Ch 19 - blood vessels
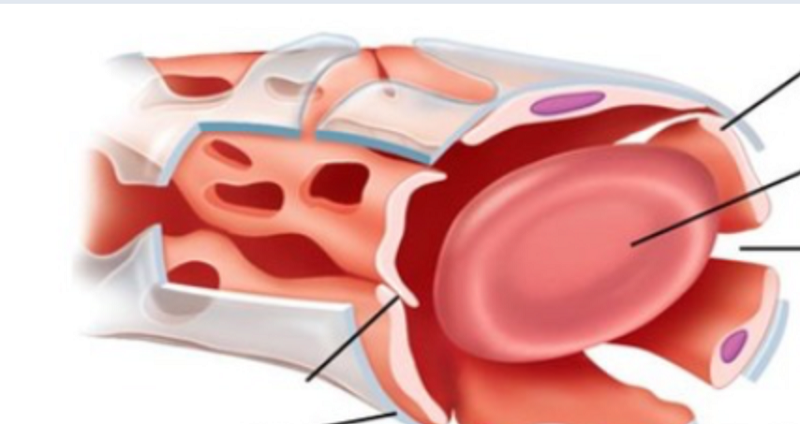
What is the following capillary?
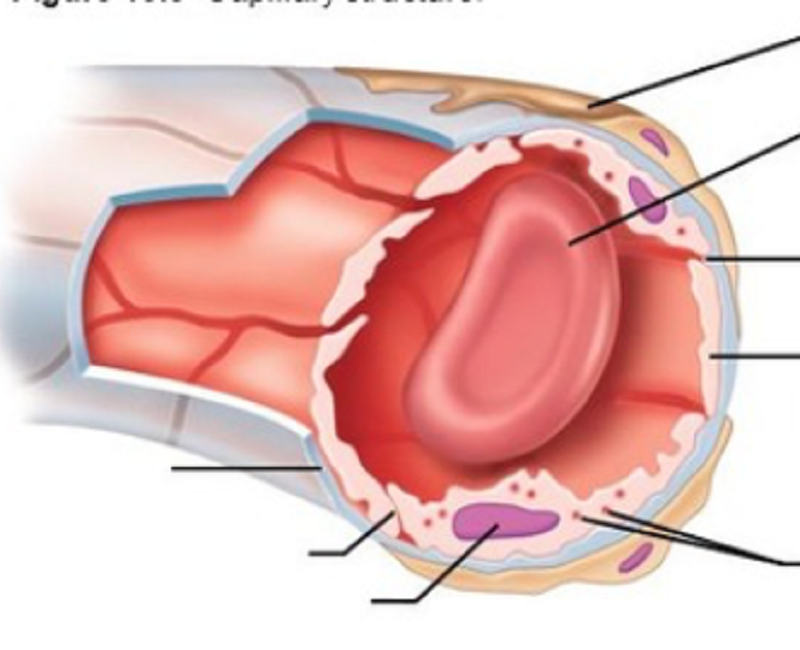
What is the following capillary?
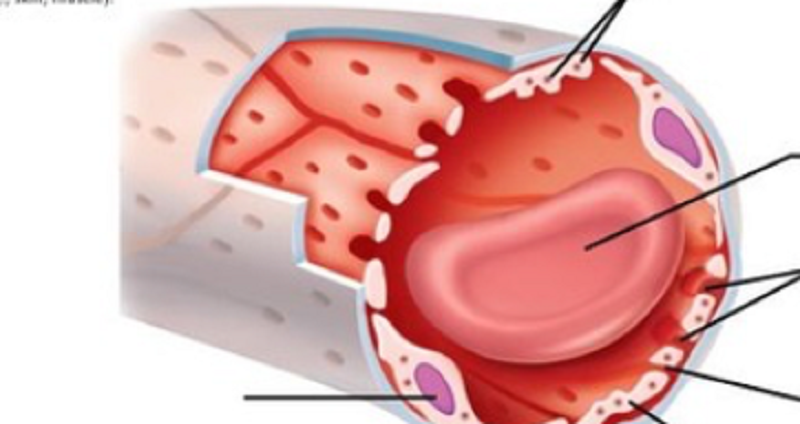
What is the following capillary?
Site that is the major determinant of peripheral resistance?
Elastic arteries
Large veins
Venules
Capillaries
Arterioles
Muscular arteries
Mainly involved in conducting blood from the heart to other vessels?
Capillaries
Arterioles
Muscular arteries
Large veins
Venules
Elastic arteries
Site where blood volume is the greatest?
Elastic arteries
Large veins
Venules
Capillaries
Muscular arteries
Arterioles
Site where the velocity of blood flow is the slowest?
Capillaries
Muscular arteries
Large veins
Venules
Elastic arteries
Arterioles
Site where exchanges of food and gases are made?
Large veins
Capillaries
Venules
Muscular arteries
Elastic arteries
Arterioles
Also known as the distributing arteries?
Elastic arteries
Capillaries
Large veins
Venules
Muscular arteries
Arterioles
Site where resistance to blood flow is the greatest?
Arterioles
Large veins
Muscular arteries
Venules
Elastic arteries
Capillaries
Site where blood pressure is the lowest?
Venules
Muscular arteries
Large veins
Capillaries
Elastic arteries
Arterioles
Which of the following is NOT a type of capillary?
Continuous
Sinusoidal
Fenestrated
Distributing
If you have a blood pressure of 120/180 mmHg, what is your systolic pressure?
120 mm Hg
80 mm Hg
200 mm Hg
40 mmHg
Capillary found in endocrine organs that allows hormones to gain rapid entry into the blood?
Sinusoid capillary
Fenestrated capillary
Continuous capillary
Capillary with intercellular clefts found in the skin and muscles?
Fenestrated capillary
Sinusoid capillary
Continuous capillary
Capillary that have a discontinuous, incomplete basement membrane?
Sinusoid capillary
Fenestrated capillary
Continuous capillary
Capillary found where active capillary absorption of filtrate occurs?
Continuous capillary
Fenestrated capillary
Sinusoid capillary
Results from heart inability to sustain adequate circulation due to myocardial damage?
Cariogenic shock
Vascular shock
Circulatory shock
Hypovolemic shock
Due to inadequate blood flow to meet tissue needs
Vascular shock
Circulatory shock
Hypovolemic shock
Cardiogenic shock
Normal blood volume but poor circulation due to extreme vasodilation?
Circulatory shock
Hypovolemic shock
Cariogenic shock
Vascular shock
Due to large-scale blood loss?
Hypovolemic shock
Cardiogenic shock
Vascular shock
Circulatory shock
The adjustment of blood flow to each tissue in proportion to its requirements at any point in time is termed autoregeneration
True
False
Arterial pressure in the pulmonary circulation is much higher than in systemic circulation because of its proximity to the heart
True
False
Osmotic pressure is created by the presence in a fluid of small diffusible molecules that easily move through the capillary membrane
True
False
The pulmonary circulation does not directly serve the metabolic needs of body tissues
True
False
An obstruction in the superior vena cava would decrease blood flow from the head and neck to the heart
True
False
Arteries supplying the same territory are often merged with one another, forming arterial anastomoses
True
False
An increase in blood viscosity will cause an increase in peripheral resistance
True
False
Whereas diffusion is more important for solute exchange between plasma and interstitial fluid, bulk flow is more important for regulation of the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid
True
False
The cerebral arterial circle (circle of willis) is an arterial anastomosis
True
False
The carotid sinus reflex protects the blood supply to the brain, whereas the aortic reflex is more concerned with maintaining adequate blood pressure in the systemic circuit as a whole
True
False
Reduction in the concentration of albumin in blood plasma would suffer capillary exchange by ____
Increasing hydrostatic pressure and blood volume, blood pressure increases
Increasing hydrostatic pressure and edema will occur
Decreasing colloid osmotic pressure and blood volume, blood pressure increases
Decreasing colloid osmotic pressure and edema will occur
If a person were to have substantial blood loss you would expect to see all of the following physiological events to except one. Select the least likely response to substantial blood loss
Increases peripheral resistance
Increasing vasomotor tone
Decreased heart rate
A weak, threaded pulse
During a marathon which of the following hormones is least likely to be released by the runner?
Epinephrine
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Angiotensin II
If a person stands up suddenly from the prone (lying) position they may feel a sudden dizzy or lightheadedness. Which of the following is the least likely physiological response to this situation?
Increasing peripheral resistance due to vasoconstriction
Increases sympathetic output to the heart
Increased parasympathetic nerve impulses to the heart
Faster heart rate and greater heart contractility
A drug that restricts the activity of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) would like result in all of the following physiologic changes but one. Which of the following is the least likely to result from a drug blocking ACE activity?
Increased urine output to reduction in circulating antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Lower levels of circulating aldosterone and lowered sodium reabsorption
Increased thirst and higher blood volume
Decreased peripheral resistance due to decreases vasomotor tone
The aorta receives the full force of blood exiting the heart during ventricular systole. Which of the following statements best describes the adaptive anatomy of the aorta?
Smooth muscle is relatively thin in the aorta to increase lumen size and systemic blood flow
The aorta's tunica media is thick with dense regular connective tissue to withstand the blood's pressure
Elastic fibers are extensive in the tunic media of the aorta and dampen the pulse pressure generated by the heart
The tunica external of the aorta is nearly absent compared ti other vessels
Which of the following statements is not true of the precapillary sphincters
They increase or decrease rates of perfusion to the tissues served by the true capillaries
They decrease the osmotic pressure in the thoroughfare channel
They allow blood to bypass the true capillaries that are fed by the metarteriole
They regulate the flow of blood to tissues served by the true capillaries
Which of the following would not promote filtration from the arteriole end of the capillary bed?
Increasing plasma protein concentration
Reducing hydrostatic pressure within the interstitial fluid
Relaxing precapillary sphincters
Increasing blood pressure
Which of the following would not promote reabsorption from the venous end of the capillary bed?
Increasing solute concentration in the plasma of the circulating blood
Increasing solute concentration in the nearby interstitial fluid
Reducing solute concentration in the nearby interstitial fluid
Decreasing hydrostatic pressure of the blood
In general it is expected that ____
Hydrostatic pressure will rise as blood moves away from the arteriole end of the capillary bed
Hydrostatic pressure will remain constant throughout the capillary bed
Osmotic pressure will be lower in the arteriole end of the capillary bed compared to the venous end
Hydrostatic pressure will drop as blood moves away from the arteriole end of the capillary bed
In general it is expected that ____
Osmotic pressure will remain relatively consistent throughout the capillary bed
Hydrostatic pressure will remain constant throughout the capillary bed
Osmotic pressure will be higher in the arteriole end of the capillary bed compared to the venous end
Osmotic pressure will be lower in the arteriole end of the capillary bed compared to the venous end
Which of the following is most likely to occur in the arteriovenous shuts present in the blood vessels of the finger types and toes?
Colder temperatures will result in vasoconstriction in the arteriovenous shuts
Exercise will result in vasoconstriction in the arteriovenous shuts
Colder temperatures will result in vasodilation in the arteriovenous shuts
Warmer temperatures will result in vasoconstriction in the arteriovenous shuts
Which of the following best describes the benefit of the vasomotor process?
It decreases hydrostatic pressure while also increasing osmotic pressure to enhance reabsorption
It lowers blood's pressure by reducing the distribution of blood flow to all of the tissues in the capillary bed
It provides a balance between adequate perfusion to all of the tissues while maintaining blood's pressure
It allows for rapid increase in blood flow to vital organs during fight or flight response
Which of the following would have the least influence on blood pressure?
White blood cell count
Blood volume
Cardiac output
Peripheral resistance
The velocity and pressure of blood is slowest and lowest in the capillary beds. Which of the following is not an accurate description of the benefits of slow, low pressure blood in the capillary beds?
Slower blood flow through capillaries allows more time for diffusion to take place in the capillary bed.
Lower pressure reduces the chance of injury to delicate capillary vessels
Lower pressure in the capillary bed helps to increase pressure in the venus circulation
Lower pressure on the venus end of the capillary bed allows for greater reabsorotion of fluid back to the plasma
Which of the following chemicals effects blood pressure for both the short and long term?
Angiotensin II
Atrial natriuretic peptide
Aldosterone
Nitric acid
Which statement best describes arteries?
All carry blood away from the heart
All contain valves to prevent the back flow of blood
All carry oxygenated blood to the heart
Only large arteries are lines with endothelium
Permitting the exchange of nutrients and gases between the blood and tissue cells is the primary function of ____
Capillaries
Arterioles
Veins
Arteries
Each of the following describes the action of aldosterone except one. Which of the following does not describe the activity of aldosterone hormone?
It will reduce urine output
It promotes an increase in sodium reabsorption from the kidney to the blood
It promotes an increase in blood pressure
It will result in higher sodium levels in the urine
The pulse pressure is ___
Systolic pressure divided by diastolic pressure
Diastolic pressure plus 1/3 (systolic pressure plus diastolic pressure)
Systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure
Systolic pressure plus diastolic pressure
Which of the choices below explains why the arterioles are known as resistance vessels?
They distribute blood to various parts of the body
The contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle in their walls can change their diameter
Their prime function is the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells
They contain a large quantity of elastic tissue
Which of the following processes provides a long-term response to changes in blood pressure?
Baroreceptor-initiated reflexes
Neural controls
Renal regulation
Chemoreceptor-initiated reflexes
Peripheral resistance ___
Decreases with increasing length of the blood vessel
Increases as blood viscosity increases
Increases as blood vessel diameter increases
Is not a major factor in blood pressure in healthy individuals
Brain blood flow autoregulation ____
Is controlled by cardiac centers in the pons
Causes constriction of cerebral blood vessels in response to a drop in systemic blood pressure
Is less sensitive to pH than to a decreased oxygen level
Is abolished when abnormally high CO2 levels persist
Blood flow to the skin ___
Is controlled mainly by decreasing pH
Is not an important source of nutrients and oxygen for skin cells
Increases when body temperature drops so that the skin does not freeze
Increases when environmental temperature rises
Which of the choices below reflects the balance (for imbalance) between the direction and amount of fluid that flows across the capillary walls?
Hydrostatic pressure only
Hydrostatic and osmotic pressure
Plasma and formed element concentration
Blood volume and viscosity
Which of the following is the most significant source of blood flow resistance?
Blood vessel diameter
Blood viscosity
Total blood vessel length
Blood vessels type
Mechanisms that do not help regulate blood pressure include ____
Chemical controls such as atrial natriuretic peptide
Nervous control that operates via reflex arcs involving baroreceptors, chemoreceptors, and higher brain centers
Renal regulation via the renin-angiotensin system of vasoconstriction
The dural sinus reflex
The velocity of blood flow is ____
In direct proportion to the total cross-sectional area of the blood vessels
Slower in the veins than in the capillaries because veins have a large diameter
Slower in the arteries than in the capillaries because arteries possess a relatively large diameter
Slowest in the capillaries because the total cross-sectional areas is the greatest
The short term controls of blood pressure, meditated by the nervous system and blood borne chemicals, primarily operate via all but which of the following?
Reflex arcs involving baroreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Reflex arcs associated with vasomotor fibers
Altering blood volume
The baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch are sensitive to which of the following?
Changes in arterial pressure
A decrease in oxygen levels
An increase in oxygen levels
A decrease in carbon dioxide
{"name":"Ch 19 - blood vessels", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"What is the following capillary?, What is the following capillary?, What is the following capillary?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/98-4838066/screen-shot-2024-02-17-at-10-44-55-am.png?sz=1200-00000000001000005300"}
More Quizzes
Are u realy my friend
1050
Extra Superlatives
13617
Quantum Leadership (1)
10598
How well do u know the biggest moink
1588
Vikings to Volvos: Scandinavia
15823934
Psychology Final Exam: Think You Can Ace It?
201029444
Free The Giver: Test Your Novel Knowledge!
201048380
Think You Know Viruses? Take the Ultimate Virus Now
201025625
How Well Do You Know Hotel Bellman Duties? Take the!
201054149
Free Fire Instructor II Knowledge Assessment
201028814
Free Medication Abbreviation Safety
201023934
How Much Am I Worth? Discover Your Worth in This Free
201032748