle of the bit provides synchronization.
A. Manchester
B. differential Manchester
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
Which of the following is not an advantage of using a fibre channel as a SAN connection?
A. Low cost
A. flexibility
C. speed
D. reliability
In____there is always a transition at the middle of the bit, but the bit values are determined at the beginning of the bit. If the next bit is 0, there is a transition; if the next bit is 1, there is none.
A. Manchester
B. differential Manchester
C. both (a) and (b)
D. neither (a) nor (b)
In Manchester and differential Manchester encoding, the transition at the middle of the bit is used for _____.
A. Bit transfer
B. Baud transfer
C. synchronization
D. None of the above
In a fibre channel, the connection to the fiber-optic cable is made through an interface card known as a
A. NIC card
B. Host bus adapter
C. Fiber bus connector
D. fiber-optic interface
The minimum bandwidth of Manchester and differential Manchester is____that of NRZ.
A. The same as
B. twice
C. thrice
None of the above
A small program designed to implement some nefarious action in a computer is
A. spam
B. A virus
C. spyware
D. A smurf attack
In encoding, we use three levels: positive, zero, and negative.
A. unipolar
B. bipolar
C. polar
D. None of the above
The____ scheme uses data patterns of size 2 and encodes the 2-bit patterns as one signal element belonging to a four- level signal.
A. 4B5B
B. 2B1Q
C. MLT-3
D. None of the above
The connection between the servers and the storage-area network is made usually by
A. fiber-optic network
B. LAN
C. router
D. NIC
The_____scheme uses three levels (+V,0, and -V) and three transition rules to move between the levels.
A. 4B5B
B. 2B1Q
C. MLT-3
D. None of the above
If the bit rate for a 16-QAM signal is 4000 bps, what is the baud rate?
A. 300
B. 400
C. 1000
D. 1200
What is the wireless technique that uses thin, inexpensive tags or labels that contain passive radio circuits which can be queried by a remote wireless interrogation unit?
A. HP IrD
B. IrDA
C. RFID
D. IDRF
If the baud rate for a 64-QAM signal is 2000, what is the bit rate?
A. 300
B. 400
C. 1000
D. 12000
Given an AM radio signal with a bandwidth of 10 KHz and the highest- frequency component at 705 KHz, what is the frequency of the carrier signal?
A. 700 KHz
B. 705 KHz
C. 710 KHz
D. Cannot be determined from given information
The linking of one Bluetooth device that serves as a master controller to up to seven other Bluetooth slave devices form what is called a
A. PAN
B. Bluenet
C. picotooth
D. piconet
In___, the peak amplitude of one signal level is 0; the other is the same as the amplitude of the carrier frequency.
A. PSK
B. OOK
C. FSK
D. None of the above
How many carrier frequencies are used in BASK?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
Which of the following is not an advantage of ultrawideband wireless?
A. Immunity to multipath propagation
B. Long range capabilities
C. license-free operation
D. Potentially low cost
How many carrier frequencies are used in BFSK?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
How many carrier frequencies are used in BPSK?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
Which of the following is a system of delivering the TV signal to home receivers by way of a coaxial cable?
A. cable TV
B. satellite TV
C. VHF antenna
D. UHF antenna
How many carrier frequencies are used in QPSK?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
The constellation diagram of BASK has ___ dots.
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
A color cathode-ray tube is coated with
A. red, yellow, and blue phosphor dots or stripes
B. red, violet, and green phosphor dots or stripes
C. red, green, and blue phosphor dots or stripes
D. red, green, and yellow phosphor dots or stripes
The constellation diagram of BPSK has ___ dots.
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. None of the above
The constellation diagram of QPSK has_____dots.
A. 2
B. 1
C. 4
D. None of the above
Which of the following is not a new display method recently brought to market?
A. liquid-crystal display
B. Monochrome display
C. plasma
D. projection
The constellation diagram of 16-QAM has___ dots.
A. 4
B. 16
C. 8
D. None of the above
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allows kHz for each AM station.
A. 5
B. 10
C. 20
D. None of the above
A nonlinear circuit that heterodynes the two IFs and generates the sum and difference frequencies is the
A. Sound modulator
B. Sound detector
C. Sound multiplexer
D. Sound synchronizer
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allows_____kHz for each FM station.
A. 20
B. 100
C. 200
D. None of the above
The sharing of a medium and its link by two or more devices is called .
A. modulation
B. encoding
C. Line discipline
D. multiplexing
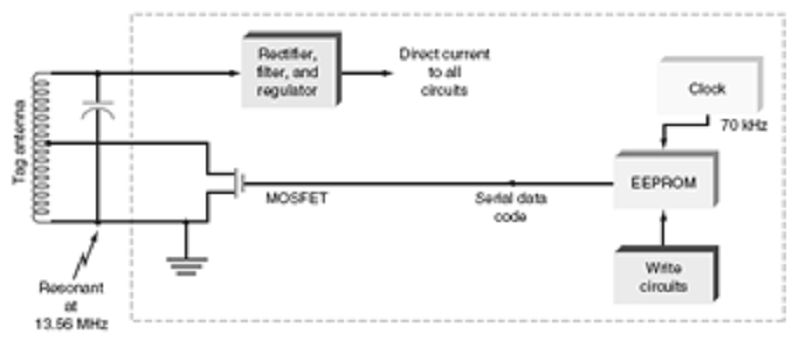
In the block diagram illustrated above, the unique ID code is stored in the
A. MOSFET
B. Resonant circuit
C. Write circuits
D. EEPROM
Which multiplexing technique transmits analog signals?
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. (a) and (c)
Which multiplexing technique transmits digital signals?
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
On average, during the busy hour, a company makes 120 outgoing calls of average duration 2 minutes. It receives 200 incoming calls of average duration 3 minutes. Find the outgoing traffic.
A. 4 E, 10 E, 14 E
B. 10 E, 4 E, 14 E
C. 6 E, 10 E, 16 E
D. 10 E, 6E, 16 E
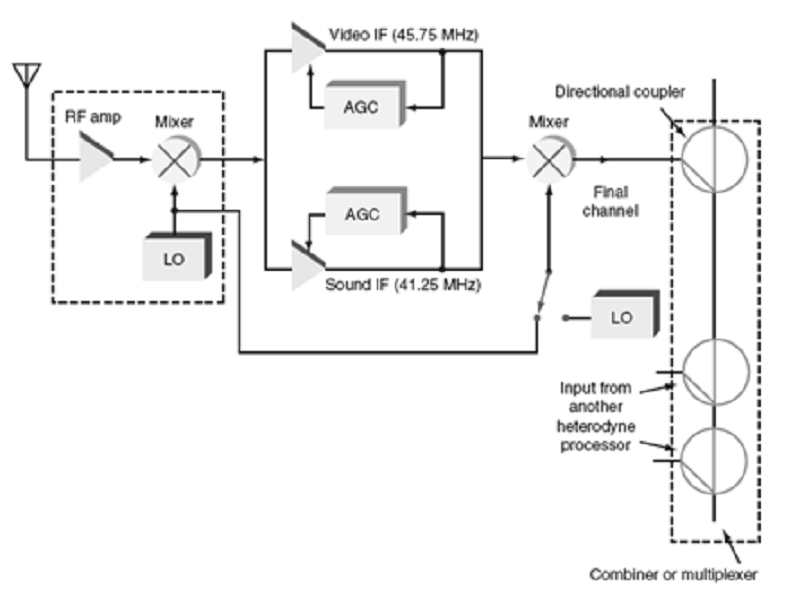
In the block diagram illustrated above, which block adjusts the signal to correct for amplitude and phase variations encountered during transmission?
A. Clock recovery
B. NTSC filter
C. equalizer
D. Reed-Solomon error correction
Which multiplexing technique shifts each signal to a different carrier frequency?
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. Both (a) and (b)
D. None of the above
Which multiplexing technique involves signals composed of light beams?
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
The path from earth to a satellite is called the
A. uplink
B. downlink
C. VoIP
D. Angle of propagation
_____ utilization is the use of available bandwidth to achieve specific goals.
A. Frequency
B. Bandwidth
C. Amplitude
D. None of the above
____ can be achieved by using multiplexing;_____ can be achieved by using spreading.
A. Efficiency; privacy and antijamming
B. Privacy and antijamming; efficiency
C. Privacy and efficiency; antijamming
D. Efficiency and antijamming; privacy
Direct broadcast satellite TV systems create a signal that can be received by a satellite dish with as small as
A. a 12-in diameter
B. a 5-ft diameter
C. a 12-ft diameter
D. an 18-in diameter
The checksum of 1111 and 1111 is _______.
1111
B. 0000
1110
0111
_____is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link.
A. Demodulating
B. Multiplexing
C. Compressing
D. None of the above
In a multiplexed system,_____lines share the bandwidth of____link
A. 1; n
B. 1; 1
C. n; 1
D. n; n
HDTV uses
A. Interlace scanning
B. Horizontal sync scanning
C. Progressive line scanning
D. Digital loop scanning
The word ___refers to the portion of a___that carries a transmission.
A. channel; link
B. link; channel
C. line; channel
D. line; link
In a group of 10 servers, each is occupied for 30 min in an observation interval of 2 hrs. Calculate the traffic carried by the group.
A. 4.5 E
B. 3.5 E
C. 2.5 E
D. 5.5 E
_____can be applied when the bandwidth of a link (in hertz) is greater than the combined bandwidths of the signals to be transmitted.
A. TDM
B. FDM
C. Both (a) or (b)
D. Neither (a) or (b)
Which of the following is not a primary benefit of digital cable?
A. More channels can be carried
B. Less bandwidth required
C. Picture quality is better
D. Will continue to support older analog TV system
FSM is an _______technique.
A. analog
B. digital
C. either (a) or (b)
D. None of the above
_____ is a digital process that allows several connections to share the high bandwidth of a link.
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
_____is a digital multiplexing technique for combining several low-rate channels into one high-rate one.
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
The checksum of 0000 and 0000 is ______.
A. 1111
B. 0000
C. 1110
D. 0111
We can divide ____into two different schemes: synchronous or statistical.
A. FDM
B. TDM
C. WDM
D. None of the above
In_____, we combine signals from different sources to fit into a larger bandwidth.
A. Spread spectrum
B. Line coding
C. Block coding
D. None of the above
On average, during the busy hour, a company makes 120 outgoing calls of average duration 2 minutes. It receives 200 incoming calls of average duration 3 minutes. Find the total traffic.
A. 4 E
B. 10 E
C. 6 E
D. 14 E
______ is a first-generation cellular phone system.
A. AMPS
B. D-AMPS
C. GSM
D. None of the above
An IPv6 address is _____bits long.
A. 32
B. 64
C. 128
D. None of the above
An IPv6 address consists of _____bytes (octets);
A. 4
B. 8
C. 16
D. None of the above
To make addresses more readable, IPv6 specifies___notation.
A. Dotted decimal
B. Hexadecimal colon
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
______ is a second-generation cellular phone system.
A. AMPS
B. D-AMPS
C. GSM
D. None of the above
An electronic system for transmitting graphic information by wire or radio is
A. POTS
B. facsimile
C. e-mail
D. telegraphy
An attempt is made to transmit a baseband frequency of 30 kHz using a digital audio system with a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz. What audible frequency would result?
A. 14.1 kHz
B. 13.2 kHz
C. 12.3 kHz
D. 11.4 kHz
_____is a digital version of AMPS
A. GSM
B. D-AMPS
C. IS-95
D. None of the above
_____ is a second-generation cellular phone system used in Europe.
A. GSM
B. D-AMPS
C. IS-95
D. None of the above
Which of the following is a type of private telephone system?
A. POP
B. LEC
C. PBX
D. LATA
A modulator transmits symbols, each of which has sixty-four different possible states, 10,000 times per second. Calculate the baud rate and bit rate.
A. 60 kbaud; 10kbps
B. 10 kbaud; 60kbps
C. 30 kbaud; 30kbps
D. 10 kbaud; 10 kbps
_____ is a second-generation cellular phone system based on CDMA and DSSS.
A. GSM
B. D-AMPS
C. IS-95
D. None of the above
The _____cellular phone system will provide universal personal communication.
A. first-generation
B. second-generation
C. third-generation
D. None of the above
Which of the following is currently the leading supplier of long-distance service?
A. AT&T
B. MCI
C. Sprint
D. WorldCom
Calculate the number of levels if the number of bits per sample is 16 (as in compact disc audio systems)
A. 255
B. 256
C. 65535
D. 65536
In a______handoff, a mobile station only communicates with one base station.
A. hard
B. soft
C. medium
D. None of the above
{"name":"RHM 3 ESAT PART 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Which address could be the beginning address of a block of 32 classless addresses?, Which address could be the beginning address of a block of 16 classless addresses?, What is the first address of a block of classless addresses if one of the addresses is 12.2.2.76\/27?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/86-4181225/untitled.png?sz=1200-00000000001000004344"}
More Quizzes
26/04/2020 (Sunday Weekly Test)
1015032
Victoria Pop Quiz
1050
French Revolution
1580
How French are you?
5243
Free Fractions: Add/Subtract, Multiply/Divide
201024311
Free Vibration Analysis Certification
201028823
Plasma Engineering
15820816
Free Find Mistakes: 50 Sentence Corrections
201021528
Free Pride: Discover if You're a Truly Prideful Person
201025846
Am I a Good Person: Discover Your True Character
201026839
Diagnostic Radiology and Non-Cardiac Nuclear Medicine
15821381
Think You're a First Aid Pro? Take This 1st Aid!
201081363