Oral Surgery II, Dr.Chhev Eangseng (51-100)
51. Plain Catgut suture’s strength retention time?
5 days
7 days
9 days
11 days
52. Which one is wrong about surgical silk suture?
Ease of handling
Good knot security
Withstand action of body fluid
Should be the choice of usage in present of infection
53. Surgical silk suture cannot be detected in tissues after?
1 year
2 years
3 years
4 years
54. Vircryl-Rapid suture could support wound up to?
12 days
16 days
20 days
24 days
55. Which suture has antibacterial effect?
Chromic Gut suture
Vicryl Plus suture
Vicryl Rapid suture
Prolene suture
56. Chromic Gut suture’s strength retention time at least?
6 – 8 days
8 - 10 days
10 – 14 days
14 – 18 days
57. Which one is wrong about Nylon suture?
Minimal tissue reaction
Has good memory
Non-pliable when moist
Useful for skin suture
58. Which one is wrong about POLYPROPYLENE (PROLENE) suture?
Minimal tissue reaction
Tensile strength for 4 years
Used in infected and contaminated wounds
Flexible
59. Things to consider when doing suture selection?
Knot-holding characteristics of the suture material
The tissues to be repaired
The tensile strength of the suture material
All are correct
60. Which one is wrong about interrupted simple suture?
Interferences between each stitch
Placed 4-8 mm apart to close large wounds, so that tension is shared
Loosening one will not produce loosening of the other
Strong and can be used in areas of stress
61. Which one is wrong about simple continuous suture?
Rapid technique and distributes tension uniformly
More water tight closure
Only 2 knots with associated tags
Free of Interferences between each stitch
62. Which one is wrong about simple locking suture?
Will avoid multiple knots
Distributes tension uniformly
Less Water tight closure
Prevents excessive tightening
63. Which one is wrong about vertical mattress suture?
Interfering with healing
To get eversion of wound margins slightly
Added support wound
For maximum tissue approximation
64. Which one is wrong about horizontal mattress suture?
Bringing greater areas of raw tissue into contact
Prevents the flap from being inverted into the cavity
Control post-operative hemorrhage from gingiva around the socket
Good blood supply to edge of incision
65. Which one is wrong about principle of knotting?
Use the simplest knot that will prevent slippage
Tying the knot as small as possible
Excessive tension
Avoid friction
66. Knotting hints?
Tying sutures too tightly strangulates the tissue
Placing the final throw as horizontally as possible to keep knot flat
Limiting extra throws to the knot
All are correct
67. Please choose the wrong one about suturing?
Close deep wounds in layers
Avoid retrieving needle by tip
Adequate tissue bite to prevent tearing
More tension is good to keep the tissue in place
68. Which one is wrong about suturing?
The bite should be about 4-6 mm from the wound margin
Usually the needle to be passed from mobile side to the fixed side from thinner to thicker & from deeper to superficial flap.
The tissues should not be closed under tension, since they will either tear or become necrotic around the suture
Knot must not lie on incision line
69. Which one is wrong about needle?
Needle should enter perpendicular to tissue surface
Needle grasped at 1/2th to half the distance from eye
Needle passed along its curve
The bite should be equal on both sides of the wound margin
70. The distance between sutures to another should be about 3-4 mm apart?
To prevent strangulation of the tissue
To allow escape of the serum or inflammatory exudate
To get more strength of the wound
To ease the suturing procedure
71. Symptoms of cellulitis?
Localized pain
Erythema
Swelling
All are correct
72. Truth about abscess?
The stage after cellulitis
No blood supply
Antibiotic cannot penetration on abscess
All are correct
73. The most common oral bacterial infection is?
Periapical infection
Periodontal infection
Herpes labialis infection
Periapical infection and periodontal infection
74. Cellulitis stage of bacterial odontogenic infection?
days 0 - 3
days 3 – 5
days 5 – 7
days 7 – 9
75. Inoculation stage of bacterial odontogenic infection?
days 0 – 3
days 3 - 5
days 5 – 7
days 7 – 9
76. Abscess stage of bacterial odontogenic infection?
days 0 - 3
days 3 - 5
days 5 – 7
days 7 – 9
77. Serial stages of bacterial odontogenic infection?
Inoculation, cellulitis, abscess and resolution stage
Cellulitis, Inoculation, abscess and resolution stage
Abscess, inoculation, cellulitis, and resolution stage
Resolution, abscess, inoculation, and cellulitis stage
78. Spread of infection?
Direct spread via tissue planes and spaces
Lymphatic spread
Haematological spread
All are correct
79. Why local anesthesia has less effect after injecting at the infection side?
High protein binding
Low pH
High pH
Higher temperature
80. What is bacteremia?
Blood poisoning, especially that caused by bacteria or their toxins
Presence of bacteria in the blood
Presence of bacteria in the brain
Presence of bacteria in the bone marrow
81. What is Septicemia?
Blood poisoning, especially that caused by bacteria or their toxins
Presence of bacteria in the blood
Presence of bacteria in the brain
Presence of bacteria in the bone marrow
82. Ophthalmic symptoms of cavernous sinus thrombosis?
Unable to move eye (ophthalmoplegia)
Drooping upper eyelid (ptosis)
Extrusion of the eye (proptosis)
All are correct
83. Symptoms of acute maxillary sinusitis?
Mid-facial pain
Upper posterior teeth are tender to percussion
Pain varies with head posture
All are correct
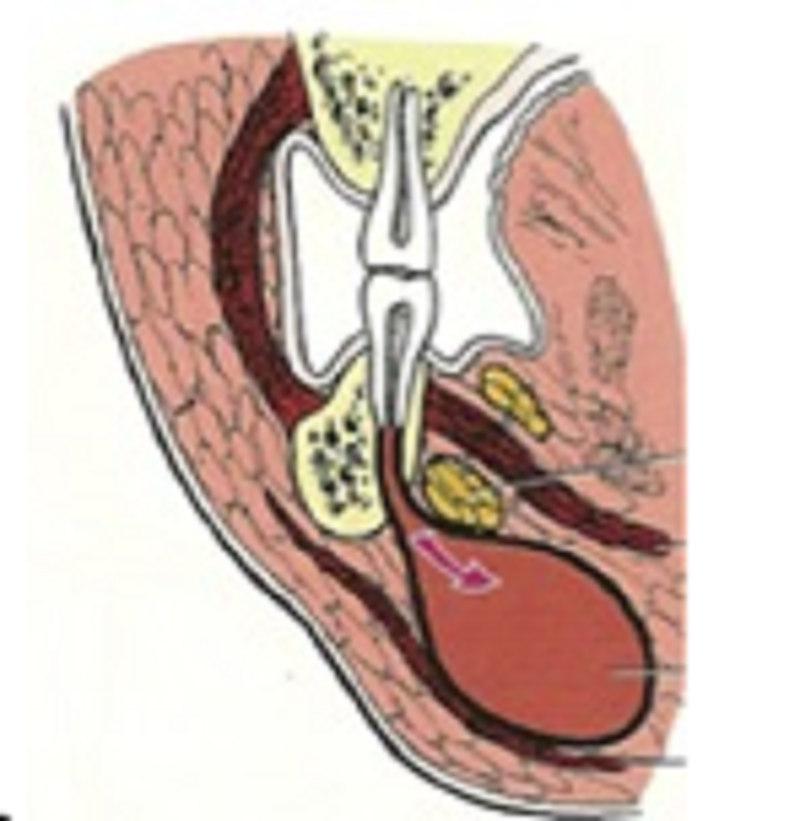
84. The following picture shows?
Sub-lingual space infection
Sub-mylohyoid infection
Submandibular infection
All are not corrects
85. Ludwig’s angina is an acute severe bilateral cellulitis of?
Submandibular spaces
Sublingual spaces
Submandibular and sublingual spaces
All are not corrects
86. Actinomycosis a chronic disease of soft tissue caused primarily by?
Aerobic bacteria
Anaerobic bacteria
Aerobic bacteria and Anaerobic bacteria
All are not corrects
87. Osteomyelitis is more common in the mandible due to?
Richer blood supply
Poorer blood supply
Genetic factor
All are corrects
88. Osteomyelitis treatment?
Aggressive surgical debridement of necrotic bone
Intravenous antibiotics with good bone penetration
Aggressive surgical debridement of necrotic bone & Intravenous antibiotics with good bone penetration
All are not corrects
89. Treatment of odontogenic infection?
Remove the cause whenever possible (e.g. Extract the tooth)
Drain pus and maintain drainage (place a drain if necessary)
Antibiotics and Supportive therapy (fluids, rest, nutrition, analgesia)
All are correct
90. What is the antibiotic prophylaxis?
Prevention of infection complication using antimicrobial therapy
Prevention supra-infection
Prevent the germ to spread in the facial space
Prevention supra-infection and Prevent the germ to spread in the facial space
91. Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid combination?
Inhibits beta lactamase
Acts against S Aureus,
H influenza and E coli
None of above
92. A drain is placed?
For the air to come in
To allow further pus and fluid to drain
For the air to come in and to allow further pus and fluid to drain
All are corrects
93. Cause of abscess treatment failure?
Inadequate drainage and antibiotic failure or wrong antibiotics
Immunosuppressed patient
Foreign body (retained root, non-vital piece of bone)
All are correct
94. Which is the correct statement define antibiotic resistance?
The ability of antibiotic killing bacterial
The ability of bacteria and other microorganisms to resist the effects of an antibiotic.
The ability of bacteria synthesis under the development period
All are not corrects
95. A triangular flap has been used commonly for?
Surgical removal of upper wisdom tooth
Surgical removal of lower wisdom tooth
Surgical removal of periapical cyst
All are correct
96. Semi-lunar flap has been used commonly in oral surgery for?
Apicoectomy
Surgical removal of mandibular torus
Surgical removal of palatal torus
All are not correct
97. The secondary intension healing means?
The wound that is healing in the surgical incision which the flap was sutured edge to edge
Wound involves considerable tissue lose and let the wound to heal spontaneously
Delay wound healing
All are correct
98. A common mistake to try to remove broken roots without surgery by using only elevators could cause?
The root is sometimes displaced into the inferior alveolar nerve canal for lower third molar
The root is sometimes displaced into the infra-temporal fossa for unerupted upper third molar
The root is sometimes displaced into the maxillary sinus
All are correct
99. A fractured root tip could be considered to leave when?
The vital root tip is 2-5 millimeters in length
The vital root tip is close to maxillary sinus
The vital root tip is close to lower inferior alveolar nerve
All are correct
100. The primary intension healing means?
The wound that is healing in the surgical incision which the flap was sutured edge to edge
Wound involves considerable tissue lose and let the wound to heal spontaneously
Delay wound healing
All are not correct
{"name":"Oral Surgery II, Dr.Chhev Eangseng (51-100)", "url":"https://www.supersurvey.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"51. Plain Catgut suture’s strength retention time?, 52. Which one is wrong about surgical silk suture?, 53. Surgical silk suture cannot be detected in tissues after?","img":"https://www.supersurvey.com/3012/CDN/101-4997910/screenshot-2024-05-24-201702.png?sz=1200-00000000001000010257"}