Head and neck anatomy 3
Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz
Test your knowledge of head and neck anatomy with our engaging quiz! This quiz consists of 30 questions focusing on various bones, sinuses, and anatomical structures in the head and neck region.
- Ideal for students and medical professionals
- Includes multiple-choice questions
- Challenging yet educational
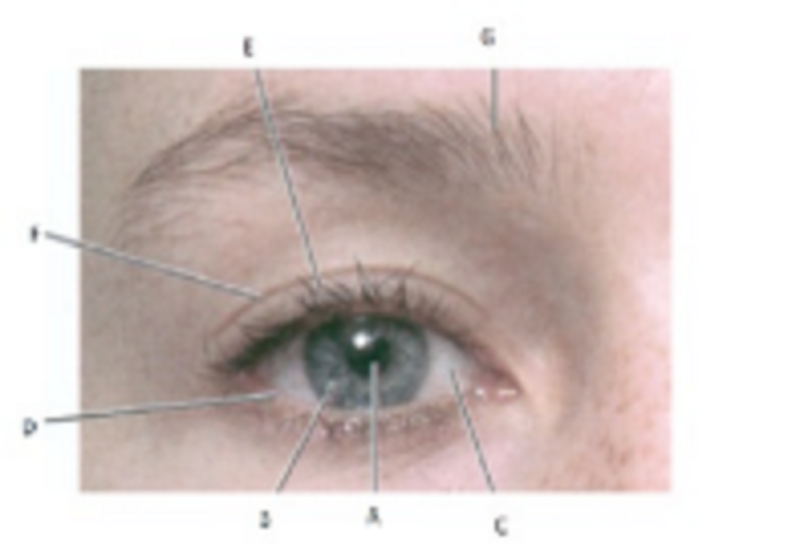
A, B and C are…………………………………………:
Pupil, Iris, and Sclera
Inferior palpebra, Superior palpebra, and Eyelashes
Eyebrow, Eyelashes and Pupil
Sclera, Inferior Palpebra and Superior Palpebra
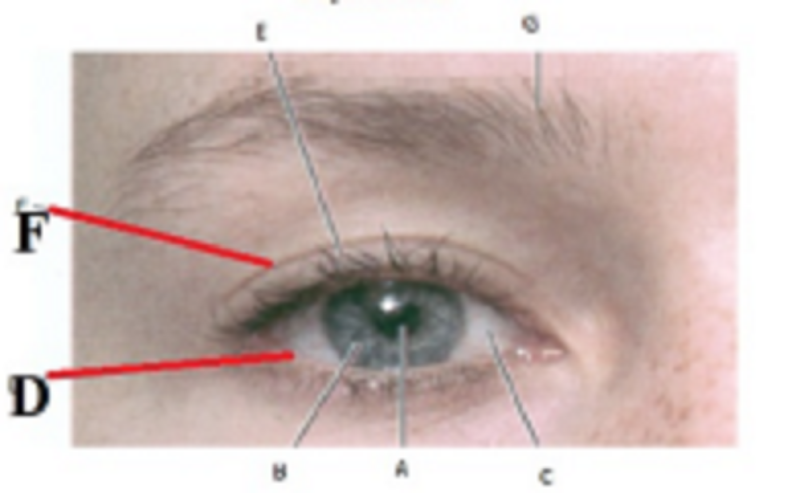
D and F are…………………………………….:
Inferior and Superior palpebra
Eyebrow and eyelashes
Pupil and Iris
Iris and Sclera

E and G are is …………………………..:
Eyelashes and eyebrow
Inferior and superior palpebra
Pupil and Iris
Pupil and Sclera
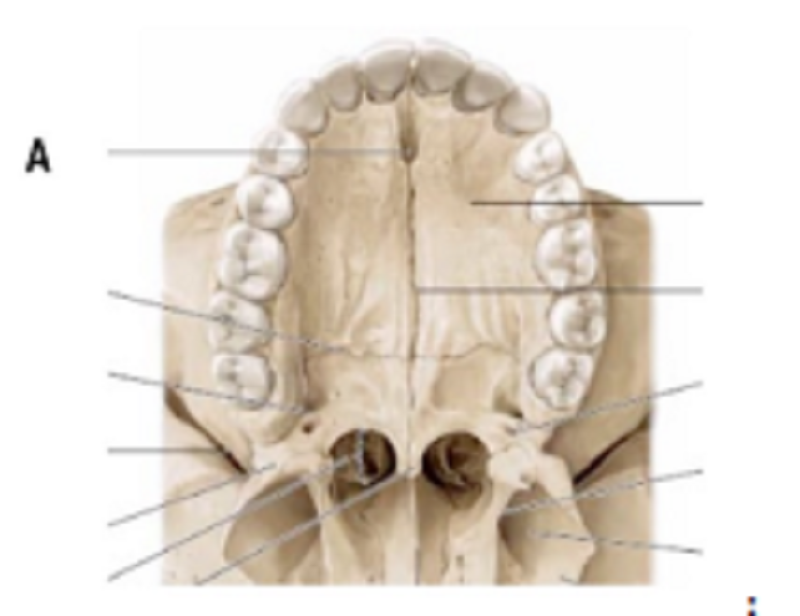
A is …………………………..
Greater Palatine foramen
Lesser Palatine foramen
Nasopalatine foramen
Transversal suture
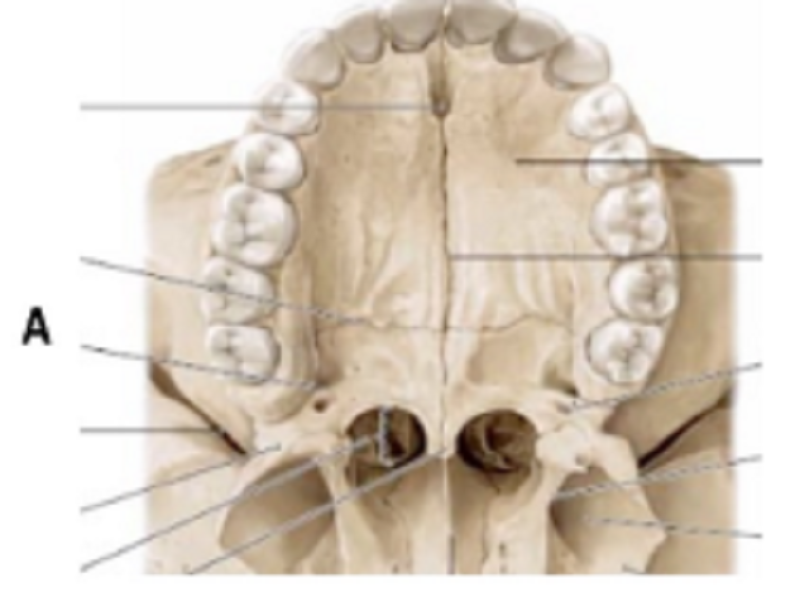
A is …………………………..
Greater Palatine foramen
Lesser Palatine foramen
Nasopalatine foramen
Transversal suture
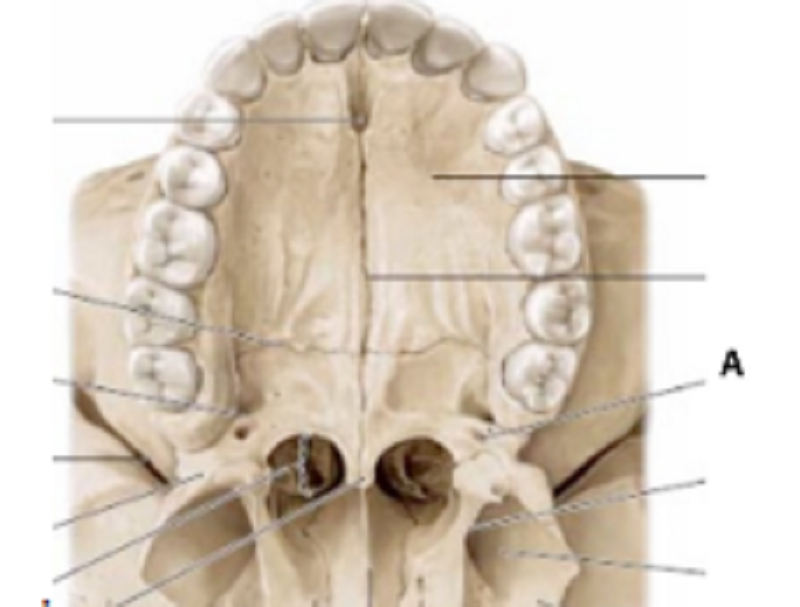
A is …………………………..
Greater Palatine foramen
Lesser Palatine foramen
Nasopalatine foramen
Transversal suture
The external nose consists of:
Nasal bones and frontal processes of maxillae
Cartilaginous part formed by alar and lateral nasal cartilages
Bony part formed by nasal bone and frontal processes of maxillae
All of them
Maxillary sinuses have the following functions:
Reduce weight of skull
Serve as resonating chambers for sound production
Increase surface area for warming and humidifying inspired air
All of them
Frontal sinuses are supply by:
Supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves and arteries
Maxillary and ophthalmic nerve and arteries
Sphenopalatine and ophthalmic nerves and arteries
All are correct
Paranasal sinuses are innervated by:
Branch of ophthalmic nerve (V1 of CNV)
Branch of maxillary nerves, pterygopalatine ganglion (V2 CNV)
Olfactory nerves
Branch of ophthalmic nerve (V1 CNV) and branch of maxillary nerve, pterygopalatine ganglion (V2 CNV)
Maxillary sinuses is connected with
Middle meatus, Frontonasal duct
Middle meatus, Semilunar hiatus
Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess
Superior meatus, opening of superior meatus
Anterior and middle ethmoidal cells are connected with:
Middle meatus, Frontonasal duct
Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess
Superior meatus, opening of superior meatus
Middle meatus, opening of middle meatus
Posterior ethmoidal cells are connected with:
Middle meatus, Frontonasal duct
Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess
Superior meatus, opening of superior meatus
Middle meatus, opening of middle meatus
Frontal sinus is connected with:
Middle meatus, Frontonasal duct
Middle meatus, Semilunar hiatus
Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess
Superior meatus, opening of superior meatus
Middle meatus, opening of middle meatus
Sphenoidal sinus is connected with:
Middle meatus, Frontonasal duct
Middle meatus, Semilunar hiatus
Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess
Superior meatus, opening of superior meatus
Middle meatus, opening of middle meatus
The infection of maxillary sinus can be caused by:
Meningitis or brain abscess
Toothache or extraction (maxillary sinusitis)
Spread of infection to cavernous sinuses, pituitary gland, optic nerves or brainstem
Orbital cellulitis
The infection of ethmoidal air cells can cause:
Meningitis or brain abscess
Toothache or extraction (sinusitis)
Spread of infection to cavernous sinuses, pituitary gland, optic nerves or brainstem
Orbital cellulitis
Infection is related to frontal sinus can cause:
Meningitis or brain abscess
Toothache or extraction (sinusitis)
Spread of infection to cavernous sinuses, pituitary gland, optic nerves or brainstem
Orbital cellulitis
The infection of sphenoidal sinus can cause:
Meningitis or brain abscess
Toothache or extraction (sinusitis)
Spread of infection to cavernous sinuses, pituitary gland, optic nerves or brainstem
Orbital cellulitis
Which statement is NOT TRUE:
Maxillary sinus is the smallest paranasal sinuses and already present at birth
Ethmoidal sinus consists of anterior, middle, and posterior ethmoidal air cells
Maxillary sinus are innervated by V1 and V2 of Trigeminal nerve
The lateral part of sphenoidal sinuses has relationship with carvenous sinus and internal carotid artery
{"name":"Head and neck anatomy 3", "url":"https://www.supersurvey.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of head and neck anatomy with our engaging quiz! This quiz consists of 30 questions focusing on various bones, sinuses, and anatomical structures in the head and neck region.Ideal for students and medical professionalsIncludes multiple-choice questionsChallenging yet educational","img":"https:/images/course7.png"}
More Surveys
Head and neck Anatomy
52260
Head and neck Anatomy 2
24120
MCQ oral pathology 3
512634
PT 6130/6131 Feedback
12623
Oral Pathology 1
61300
Clinical biochemistry L4
168123
Physiology Review
3230
Medical biology 1
74109
Kinesiology Concept Confidence
191025
Biochemistry 2021
5930110
Neuroophthalmology-Basic clinical aspects
147466
Clinical Biochemistry L5
3116114





















