RHM 1 ESAT PART 3
Once the AM signal is amplified, it is fed to antenna with characteristic impedance that is ideally
A. inductive
B. capacitive
C. resistive
D. infinite
With AM which of the following conveys no information?
A. Lower sideband
B. Upper sideband
C. Both sidebands
D. carrier
In a frequency modulation receiver, the output of the high frequency oscillator is fed to the:
A. Radio frequency amplifier
B. limiter
C. antenna
D. mixer
In a frequency modulation receiver, the output of the _______ is connected to the mixer.
A. Frequency discriminator
B. Intermediate frequency amplifier
C. Speaker and/or headphones
D. High frequency oscillator
In an FM stereo multiplex transmission, the
A. Sum signal modulates 19 kHz subcarrier
B. Difference signal modulates the 19 kHz subcarrier
C. Difference signal modulates the 38 kHz subcarrier
D. Difference signal modulates the 67 kHz subcarrier
Interference generated by lightning, motors, automotive ignition systems, and any power line switching that produces transient signals is referred to as
A. Magnetic radiation
B. Stray reactance
C. Induced signals
D. noise

A three-stage amplifier has stages with the following specifications: Calculate the power gain, noise factor, and noise temperature for the entire amplifier, assuming matched conditions.
A. 2750; 2.46; 423.4 K
B. 300; 2.12; 287.1 K
7500; 2.316; 382 K
D. 65; 2.46; 423.4 K
One of the primary benefits of FM over AM is its
A. Line of sight transmission
B. Superior noise immunity
C. Lower signal-to-noise ratio
D. Smaller bandwidth
A technique that helps offset high-frequency noise interference by passing a modulating signal through a simple network that amplifies high-frequency components more than the low-frequency components is called
A. preamplification
B. deemphasis
C. preemphasis
D. Crossover boost
For a 10-MHz crystal with a temperature coefficient k=+10 Hz/MHz/°C, determine the frequency of operation if the temperature increase is 10°C and temperature decrease is 5°C.
A. 10.005 MHz; 9.9991 MHz
B. 10.005 MHz; 9.9995 MHz
C. 10.001 MHz; 9.9995 MHz
D. 10.001 MHz; 9.9991 MHz
In a frequency modulation receiver, the _______ is in between the mixer and the intermediate frequency amplifier.
A. filter
B. limiter
C. Frequency discriminator
D. Radio frequency amplifier
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the antenna is connected to the _______.
A. Product detector
B. High frequency oscillator
C. Intermediate frequency amplifier
D. Radio frequency amplifier
In high-level AM, the modulator varies the voltage and power in the
A. Carrier oscillator
B. Audio amplifier
C. intermediate RF amplifier
D. final RF amplifier
The modulation index of an AM wave is changed from 0 to 1. The transmitted power is
A. unchanged
B. halved
C. doubled
D. Increase by 50 percent
If a class C amplifier has an input of 1000 W, the modulator must be able to deliver
A. 100 W
B. 200 W
C. 400 W
D. 500 W
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the output of the _______ is connected to the mixer.
A. filter
B. Intermediate frequency amplifier
C. Audio frequency amplifier
D. Radio frequency amplifier
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the _______ is in between the filter and product detector.
A. Intermediate frequency amplifier
B. Audio frequency amplifier
C. Beat frequency oscillator
D. Radio frequency amplifier
Which of the following is not a basic element of a phase-locked loop circuit?
A. Phase detector
B. Parallel tuned circuit
C. voltage-controlled oscillator
D. low-pass filter
When dealing with random noise calculations it must be remembered that
A. All calculations are based on peak to peak values
B. Calculations are based on peak values
C. Calculations are based on average values
D. Calculations are based on RMS values
A receiver has a sensitivity of 0.5μV and a blocking dynamic range of 70 dB. What is the strongest signal that can be present along with a 0.5 μV signal without blocking taking place?
A. 3.16 mV
B. 0.79 mV
C. 4.74 mV
D. 1.58 mV
Circuits that make use of techniques for varying the frequency of the carrier oscillator in accordance with the modulating signal are referred to as
A. direct FM
B. indirect FM
C. Phase modulation
D. demodulation
In a single sideband transmitter, the output of the _______ is connected to the balanced modulator.
A. Radio frequency oscillator
B. Variable frequency oscillator
C. Linear amplifier
D. mixer
In a single sideband transmitter, the output of the _______ is connected to the balanced modulator.
A. filter
B. Variable frequency oscillator
C. Speech amplifier
D. Linear amplifier
Which list of emission types is in order from the narrowest bandwidth to the widest bandwidth?
A. CW, SSB voice, RTTY, FM voice
B. CW, FM voice, RTTY, SSB voice
C. CW, RTTY, SSB voice, FM voice
D. RTTY, CW, SSB voice, FM voice
Moving towards the clockwise direction in the Smith chart implies moving
A. Towards generator
B. Towards load
C. Towards stub
D. Towards waveguide
An FM Modulator has k_f= 30 kHz/V and operates at a carrier frequency of 175 MHz. Find the output frequency for an instantaneous value of the modulating signal equal to 150 mV.
A. 174.94 MHz
B. 127.2 kHz
C. 175.0045 MHz
D. None of the above
The figure in a receiver's specifications which indicates its sensitivity is the:
A. Signal plus noise to noise ratio
B. Audio output in watts
C. Bandwidth of the IF in kilohertz
D. Number of RF amplifiers
The output stage of a television transmitter is most likely to be a
A. plate-modulated class C amplifier
B. grid-modulated class C amplifier
C. screen-modulated class C amplifier
D. grid-modulated class A amplifier
Which of the following is not a benefit of using a frequency synthesizer over a simple VFO design?
A. Output is locked to a crystal oscillator reference
B. Incremental frequency changes
C. Continuous frequency changes
D. Local oscillator design is simple and inexpensive
What can you do if you are told your FM hand-held or mobile transceiver is overdeviating?
A. Talk louder into the microphone
B. Let the transceiver cool off
C. Change to a higher power level
D. Talk farther away from the microphone
What kind of emission would your FM transmitter produce if its microphone failed to work?
A. A frequency-modulated carrier
B. An amplitude-modulated carrier
C. An unmodulated carrier
D. A phase-modulated carrier
What is used to reduce image interference caused by crowding of the RF spectrum?
A. low-Q tuned circuits ahead of the mixer
B. high-Q tuned circuits after the RF amplifier
C. low-Q tuned circuits after the mixer
D. high-Q tuned circuits ahead of the mixer
A phase modulator has kp=2rad/V. What RMS voltage of a sine wave would cause a peak phase deviation of 60°?
A. 0.524 V
B. 30 V
C. 21.21 V
D. 0.37 V
If two receivers of different sensitivity are compared, the less sensitive receiver will produce:
A. A steady oscillator drift
B. More than one signal
C. Less signal or more noise
D. More signal or less noise
Which of the following modes of transmission is usually detected with a product detector?
A. Double sideband full carrier
B. Frequency modulation
C. Pulse modulation
D. Single sideband suppressed carrier
A phase-locked loop has a VCO with a free-running frequency of 12 MHz. As the frequency of the reference input is gradually raised from zero, the loop locks at 10 MHz and comes out of lock again at 16 MHz. Find the capture range and lock range.
A. 4 MHz; 8 MHz
B. 8 MHz; 10 MHz
C. 6 MHz; 9 MHz
D. 2 MHz; 7 MHz
When the modulation index of an AM wave is doubled, the antenna current is also doubled. The AM system being used is
A. Single-sideband, full carrier (H3E)
B. Vestigial sideband (C3F)
C. Single-sideband, suppressed carrier (J3E)
D. Double-sideband, full carrier (A3E)
A receiver designed for SSB reception must have a BFO (beat frequency oscillator) because:
A. It beats with the received carrier to produce the other sideband
B. It reduces the passband of the IF stages
C. The suppressed carrier must be replaced for detection
D. It phases out the unwanted sideband signal
If the carrier of a 100 percent modulated AM wave is suppressed, the percentage power saving will be
A. 50
B. 150
C. 100
D. 66.66
The rate of change of amplitude with frequency in a filter is the
A. Shape factor
B. roll-off
C. Insertion loss
D. attenuation
Which of the following, also known as a Thomson filter provides the desired frequency response, but has a constant time delay in the passband?
A. Butterworth
B. Chebyshev
C. Cauer
D. Bessel
What circuit has a variable-frequency oscillator connected to a driver and a power amplifier?
A. A crystal-controlled transmitter
B. A VFO-controlled transmitter
C. A single-sideband transmitter
D. A packet-radio transmitter
What type of modulation system changes the amplitude of an RF wave for the purpose of conveying information?
A. Phase modulation
B. Amplitude modulation
C. Amplitude-rectification modulation
D. Frequency modulation
The ratio of the frequency deviation to the modulating frequency is known as the
A. Deviation factor
B. frequency-shift keying
C. Modulation index
D. Ratio of modulation
What type of filter should be connected to a TV receiver as the first step in trying to prevent RF overload from an amateur HF station transmission?
A. High-pass
B. Low-pass
C. Band-pass
D. No filter
The higher the modulation index in FM
A. The greater the number of sidebands and the wider the bandwidth
B. The greater the number of sidebands and the narrower the bandwidth
C. The fewer the number of sidebands and the wider the bandwidth
D. The fewer the number of sidebands and the narrower the bandwidth
What is the term for the average power supplied to an antenna transmission line during one RF cycle, at the crest of the modulation envelope?
A. Peak output power
B. Peak envelope power
C. Average radio-frequency power
D. Peak transmitter power
In a typical single-sideband phone transmitter, what circuit processes signals from the balanced modulator and sends signals to the mixer?
A. IF amplifier
B. Filter
C. RF amplifier
D. Carrier oscillator
A low ratio of the ac to the dc load impedance of a diode detector results in
A. Diagonal clipping
B. poor AGC operation
C. negative-peak clipping
D. poor AF response
What may happen if an FM transmitter is operated with the microphone gain or deviation control set too high?
A. It may cause digital interference to computer equipment
B. It may cause atmospheric interference in the air around the antenna
C. It may cause interference to other stations operating on a higher frequency band
D. It may cause interference to other stations operating near its frequency
When a receiver has good blocking performance, this means that
A. It does not suffer from double-spotting
B. Its image frequency rejection is poor
C. It is unaffected by AGC derived from nearby transmissions
D. Its detector suffers from burnout
With regard to a transmission line, which of the following statements is correct?
A. Any impedance repeats itself every 1/4 on the Smith chart.
B. The S.W.R. = 2 circle and the magnitude of reflection coefficient = 0.5 circle coincide on the Smith chart.
C. Any point on a transmission line, the current reflection coefficient is the reciprocal of the voltage reflection coefficient.
D. Matching eliminates the reflected wave between the source and the matching device location.
Why is FM voice best for local VHF/UHF radio communications?
A. It has high-fidelity audio which can be understood even when the signal is somewhat weak
B. The carrier is not detectable
C. It is more resistant to distortion caused by reflected signals
D. Its RF carrier stays on frequency better than the AM modes
One way to obtain selectivity while eliminating the image problem is to use
A. A single-conversion superheterodyne receiver
B. A dual-conversion superheterodyne receiver
C. More tuned circuits
D. a TRF receiver
One of the following cannot be used to demodulate SSB:
A. Product detector
B. Diode Balance modulator
C. Bipolar transistor balanced modulator
D. Complete phase-shift generator
A special version of the superheterodyne that converts the incoming signal directly to baseband is known as the
A. Indirect conversion receiver
B. zero-IF receiver
C. dual-conversion receiver
D. Special conversion receiver
What is the usual bandwidth of a frequency-modulated amateur signal?
A. Between 10 and 20 kHz
B. Less than 5 kHz
C. Between 5 and 10 kHz
D. Greater than 20 kHz
What should you do for safety if you put up a UHF transmitting antenna?
A. Make sure the antenna is near the ground to keep its RF energy pointing in the correct direction
B. Make sure the antenna will be in a place where no one can get near it when you are transmitting
C. Make sure you connect an RF leakage filter at the antenna feed point
D. Make sure that RF field screens are in place
In a broadcast superheterodyne receiver, the
A. Local oscillator operates below the signal frequency
B. Mixer input must be tuned to the signal frequency
C. Local oscillator frequency is normally double the IF
D. RF amplifier normally works at 455 kHz above the carrier frequency
What is one way to tell if radio frequency interference to a receiver is caused by front-end overload?
A. If grounding the receiver makes the problem worse
B. If connecting a low pass filter to the receiver greatly cuts down the interference
C. If the interference is about the same no matter what frequency is used for the transmitter
D. If connecting a low pass filter to the transmitter greatly cuts down the interference
Determine the %m for the following conditions if the unmodulated carrier is 80 V peak-to-peak, modulated carrier max is 100V and modulated carrier min is 60V.
A. 15%
B. 25%
C. 35%
D. 50%
If a neighbour reports television interference whenever you transmit, no matter what band you use, what is probably the cause of the interference?
A. Incorrect antenna length
B. Receiver VR tube discharge
C. Receiver overload
D. Too little transmitter harmonic suppression
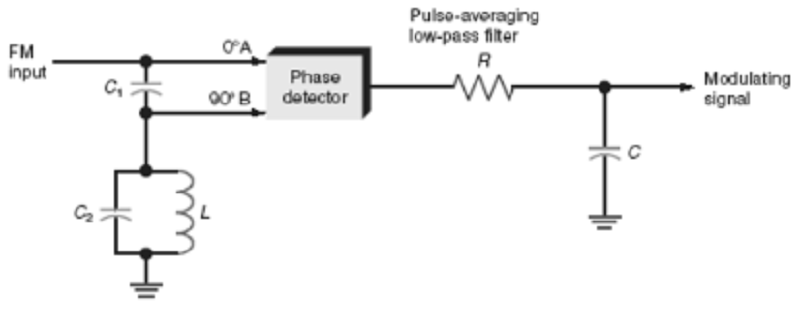
When the frequency-modulated signal is applied through C1 in the circuit illustrated above, the
A. Tuned circuit appears as an inductance
B. Tuned circuit appears as a low value of pure resistance
C. Tuned circuit appears as a high value of pure resistance
D. Output across the tuned circuit at the carrier frequency is very close to 45°
The local oscillator of a broadcast receiver is tuned to a frequency higher than the incoming frequency
A. To help the image frequency rejection
B. To permit easier tracking
C. Because otherwise an intermediate frequency could not be produced
D. To allow adequate frequency coverage without switching
Oscillators whose frequencies are controlled by an external input voltage are generally referred to as
A. phase-locked loops
B. Crystal oscillators
C. voltage-controlled oscillators
D. Colpitts
When the signal from a transmitter overloads the audio stages of a broadcast receiver, the transmitted signal:
A. Is distorted on voice peaks
B. Can appear wherever the receiver is tuned
C. Appears only on one frequency
D. Appears only when a station is tuned
A receiver has poor IF selectivity. It will therefore also have poor
A. blocking
B. double-spotting
C. Diversion reception
D. sensitivity
What devices would you install to reduce or eliminate audio-frequency interference to home entertainment systems?
A. Bypass resistors
B. Metal-oxide varistors
C. Bypass capacitors
D. Bypass inductors
Three-point tracking is achieved with
A. Variable selectivity
B. The padder capacitor
C. Double spotting
D. Double conversion
What should be done if a properly operating amateur station is the cause of interference to a nearby telephone?
A. Ground and shield the local telephone distribution amplifier
B. Stop transmitting whenever the telephone is in use
C. Ask the telephone company to install RFI filters
D. Make internal adjustments to the telephone equipment
Indicate the false statement. Noting that no carrier is transmitted with J3E, we see that
A. The receiver cannot use a phase comparator for AFC
B. adjacent-channel rejection is more difficult
C. Production of AGC is a rather complicated process
D. The transmission is not compatible with A3E
How can you prevent key-clicks?
A. By increasing power
B. By using a key-click filter
C. By using a better power supply
D. By sending CW more slowly
If the intermediate frequency is very high (indicate false statement)
A. Image frequency rejection is very good
B. The local oscillator need not be extremely stable
C. The selectivity will be poor
D. Tracking will be improved
Given a Three-stage system comprised of two amplifiers and one filter. The input power Pin=0.1 mW.The absolute power gains are A(P1)=100, A(P2)=40,and A(P3) =0.25. Determine the dB gain of each of the three stages and the total dB gain.
A. 20dB; 16dB; -6dB; 42 dB
B. 40dB; 32dB; -12dB; 60 dB
C. 20dB; 16dB; -6dB; 30 dB
D. 40dB; 32dB; -12dB; 84 dB
If someone tells you that signals from your hand-held transceiver are interfering with other signals on a frequency near yours, what may be the cause?
A. Your hand-held may be transmitting spurious emissions
B. You may need a power amplifier for your hand-held
C. Your hand-held may have chirp from weak batteries
D. You may need to turn the volume up on your hand- held
If your transmitter sends signals outside the band where it is transmitting, what is this called?
A. Side tones
B. Transmitter chirping
C. Spurious emissions
D. Off-frequency emissions
What problem may occur if your transmitter is operated without the cover and other shielding in place?
A. It may transmit a weak signal
B. It may transmit spurious emissions
C. It may interfere with other stations operating near its frequency
D. It may transmit a chirpy signal
An AM broadcast transmitter has a carrier power output of 50 kW. What total power would be produced with 80% modulation?
A. 54 kW
B. 74.5 kW
C. 66 kW
D. 62.5 kW
The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 12 A when unmodulated but increases to 13 A when modulated. Calculate% m.
A. 40%
B. 92%
C. 59%
D. 41%
In Morse code transmission, local RF interference (key-clicks) is produced by:
A. The making and breaking of the circuit at the Morse key
B. Frequency shifting caused by poor voltage regulation
C. The power amplifier, and is caused by high frequency parasitics
D. Poor waveshaping caused by a poor voltage regulator
Indicate which of the following statements about the advantages of the phase discriminator over the slope detector is false:
A. Much easier alignment
B. Better linearity
C. Greater limiting
D. Fewer tuned circuits
To prevent overloading of the IF amplifier in a receiver, one should use
A. squelch
B. Variable sensitivity
C. Variable selectivity
D. Double conversion
A superheterodyne receiver with an IF of 450 kHz is tuned to a signal at 1200 kHz. The image frequency is
A. 750 kHz
B. 900 kHz
C. 1650 kHz
D. 2100 kHz
Two resistors, 5 kΩ and 20 KΩ are at 27°C. Calculate the thermal noise power for a 10-kHz bandwidth.
A. 4.14×10^-12 W
B. 3.22×10^-12 W
C. 9.61×10^-12 W
D. 2.01x10^-12 W
If a neighbor reports television interference on one or two channels only when you transmit on 15 meters, what is probably the cause of the interference?
A. De ionization of the ionosphere near your neighbor’s TV antenna
B. Harmonic radiation from your transmitter
C. TV receiver front-end overload
D. Too much low pass filtering on the transmitter
A portable radio transmitter has to operate at temperatures from -5°C to 35 °C. If its signal is derived from a crystal oscillator with a temperature coefficient of +1 ppm/degree/°C and it transmits at exactly 146 MHz at 20 °C, find the transmitting frequency at the two extremes of the operating temperature range
A. 146.00419 MHz; 145.99317 MHz
B. 146.00219 MHz; 145.99317 MHz
C. 146.00219 MHz; 145.99635 MHz
D. 146.00419 MHz; 145.99635 MHz
Tinier microstrip and striplines made by using monolithic, thin-film, and hybrid techniques when combined with diodes, transistors, and other components form what are called
A. Microstrip integrated circuits
B. Microwave integrated circuits
C. Stripline integrated circuits
D. high-frequency integrated circuits
In a radio receiver with simple AGC
A. An increase in signal strength produces more AGC
B. The audio stage gain is normally controlled by the AGC
C. The faster the AGC time constant the more accurate the output
D. The highest AGC voltage is produced
A sophisticated graph that permits visual solutions to transmission line calculations is the
A. Karnaugh map
B. Smith chart
C. Boolean table
D. Frequency response curve
What is meant by harmonic radiation?
A. Unwanted signals at frequencies which are multiples of the fundamental (chosen) frequency
B. Unwanted signals that are combined with a 60-Hz hum
C. Unwanted signals caused by sympathetic vibrations from a nearby transmitter
D. Signals which cause skip propagation to occur
Show which of the following statements about the amplitude limiter is untrue:
A. The circuit is always biased in class C, by virtue of the leak-type bias
B. When the input increases past the threshold of the limiting, the gain decreases to keep the output constant.
C. The output must be tuned
D. Leak-type bias must be used
Why is harmonic radiation from an amateur station not wanted?
A. It uses large amounts of electric power
B. It may cause sympathetic vibrations in nearby transmitters
C. It may cause auroras in the air
D. It may cause interference to other stations and may result in out-of-band signals
What type of interference may come from a multi-band antenna connected to a poorly tuned transmitter?
A. Parasitic excitation
B. Harmonic radiation
C. Intermodulation
D. Auroral distortion
The signal at the input of an amplifier has an S/N of 42 dB. If the amplifier has a noise figure of 6 dB, what is the S/N at the output (in decibels)?
A. 48 dB
B. 7 dB
C. 16 dB
D. 36 dB
Why do modern HF transmitters have a built-in low pass filter in their RF output circuits?
A. To reduce fundamental radiation
B. To reduce low frequency interference to other amateurs
C. To reduce harmonic radiation
D. To reduce RF energy below a cut-off point
The characteristic impedance of a transmission line is determined by the:
A. Length of the line
B. Physical dimensions and relative positions of the conductors
C. Frequency at which the line is operated
D. Load placed on the line
The equation that expresses the phase angle in terms of the sine wave modulating signal can be solved by using a complex mathematical process known as
A. Fourier analysis
B. Bessel functions
C. Superposition analysis
D. Thevenin’s Theorem
The image frequency of a superheterodyne receiver
A. Is created within the receiver itself
B. Is due to insufficient adjacent channel rejection
C. Is not rejected by the IF tuned circuits
D. Is independent of the frequency to which the receiver is tuned
The primary purpose of narrowband FM is
A. To be able to use frequencies above 108 MHz
B. Reduce channel noise
C. To conserve spectrum space
D. To be able to use frequencies below 88 MHz
The characteristic impedance of a 20 metre piece of transmission line is 52 ohms. If 10 metres were cut off, the impedance would be:
A. 52 ohms
B. 26 ohms
C. 39 ohms
D. 13 ohms
{"name":"RHM 1 ESAT PART 3", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Once the AM signal is amplified, it is fed to antenna with characteristic impedance that is ideally, With AM which of the following conveys no information?, In a frequency modulation receiver, the output of the high frequency oscillator is fed to the:","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/86-4179902/untitled.png?sz=1200-00000000001000001906"}
More Quizzes
KVÍZ - Poznáte futbalistov podľa tváre?
1050
SLEEP QUIZ
1050
What Kind of Soil Texture Are You?
14713
What black butler character are you?
320
Crack the Galaxy Formation: Spiral Galaxy Challenge
201082318
Free Laxative Pharmacology Knowledge Test
201025580
Basic DC Circuits: Test Your Direct Current Skills
201039024
Free Alumni Knowledge - Test Your Campus IQ
201022771
Discover Your Rebel Spirit With Our Anarchist Test
201029120
Free Basic Korean Verbs: Test Your Verbal Skills Now!
201037800
Free Algebra 1 & 2 Unit Test Answer Keys
201024906
Do I Have Sjögren's Syndrome: Test Your Dry Eye IQ
201073591