Dental Imagery II 1

Dental Radiography Knowledge Quiz
Test your knowledge of dental imagery with our comprehensive quiz designed for dental professionals and students alike. This quiz covers essential concepts related to digital and traditional radiography, including techniques, structures, and safety measures.
Join now to enhance your understanding of:
- Types of radiographic films
- Digital imaging benefits
- Radiation safety practices
- Exam techniques and processing methods
What type of film allows the entire dentition to be viewed on a single film?
Occlusal
Cephalometric
Panoramic
All of are corrected
What type of device does digital radiography use to record images taken of the patient's teeth?
Standard x-ray film, with scanner
Electronic sensor
MRI sensor
All of are corrected
What step helps prevent a large radiolucent area near the palate as seen on panoramic x-rays?
Placing the patient's midsagittal plane perpendicular to the floor
Having the patient stand as straight as possible
Having the patient place their tongue in the roof of their mouth
Having the patient smile with their lips apart
Why does digital radiography require less radiation than traditional x-rays?
The x-ray beams are more powerful
It uses lower wave-length radiation
Sensors are more sensitive.
All of are corrected
Use of the FDI index of tooth charting enables dental professionals from many countries to accurately read dental charts. Which of the following is the FDI notation for the upper left deciduous first molar?
35
55
64
74
Some patient attends with a suspected carious lesion in the lower right first molar tooth. Which radiographic view would normally be taken to diagnose this lesion?
Horizontal bite-wing
Occlusal
Periapical
Vertical bite-wing
When an x-ray film has been exposed to ionizing radiation, it requires processing to develop the image. Which of the following is not a feature of an automatic processor?
Developing tank
Fixing tank
Sensor
Water tan
Digital x-ray sensors:
Cannot be sterilized
Are sealed and waterproofed
Must be covered with a barrier
All of are corrected
What absorbs more of the long wave length radiation not useful in producing a good diagnostic image?
Aluminum filter
Film packet
Lead apron
Patient
Panoramic radiographs are?
All of are corrected
Used in diagnosing temporomandibular joint disorders
Used with annual posterior bitewings
Useful to see impacted, supernumerary teeth and unerupted teeth
. Digital X-ray systems:
A traditional X-ray tube head is used
All of are corrected
Reduces radiation exposure by 90% to the patient
Use an intraoral sensor
Following which procedures as the X-ray operator will reduce your exposure to radiation:
All of are corrected
Never holding the film or X-ray tube head while exposing an X-ray
Standing 6 feet or more away from the X-ray tube head
Standing behind a barrier or outside of the treatment room
What is the term used to describe the appearance of dental caries in a processed radiograph?
Contrast
Overlapped
Radiolucent
Radiopaque
Pick all the benefits of digital imaging:
All of are corrected
Diagnostic capability is better and higher resolution quality
Less storage space is needed
Radiation exposure is less for the patient
Hat error occurred when a foreshortened image appears on a radiograph?
Excessive horizontal angulation
Excessive vertical angulation
Insufficient angulation
All of are none corrected
. What is an example of a radiopaque anatomical structure on a processed radiograph?
Decay
Enamel
Pulp
Sinus
The two major types of dental examination are:
Extraoral and bite wings
Extraoral only
Intraoral and extraoral
Intraoral only
Debris/Dark spots on processed radiograph is most likely caused by?
Film was handled incorrectly
Patient had not brushed their teeth
Processing rollers were not cleaned properly
Wrong sized film was used
What is one way you can reduce exposure of radiation to the patient?
Decreasing horizontal angulation
Using a rinn
Using F speed film
Vertical angulation
The purpose of the collar on the lead apron is to reduce the dose of radiation to the:
Blood vessels
Reproductive system
Saliva glands
Thyroid
Pick an advantage of being able to in hance a digital image?
Almost instant viewing of the radiograph
Films are not easier to see decay
Negative images are available
Radiation exposure time is reduced
An elongated image on a dental radiographic is most likely the result of:
Excessive horizontal angulation
Excessive vertical angulation
Insufficient horizontal angulation
Insufficient vertical angulation
The advantages of digital radiographs are?
All of are corrected
Electronic messaging (email)
Immediate viewing of the film
Less radiation exposure to the patient
. What region do you begin exposing if the patient has a bad gag reflex?
Anterior region
Mandibular region
Maxillary region
Posterior region
What is an example of X-ray equipment that can be sterilized?
Control panel
Film placement holder
Lead apron
Tube head
What tissue is the most radio-resistant?
Blood vessels and blood forming organs
Muscle and nerve
Salivary glands
The reproductive system
He film captures a major part of the maxillary or mandibular on a single radiograph?
Bitewing
Occlusal
Panoramic
Periapical
. Choose the infection control guidelines for the darkroom:
All of are corrected
Place barriers on countertops
Use over gloves and change your gloves
Wash and dry hands after films are placed in the processor
Which of the following best describes the appearance of bone on a radiograph?
Cortical bone appears radiopaque, cancellous bone appears radiolucent
Cortical bone appears radiolucent, cancellous bone appears radiopaque
All bones appear radiolucent
All bones appear radiopaque
The inverted Y landmark is composed of which two structures?
Junction of the right and left nasal cavities
Inferior border of the nasal cavity and anterior border of maxillary sinus
Floor of orbit and floor of maxillary sinus
Floor of orbit and anterior border of maxillary sinus
Which of these structures appear radiopaque?
Maxillary sinus
Nasal fossa
Maxillary tuberosity
Mental foramen
. Which is the proper method for mounting radiographs?
As if you were facing the patient
If you were looking out from patients tongue
Mounted with dot toward the distal
Should be mounted with dot toward the mesial
Who is allowed to make an initial interpretation of a dental radiograph?
The patient
The assistant
Trained assistant who passes DANB Radiation exam
All of are not corrected
To whom should an initial interpretation be given?
Dentist
Patient
anyone who asks
All of are not corrected
Name the following intraoral radiograph:
Periapical radiograph
Bitewing radiograph
Occlusal radiograph
All of are corrected
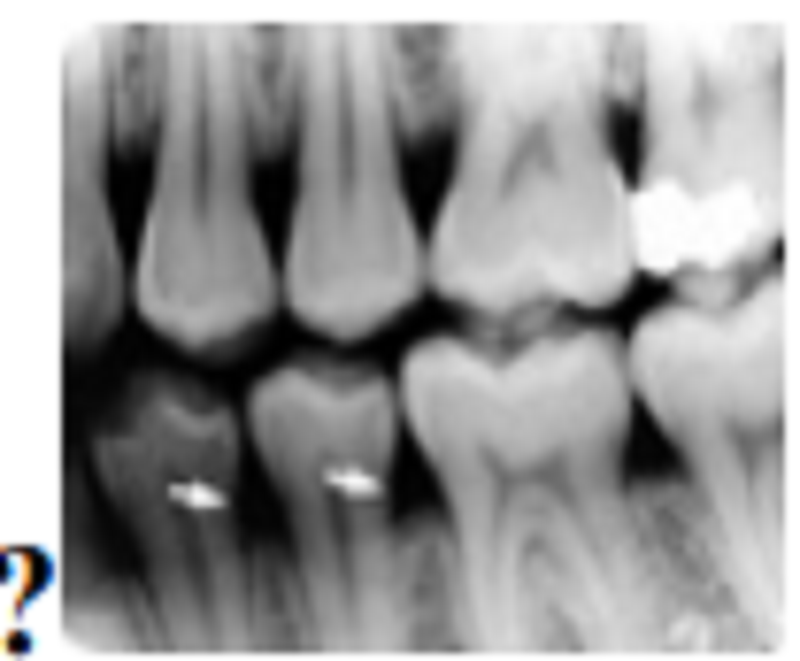
Which of these structures appear radiolucency?
Periodontal disease
Diastema
Cervical burnout
Resorbing alveolar crest
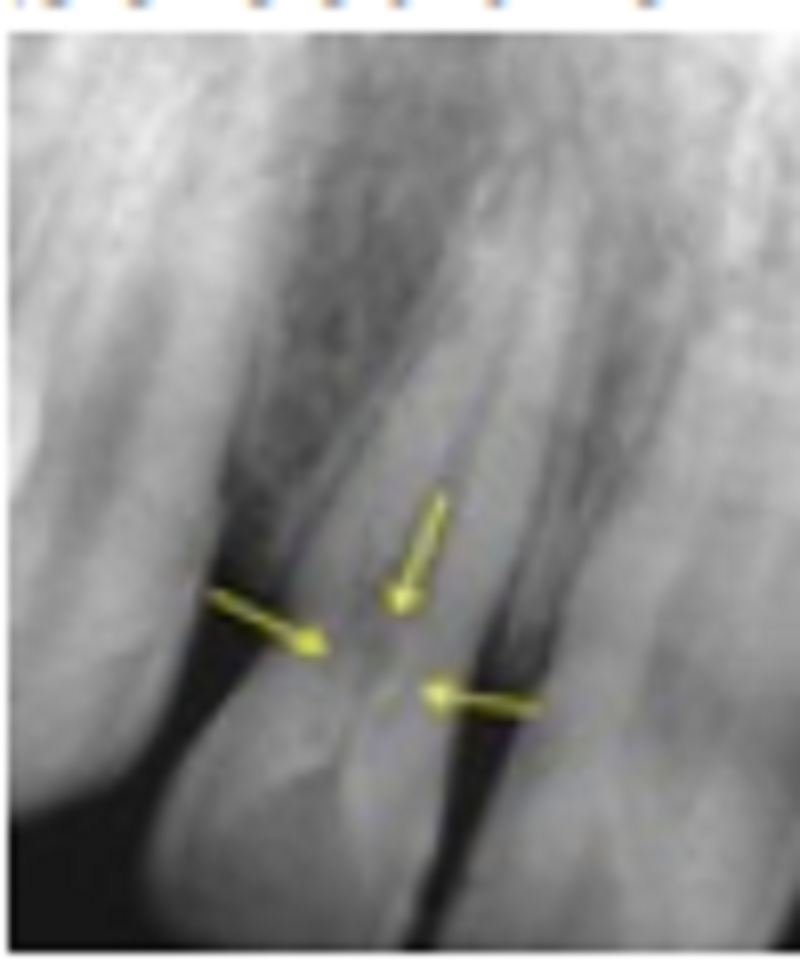
Select the most appropriate term for the anomaly associated with the 1st (most mesial) molar:
Diastema
Concrescence
Dilaceration
Dens invaginatus
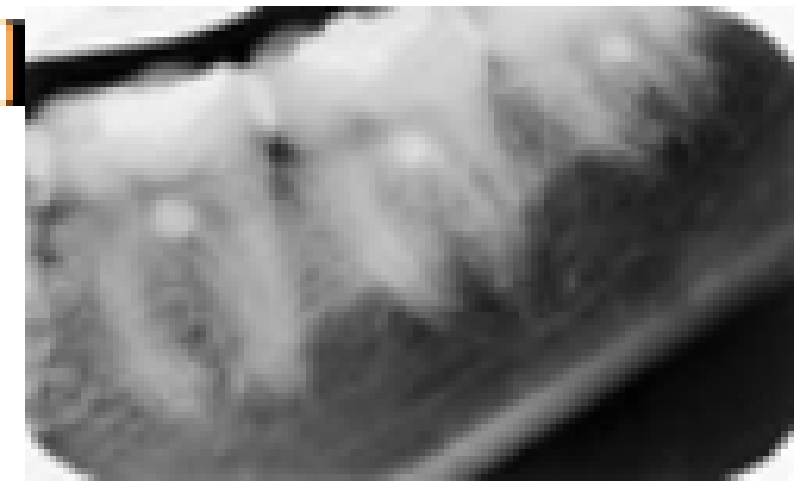

Observe the bifurcation area of these three molars. All have the same round, radiopaque,anomalous appearance. What term best describes this?
Pulp stone
Dentine
Buccal enamel defect
Enamel pearl
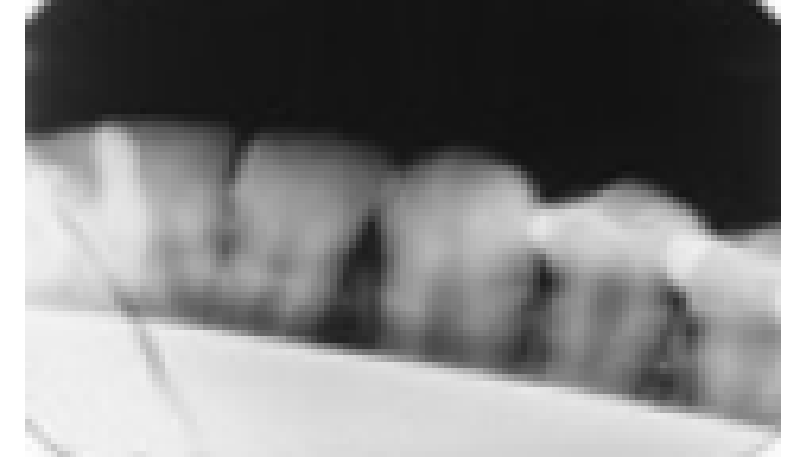

. We can see at least two errors in this image. Which do you think they are?
Rectangular BID cone cut and film bending
Rectangular BID cone cut and static electricity
Lead apron and static electricity
Lead apron and film bending
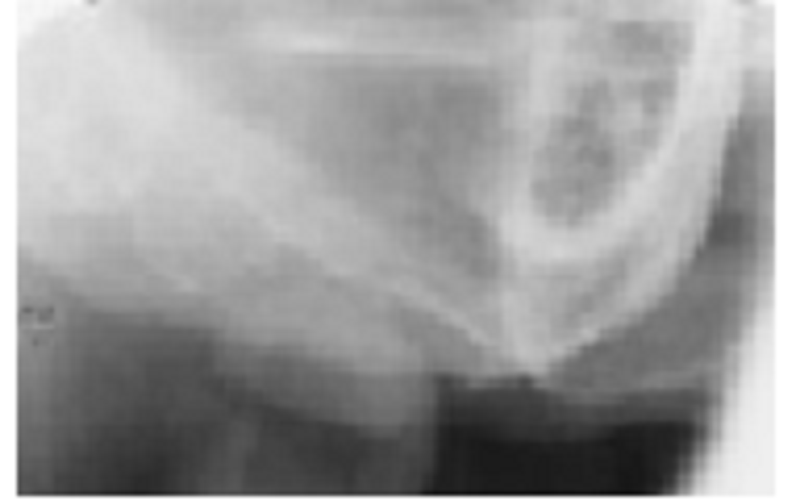
At least two errors are in this edentulous maxillary posterior periapical view. Select the best choice:
cImproper horizontal and vertical angulation of the beam
Excessive vertical angulation of the BID and round BID cone cut
Excessive vertical angulation of the BID and bent film in the processor
Round BID cone cut and excessive distal angulation of the BID
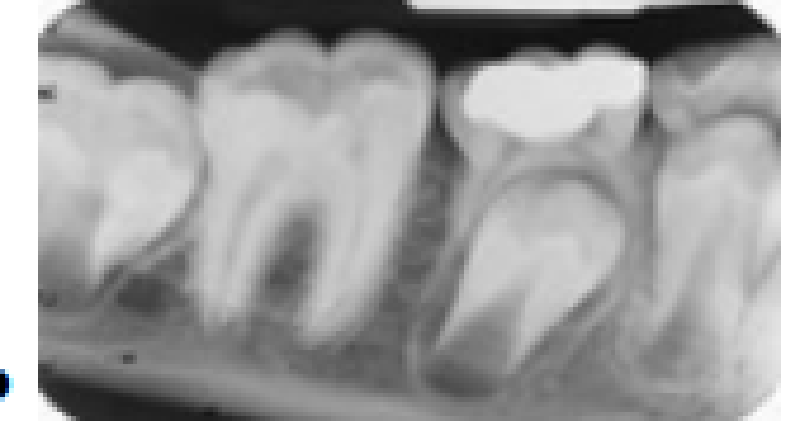
One major error is in this radiograph. What is the cause?
Foreshortening
Elongation
Improper horizontal angulation of the BID
Excessive negative vertical angulation of the BID
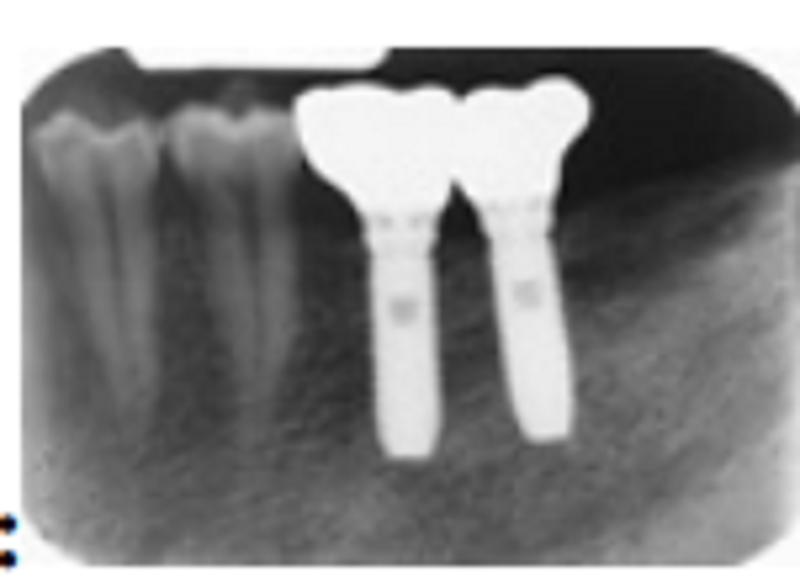
The correct term(s) that best describe the radiopaque objects is:
Implants
Implants and appliances
Implants, appliances, and crowns
Screw-teeth
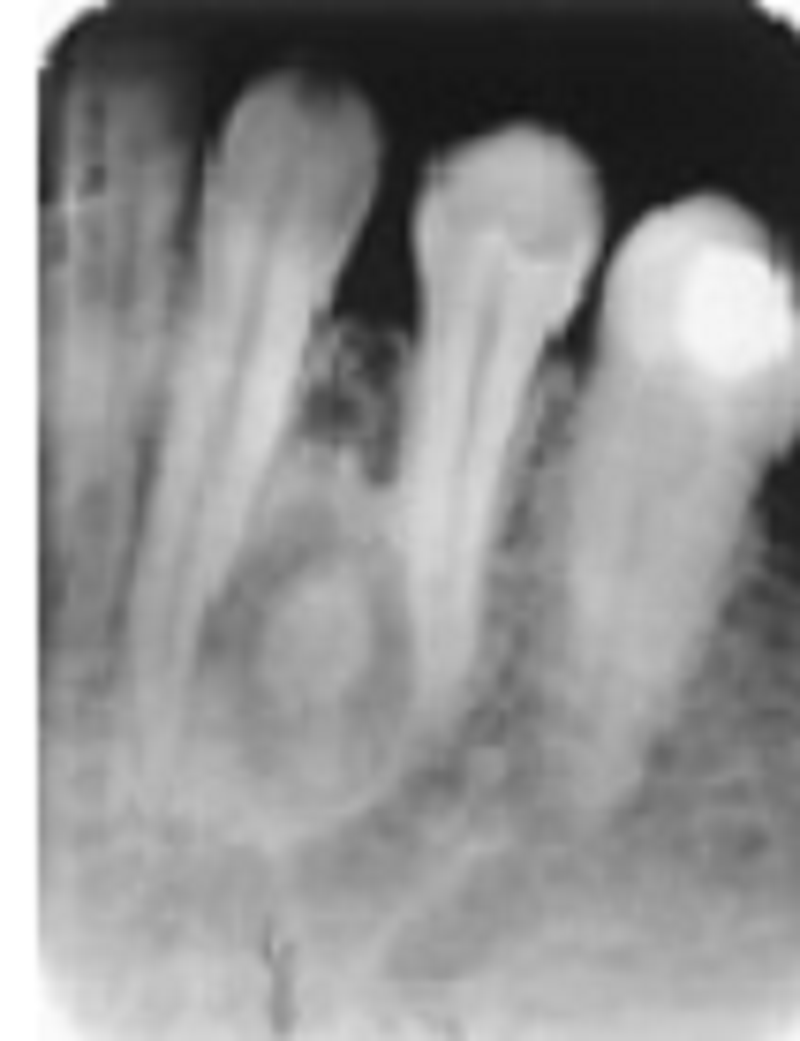
This patient is a 32-year-old white woman. This was the only lesion she had, and the adjacent teeth were vital. The condition we see here is:
Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia
Ossifying fibroma
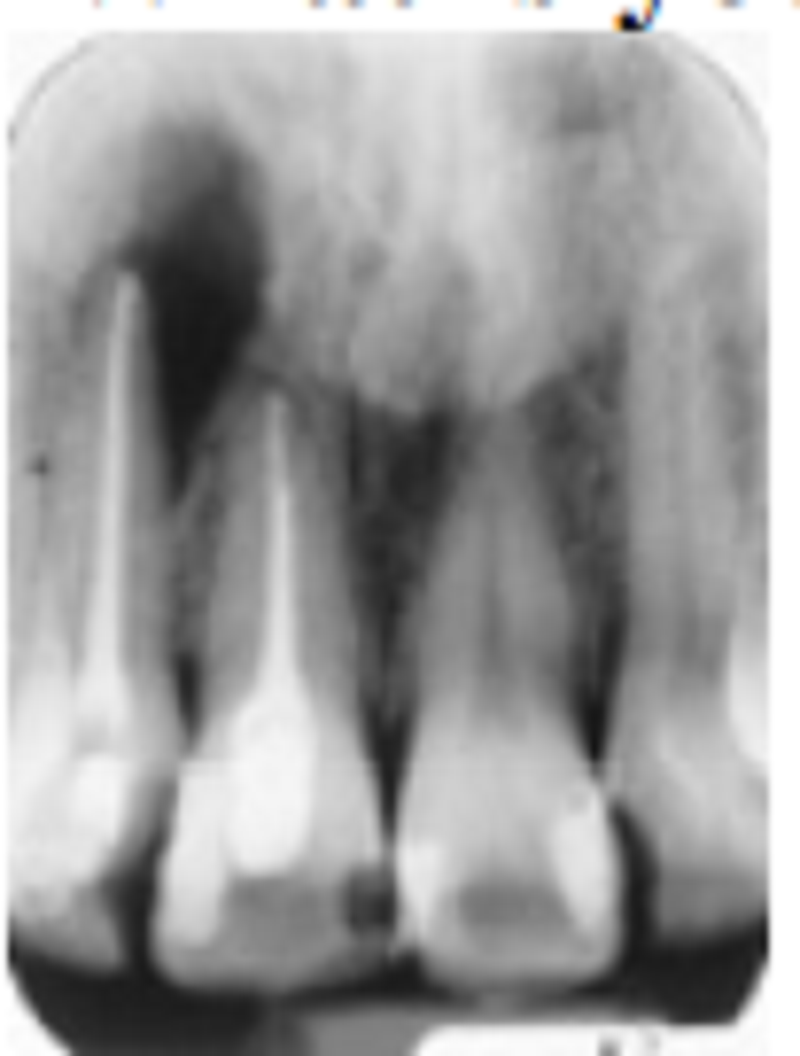
What is your assessment of the periapical radiolucent area at the apex of the lateral incisor?
Recurrent abscess formation
Periapical cementum dysplasia
Surgical traumatic cyst
Apical scar
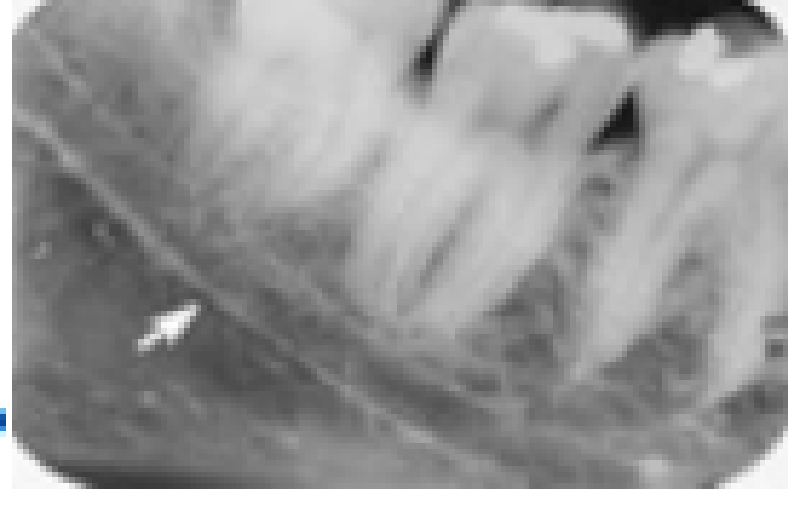
The arrow points to a normal anatomic structure. Which one is it?
Inferior mandibular canal
Posterior alveolar canal
Lingual canal
Mylohyoid line or ridge
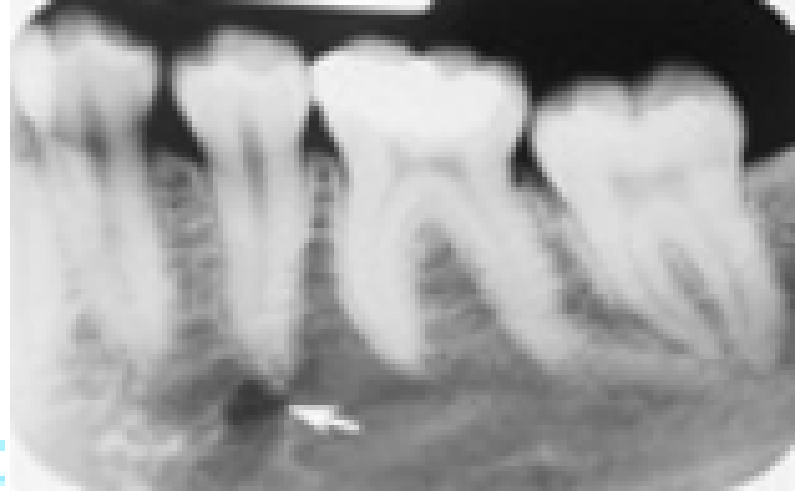
The 2nd premolar is vital and asymptomatic, and the patient is a black female. Identify the radiolucency to which the arrow is pointing:
Periapical cementum dysplasia
Periapical cyst or granuloma
Mental foramen
Lateral periapical cyst
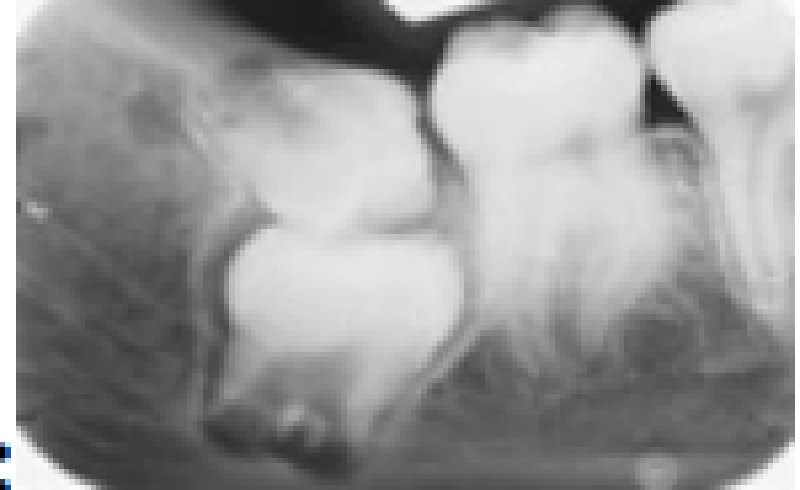
Here we see a very good radiograph of the 3rd molar region. List the anomalies seen in this radiograph:
Impacted 2nd molar and microdontic 3rd molar
Impacted 3rd molar and supernumerary 4th molar
Impacted 2nd molar, microdontic impacted 3rd molar, and dilacerated mesial root of the 2nd molar
Mpacted 3rd molar, impacted supernumerary 4th molar, and dilacerated mesial root of the 2nd molar
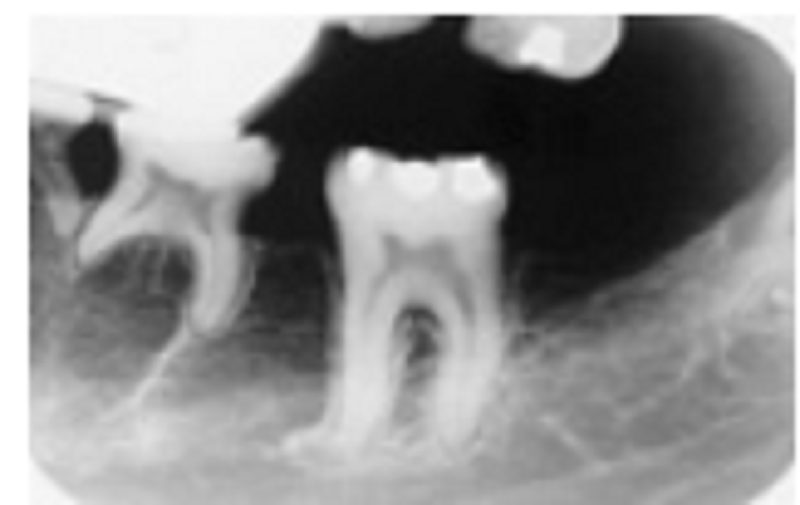
Notice that there are at least two, possibly three, missing permanent teeth with the retention of at least one or two primary teeth. Among the following list, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Cleidocranial dysplasia
Hypohydrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Gardner’s syndrome
Cherubism
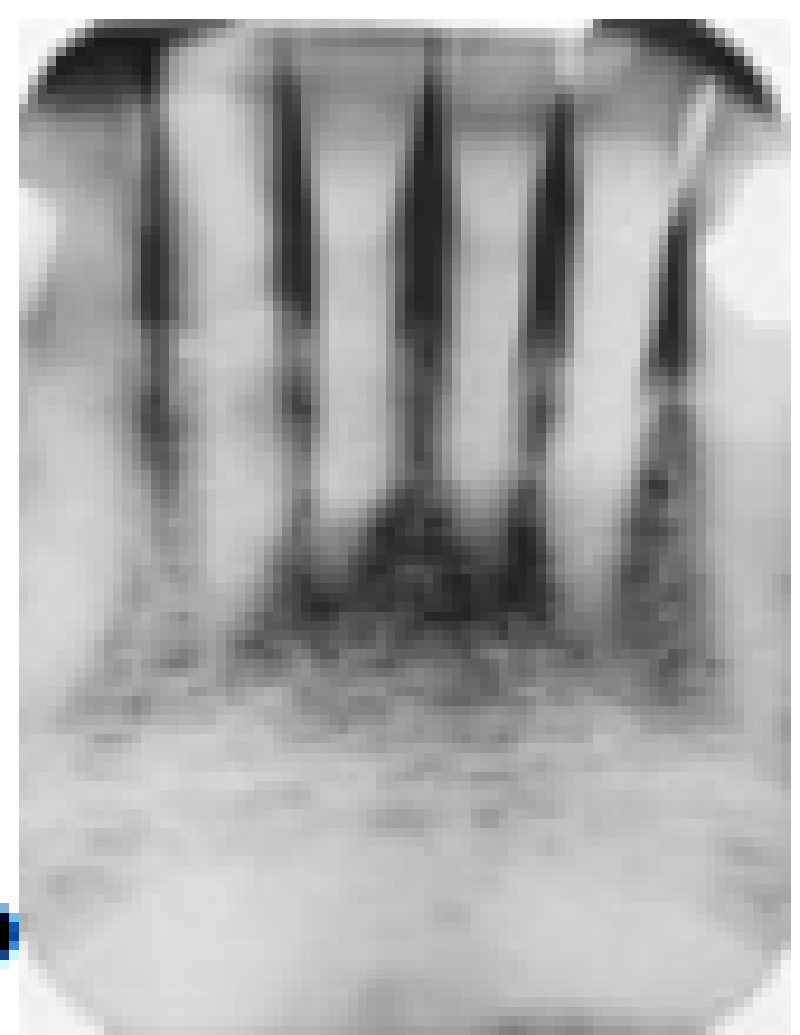
This patient is a 72-year-old man. Notice that the pulp and root canal spaces are significantly diminished. What is the cause of this?
Attrition and age
Amelogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentin dysplasia type 1
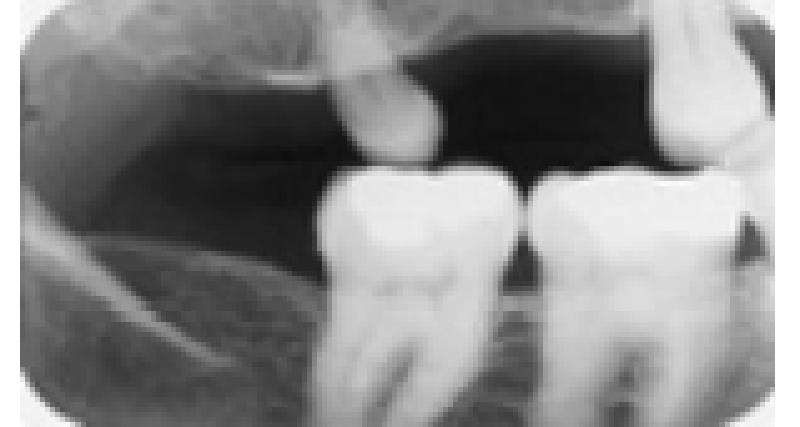
Observe the posterior maxillary tooth. What term(s) best describe(s) this tooth?
Microdontia
Disto/para molar
Macrodontia
Anodontia
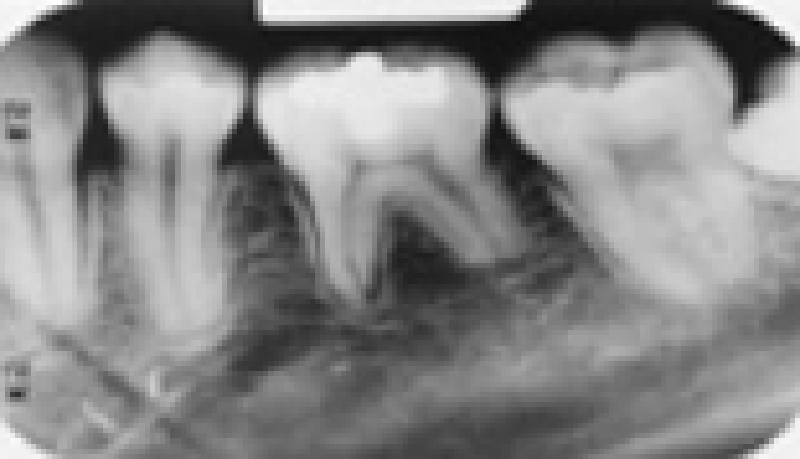
This young adult is missing her 1st premolars; there is also a technique error in this film. Which choice best represents this case?
Bent film and foreshortening
Static electricity and shovel-shaped incisor syndrome
Nasolabial fold and taurodontism
Bent film and orthodontic root resorption
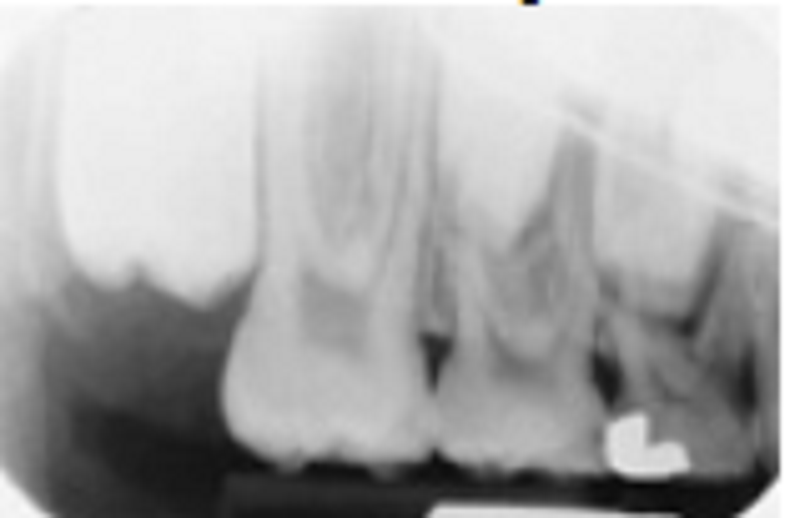
. Two technique errors are visible in this image. Identify the cause of the two errors?
Excessive positive vertical angulation and bent film
Insufficient vertical film placement and rectangular BID cone cut
Insufficient positive vertical angulation and processor damage to bent film
Elongation and partial image obscurity
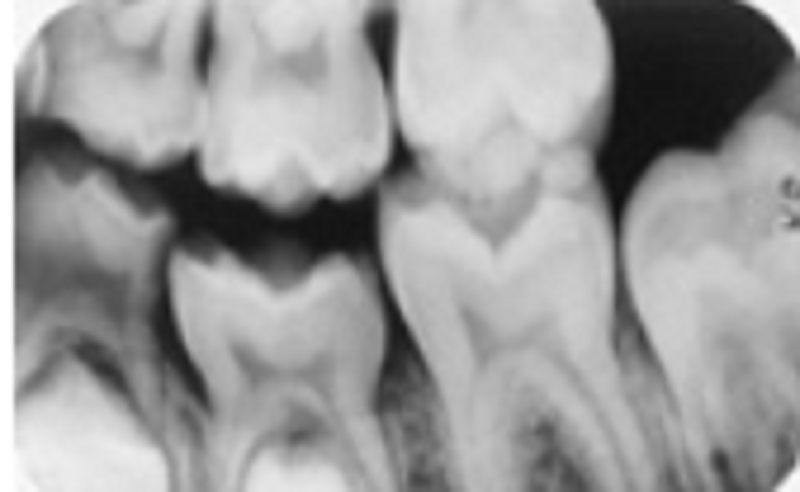
Though the contacts occlusion is mostly open, what went wrong with this bitewing?
Excessive positive vertical angulation
Movement
Excessive negative vertical angulation
Nothing went wrong; it is okay
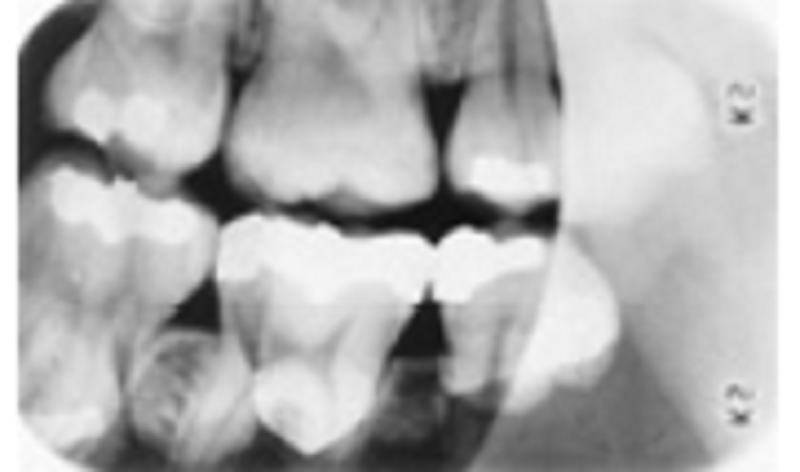
Observe this radiograph. One of the other films in the series was blank. What went wrong here?
Round BID cone cut
Fog
Double exposure
Bending film
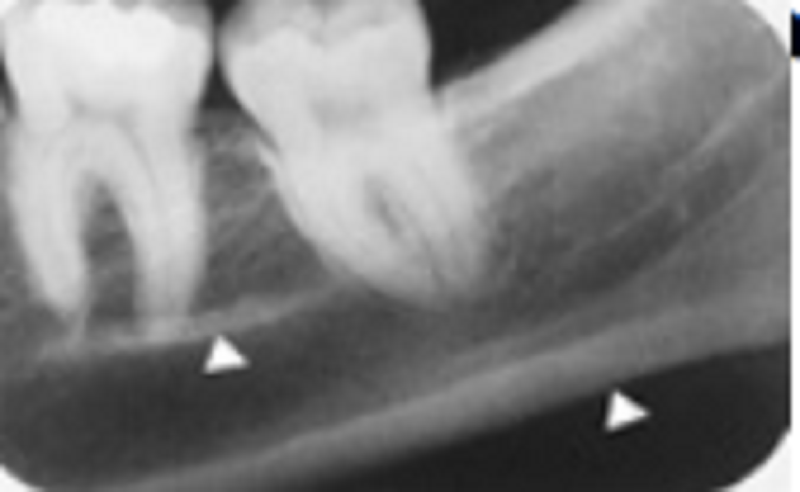
N this periapical radiograph, there are two white arrow heads. To what structures do they point?
Nferior mandibular canal and inferior cortex
Submandibular fossa and inferior cortex
Inferior cortex and external oblique ridge
Mylohyoid ridge and inferior cortex
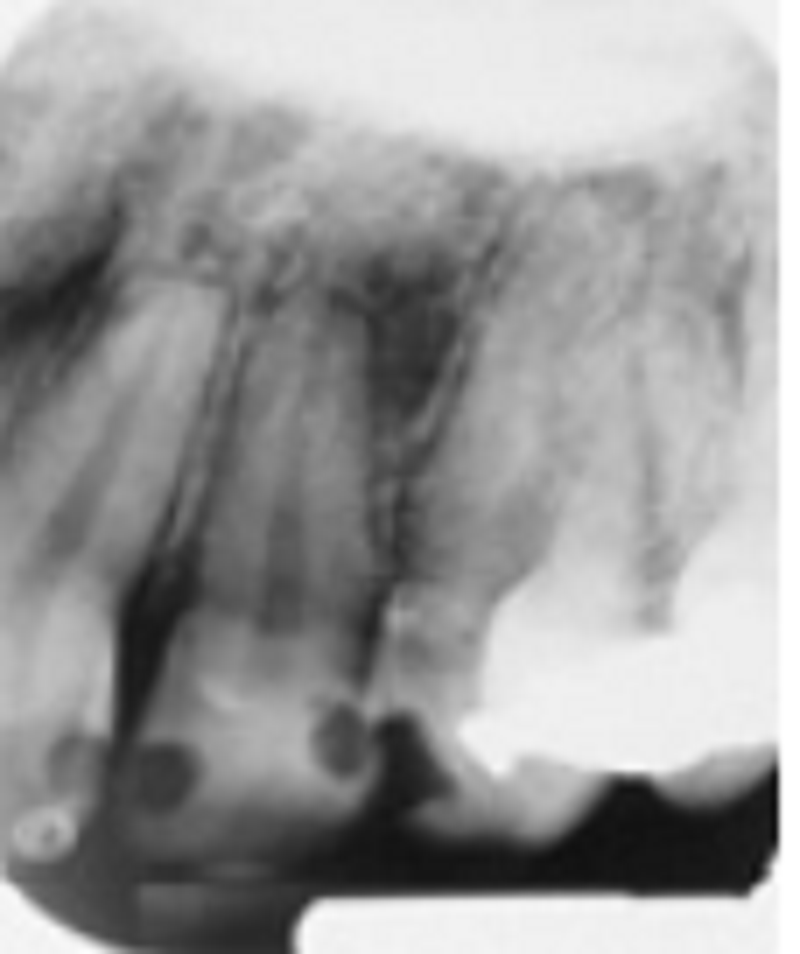
Regarding this image, select the one most accurate choice listing what can be seen in this image:
Orthodontic root resorption, radiolucent restorations, palatal torus
Shovel-shaped incisor syndrome, class 3 caries, film bent and damaged in processor
External root resorption, class 3 caries, palatal torus
Orthodontic root resorption, radiolucent restorations, film bent and damaged in processor
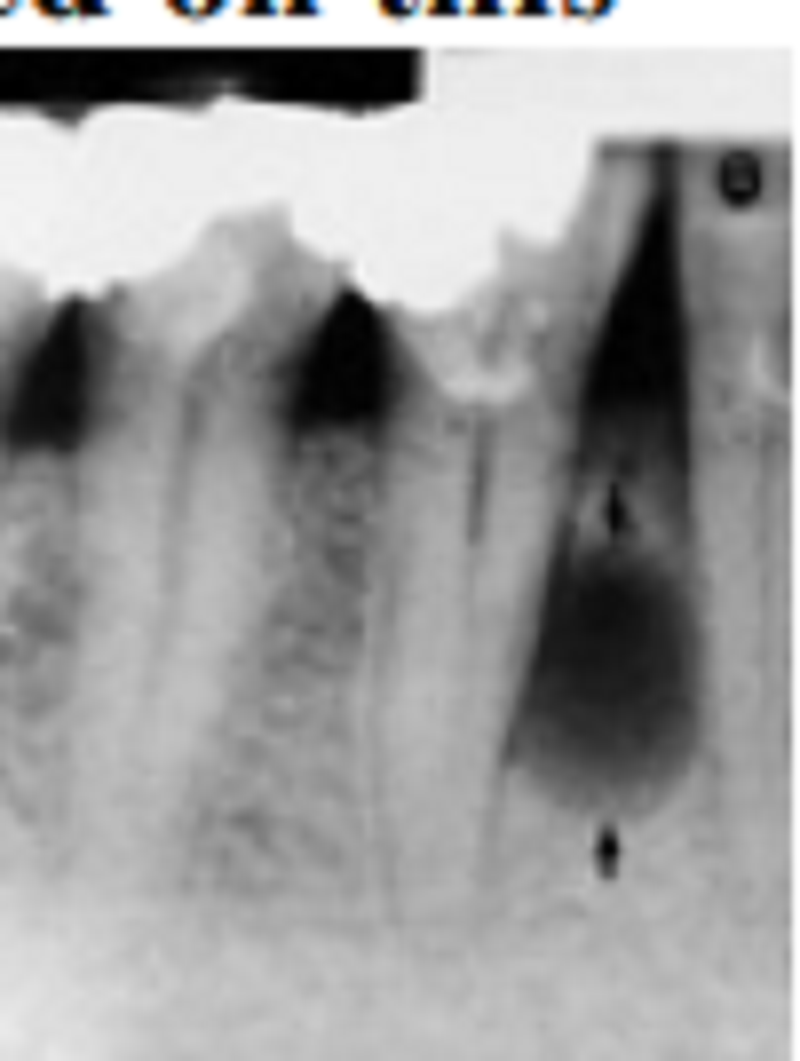
We are considering the radiolucent lesion between the lower premolars. Based on this radiograph, what would be your most likely clinical diagnosis before biopsy:
Lateral periodontal cyst
Lateral radicular cyst
Odontogenic keratocyte cyst
Botryoid odontogenic cyst

Observe the radiograph of this fixed 4-unit prosthesis (bridge). What materials is the prosthesis made of?
All gold
Gold with porcelain facings
Gold with acrylic facings
Gold with acrylic facings
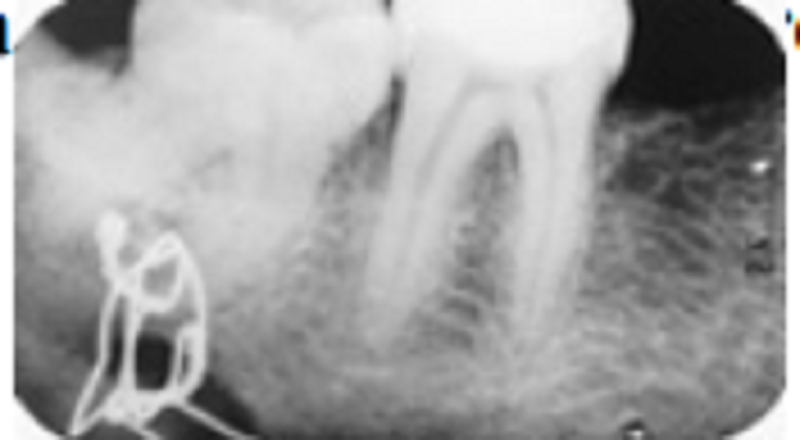
This patient has a history of a fractured mandible. What do you make of what we see at the apex of the 2nd molar?
Ligature wire
Ligature wire and fibrous scar
Scratched film and abscessed tooth
Some type of double exposure
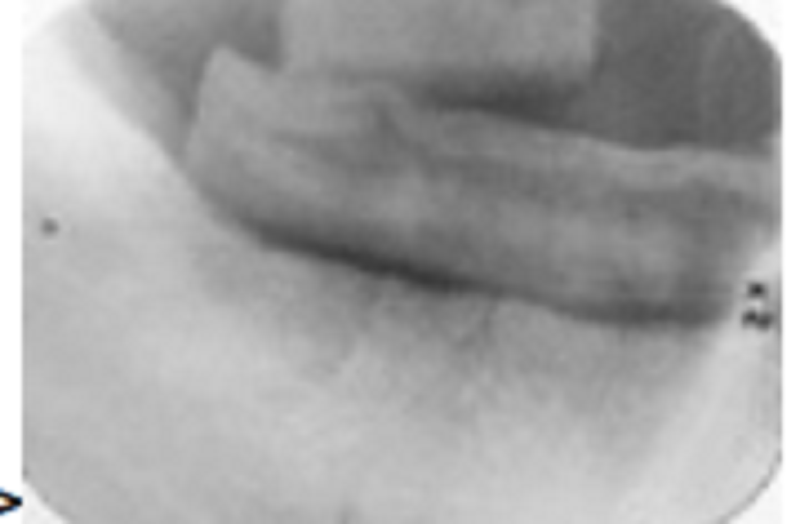
Ame two materials associated with taking the radiograph:
Ame two materials associated with taking the radiograph:
Bite-block and cotton roll
Bent film and grainy image caused by depleted developer
Bite-block and acrylic stent for implant imaging
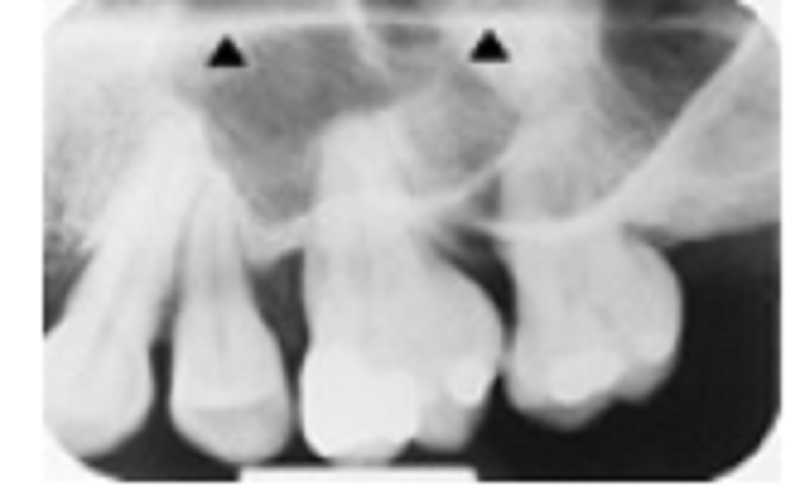
This question deals with only the structure indicated by the arrow heads. Select the best choice?
Hard palate
Floor of the nose
Roof of the sinus
Soft palate
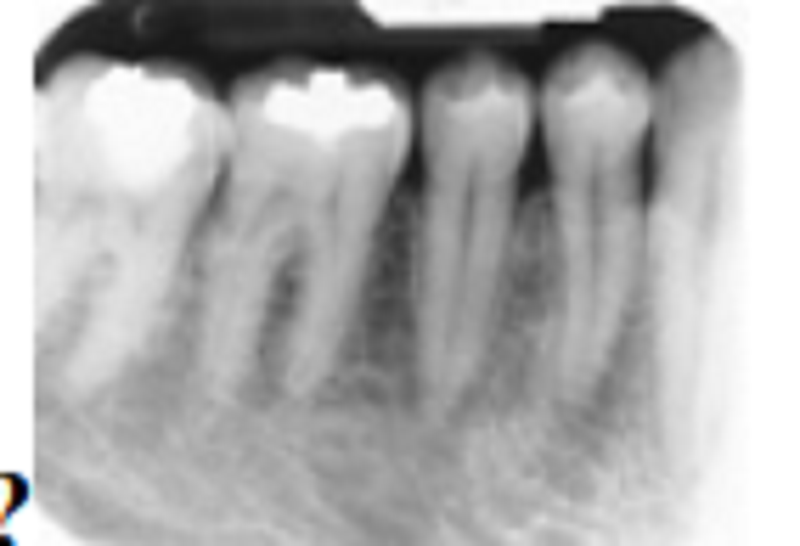
Match the descriptive term that indicates the problem; after that, list the cause:?
Shortened roots; orthodontics
Shortened roots; shovel-shaped incisor syndrome
Foreshortening of the roots; excessive negative vertical angulation of the BID
This is a problem without a cause because there is no problem or error
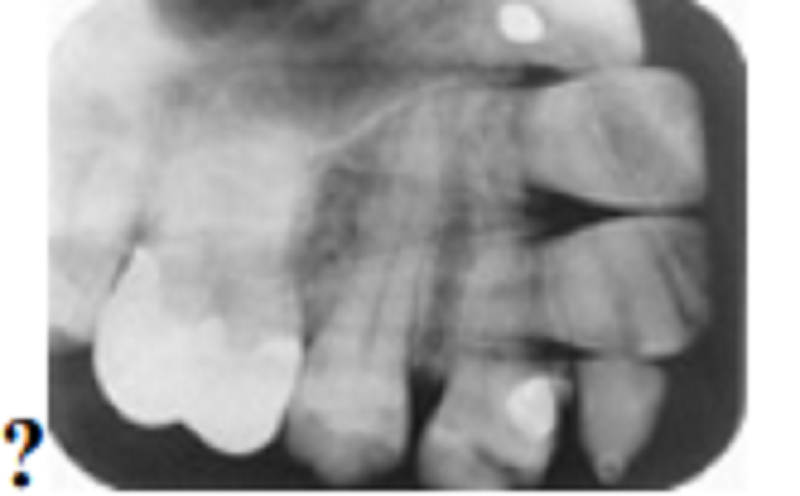
Okay, this is the one you have been waiting for. What happened?
Chemical stains
Class 4 partial denture with porcelain teeth
that have become dislodged
Double exposure
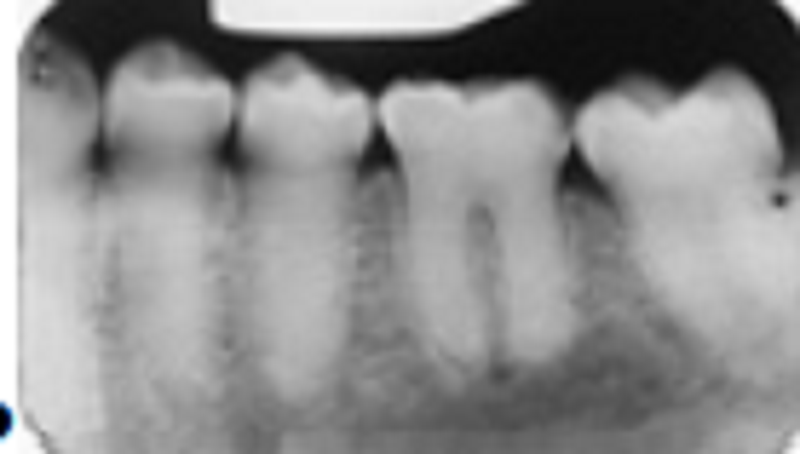
Observe these teeth carefully. What condition is present?
Amelogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentin dysplasia type 2
Age-related pulp obliteration
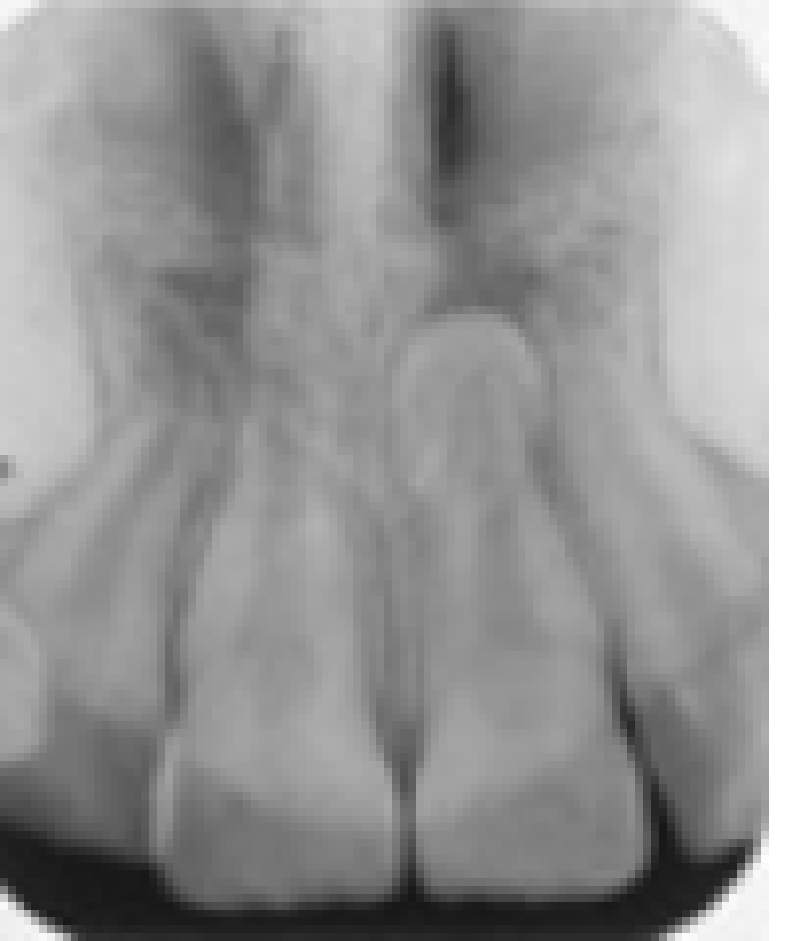
An anomaly is present in this patient. It is:?
Snow-capped tooth
Periapical cementum dysplasia
Rare double-crowned tooth
Mesiodens
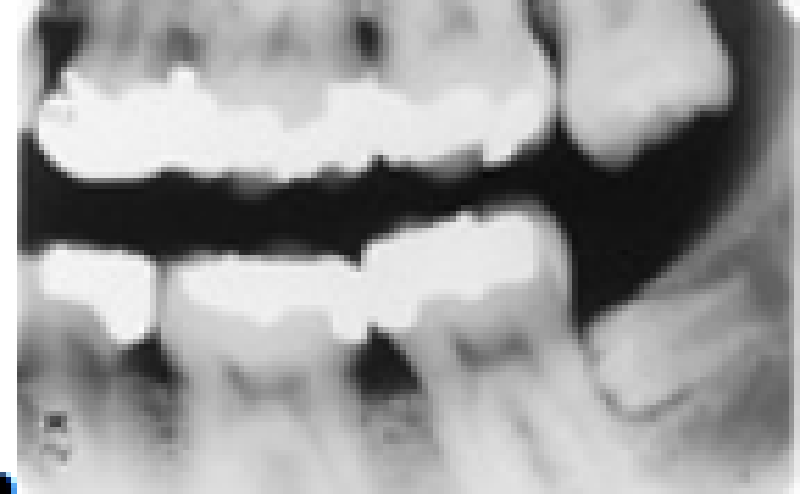
Note the extruded maxillary 3rd molar. What term(s) best describe?
Distomolar
Microdontia
Impacted
All of the above
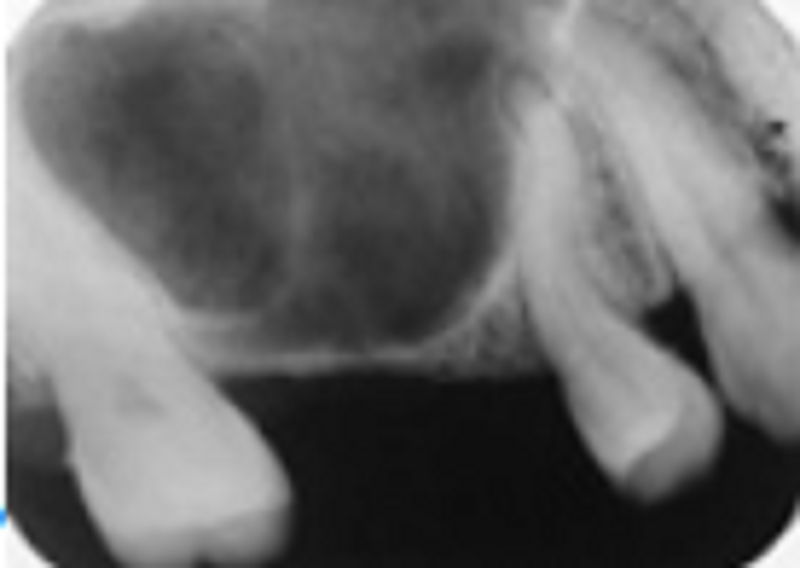
Note the dilacerated premolar root. The condition that affects this sinus is: ?
Acute sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis
Sinus elongation
Pneumatizing
{"name":"Dental Imagery II 1", "url":"https://www.supersurvey.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of dental imagery with our comprehensive quiz designed for dental professionals and students alike. This quiz covers essential concepts related to digital and traditional radiography, including techniques, structures, and safety measures. Join now to enhance your understanding of: Types of radiographic films Digital imaging benefits Radiation safety practices Exam techniques and processing methods","img":"https:/images/course4.png"}
More Surveys
Dental Imagery II 2
72360
Periodontology
5025378
Endodontics Knowledge Quiz
7437250
Fix Prostodontic 5
60300
Partial Denture 2
763825
Complete Denture 2 (សូមមេត្តាកុំចែកចាយ Link ដោយគ្មានការអនុញ្ញាត)
60300
Endodontics
6030306
Periodontology
5728820
Oral surgery Ep2
502559
Endodontic 1
723625
Periodontology
4724466
Endodontics II 2 Dr.Khoeung RathVisal
502538


